The most serious danger when working with electronic components is posed by electrostatic discharge (ESD). Sudden discharge of static electricity, or ESD, is very common. Everyday materials (such as glass, ceramic and plastic) are inherently charge-generating, and with miniaturisation of today’s complex devices, technology has multiplied the number of circuits and decreased their size, thereby increasing the risk of damage by ESD.
While the human body might not be susceptible to harm from this inevitable natural phenomenon, it is highly probable for electronic circuitry and components to be affected by ESD catastrophically or latently. In the latter case, although the electronic device could appear to work just fine, it could fail to function sometime in the future.


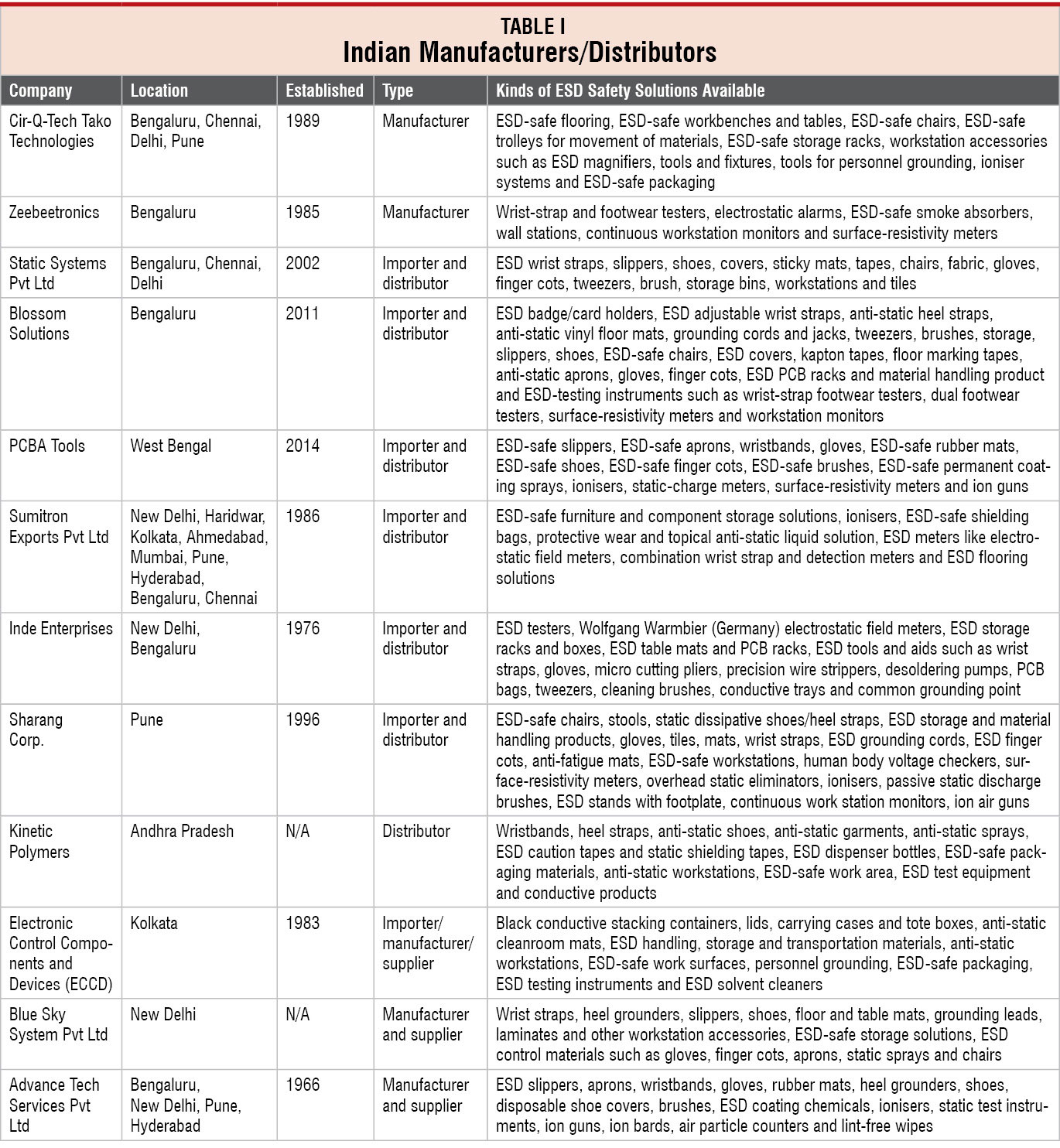
In this article, we focus on solutions that could help you control ESD and create a static-safe work area.
Those who wish to counter this problem must take various aspects into account, such as ESD-safe workstations where electrostatic discharge is safely channelled to earth, electrostatically discharging shoes, work-wear and ESD armbands with spiral cable that discharges voltage softly and safely via a large resistance (approximately one megaohm) from the operator to earth.
Tools for ESD detection and control
ESD materials are generally subdivided into three main categories: anti-static (109 ohms to 1012 ohms), dissipative (105 ohms to 109 ohms) and conductive (103 ohms to 105 ohms). ESD tools are equipped with electro-statically discharging (dissipative) handles that have a defined surface resistance of about 106-109 ohms. That guarantees soft discharging within a set period of time and in a controlled and safe manner, so that sensitive components cannot be damaged. Most ESD-safe hand tools with static dissipative handles are made of carbon steel or stainless steel.
IEC61340-5-1 standard specifies technical requirements for the design, use and control of a protected area so that electrostatic-sensitive devices, having sensitivity of 100V (human body model test) or higher, can be handled with minimal risk of damage from procurement to end of their life.
There are diverse kinds of tools and systems available for detection, restriction and protection from ESD. Electronic facilities require ESD protection during inspection, storage and warehouse, assembly, research and development (R&D), packaging, test and inspection and field service repair. Dedicated manufacturers adopt various anti-static safety measures while designing their products.




