A team of researchers from Sydney have developed a high-speed motor that provides maximum power and speed to accelerate electric vehicles
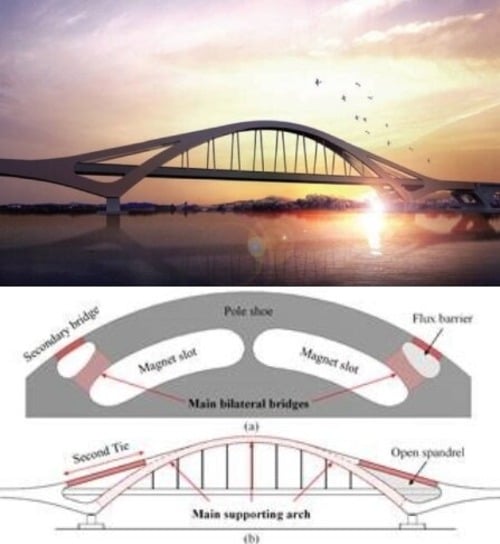
An Interior Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor (IPMSM) consists of magnets embedded within its rotor to produce strong torque for a high-speed range. Since existing IPMSM experience low mechanical strength due to thin iron bridges within its rotors that results in a reduction in their maximum speed. Engineers from the University of South Wales (UNSW) developed a new high-speed motor that has the potential to increase the range of electric vehicles. The structure of the prototype IPMSM type motor was inspired by the shape of the longest railroad bridge in South Korea.
“One of the trends for electric vehicles is for them to have motors which rotate at higher speeds,” says Dr. Chu, Associate Professor, from the UNSW School of Electrical Engineering and Telecommunications. Every EV manufacturer is trying to develop high-speed motors and the reason is that the nature of the law of physics then allows you to shrink the size of that machine. And with a smaller machine, it weighs less and consumes less energy, and therefore that gives the vehicle a longer range.
The motor invented was capable of exhibiting a very high power density that was useful for EVs in reducing overall weight and therefore increasing range for any given charge. The range of different physical aspects such as electrical, magnetic, mechanical, and thermal was evaluated by using the UNSW team’s AI-assisted optimization program.
“With this research project we have tried to achieve the absolute maximum speed, and we have recorded over 100,000 revolutions per minute and the peak power density is around 7kW per kilogram. For an electric vehicle motor we would reduce the speed somewhat, but that also increases its power. We can scale and optimize to provide power and speed in a given range—for example, a 200kW motor with a maximum speed of around 18,000 rpm that perfectly suits EV applications.”
This motor has many other potential applications such as large heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems that need high-speed compressors to use a new form of refrigerant that results in a reduction of its impact on global warming. It can also be used in high-precision CNC machines that are in great demand by the aviation and robot industries.






