Researchers have developed a microneedle patch using artificial intelligence (AI) to predict compounds that could neutralize baldness-causing reactive oxygen species in the scalp
It is essential to have healthy hair for physical and mental well-being. It is proven that healthier and more beautiful hair can boost self-confidence. Presently, hair loss has become very common due to overall lifestyle and pollution. The reason for substantial hair loss is due to androgenic alopecia, also called male or female pattern baldness. This results in damage to hair follicles by androgens, inflammation, or an overabundance of reactive oxygen species, such as oxygen free radicals.
High levels of these oxygen free radicals can affect the body’s antioxidant enzymes which typically keep them in check. Superoxide dismutase (SOD) is one of these enzymes, and researchers have recently created SOD mimics called “nanozymes.” But so far, those reported aren’t very good at removing oxygen-free radicals. To overcome this problem, researchers reporting in ACS’ Nano Letters implemented machine learning, a form of AI, that could help them fabricate a better nanozyme for treating hair loss.
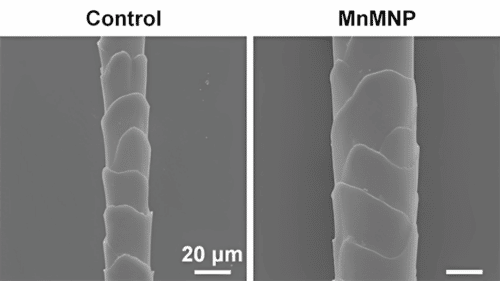
Transition-metal thiophosphate compounds are used as potential nanozyme candidates. They experimented with machine-learning models with 91 different transition-metal, phosphate, and sulfate combinations, and the techniques predicted that MnPS3 would have the most powerful SOD-like ability. Further, MnPS3 nanosheets were synthesized through the chemical vapor transport of manganese, red phosphorus, and sulfur powders. Preliminary tests with human skin fibroblast cells revealed the nanosheets significantly reduced the levels of reactive oxygen species without causing harm.
Based on these results, the team prepared MnPS3 microneedle patches and treated androgenic alopecia-affected mouse models with them. Within 13 days, the animals regenerated thicker hair strands that more densely covered their previously bald backsides than mice treated with testosterone or minoxidil.
The researchers claim that their study both produced a nanozyme treatment for regenerating hair and indicated the potential for computer-based methods for use in the design of future nanozyme therapeutics.
Click here for the Published Research Paper






