- Researchers at the Korea Research Institute of Chemical Technology and Kyungpook National University have developed a material capable of repairing scratches on autonomous vehicle sensors.
- The material is capable of preventing car accidents caused by signal distortion.
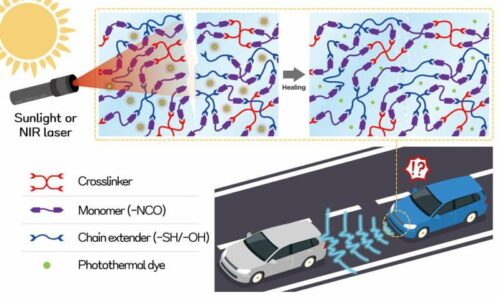
Ensuring the safety of self-driving cars is crucial for protecting lives, minimizing accidents, and building public trust in autonomous vehicle technology. The frequent occurrence of traffic accidents has raised safety concerns regarding self-driving cars.
Researchers at the Korea Research Institute of Chemical Technology (KRICT) and Kyungpook National University (KNU) have developed a material capable of healing scratches on autonomous vehicle sensors. The material is capable of preventing car accidents caused by signal distortion. By healing scratches on the sensor surface of self-driving cars, this material aims to enhance safety on the road. Applying this self-healing optical material to autonomous vehicle sensors increases product lifespan and holds promise for future technologies that prevent malfunctions caused by surface damage.
Scratched lenses distort images, impacting device function in cameras, cell phones, and glasses. The team developed a transparent lens material removing scratches on sensors in the 60s using sunlight and a magnifying glass. Flexible materials favor self-healing due to molecular movement, but hard lenses/coatings lack this ability. To overcome this, the team combined thiourethane with a photothermal dye, creating a “dynamic chemical bond” that disassembles and recombines under sunlight. The transparent organic photothermal dye absorbs near-infrared light without affecting visible light or Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR) sensors’ near-infrared region.
As photothermal dyes absorb sunlight, they convert light energy into thermal energy, causing the surface temperature of the lens material to rise. This elevated temperature enables the polythiourethane structure to self-heal by repeatedly breaking and reforming chemical bonds, repairing surface scratches. The advanced lens material demonstrates remarkable self-healing capabilities, even when scratches intersect. It exhibits exceptional resilience, maintaining a 100% self-healing efficiency even after repeatedly scratching and healing at the same spot, for more than five cycles.
The researchers believe that this self-healing lens technology combines affordable high-refractive polymer and photothermal dye, finding wide use in autonomous vehicle sensors, glasses, and cameras.
Reference : Ji-Eun Jeong et al, NIR-Triggered High-Efficiency Self-Healable Protective Optical Coating for Vision Systems, ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces (2023). DOI: 10.1021/acsami.2c21058







