IonQ has demonstrated the first known commercial demonstration of ion-photon entanglement outside of academic environments.
Researchers have generated photons entangled with ions repeatedly and reproducibly, important to enable future quantum systems to communicate and transfer information between each other. This is a major step towards connecting quantum systems and developing networked quantum computers.
The research team at IonQ has successfully generated and collected single photons from an ion qubit and routed those photons to specialised detection optics to verify ion-photon entanglement. They have successfully created a special quantum state by entangling (linking) photons (particles of light) with ions (charged atoms).
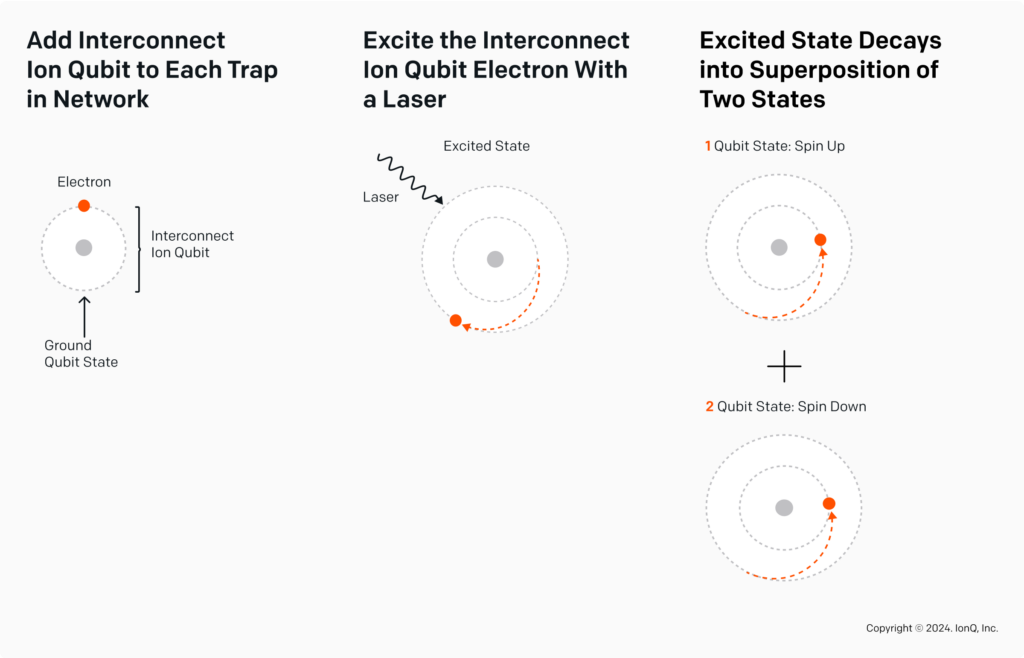
This is a crucial first step towards developing photonic interconnect protocols for quantum computing applications running across multiple quantum processing units (QPUs). Photonic interconnects are expected to lead to integrated computation across quantum networks, allowing for more powerful quantum computers capable of running complex algorithms by entangling cores.

Think of it like this: in classical computing, we have multiple processors that work independently to perform tasks. In quantum computing, we want to link these processors together in a way that they can work as one powerful computer. This is what IonQ is working towards with their photon-ion entanglement.
IonQ has expanded its capabilities by acquiring Entangled Networks, a Canada-based startup, and has strengthened its relationship with the Air Force Research Lab (AFRL) through a $25.5M deal to deploy two quantum computing systems for quantum networking research and development.





