Researchers from the Chinese University of Hong Kong and other Chinese institutes have developed a new, small, portable, affordable optical spectrometer.
Optical spectrometers measure light properties across the electromagnetic spectrum for applications like medical diagnostics and material analysis. Traditional designs are bulky and expensive, limiting their use to specialized facilities. Recently, engineers have developed more compact, affordable spectrometers for broader deployment, using principles from conventional spectrometers or arrayed broadband photodetectors with computational algorithms.
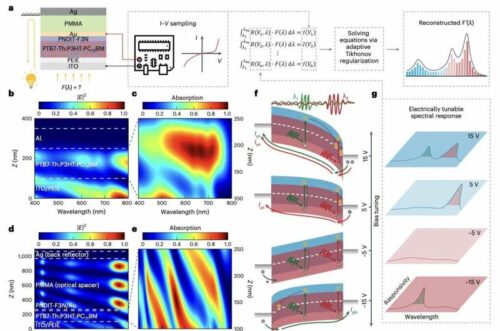
Researchers at the Chinese University of Hong Kong and other Chinese institutes have recently designed and fabricated a new micro-sized, portable, cost-effective optical spectrometer. This innovative spectrometer, detailed in a paper published in Nature Electronics, utilizes an organic photodetector with a bias-tunable spectral response.
The new optical spectrometer developed by these researchers employs a novel method to manipulate the wavelength-dependent location of photocarrier generation in photodiodes. This technique uses a trilayer contact consisting of a transparent back contact, an optical spacer, and a back reflector.
By combining this contact with a Schottky diode and an organic ternary bulk heterojunction, the team created a photo multiplication-type organic photodetector (PM-OPD). The data collected by this photodetector were then analyzed using a reconstruction algorithm.
The researchers tested their miniaturized optical spectrometer and found it achieved remarkable results, operating across the entire visible spectrum (~400–760 nm) with sub-5 nm resolution. To demonstrate its potential, they used it to fabricate an 8 x 8 spectroscopic sensor array for hyperspectral imaging, a technique that detects unique spectral signatures of specific objects by processing information across the electromagnetic spectrum.
The new approach presented in this paper could inspire the development of other similar micro-sized and more affordable optical spectrometers. These devices could lead to new cutting-edge technologies that advance research and medical practices.
Reference: Xie He et al, A microsized optical spectrometer based on an organic photodetector with an electrically tunable spectral response, Nature Electronics (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41928-024-01199-9







