With an increase in global warming and the depletion of fossil fuels, the world is moving towards renewable energy.
Solar energy is one of the most important sources of renewable energy generation throughout the globe. There is no recurring cost for fuel as the energy depends on solar irradiance which is available to most places throughout the year.
Moreover, solar energy harnessing requires a single time investment used for procuring and setting up the solar panels and energy storage system.
In order to maximize our return and harness the most amount of energy from the sun, it is essential to select the best type of solar panels.
There are 3 main types of solar cells–
- Monocrystalline Cells
- Polycrystalline Cells
- Thin Film Solar cells
Each of the three types has its own pros and cons that we will discuss in another article. In this article, we will discuss the most important terminologies which we should know before we select a suitable solar panel for our application.
Solar panels or photovoltaic (PV) modules have different specifications. There are several terms associated with a solar panel and their ratings such as nominal voltage, the voltage at open circuit (Voc), the voltage at maximum power point (Vmp), open circuit current (Isc), current at maximum power (Imp), etc.
All these parameters are crucial to know before purchasing or installation of solar panels.
The characteristics of solar panels can be understood by using the current vs voltage graph. The VI graph is shown below:
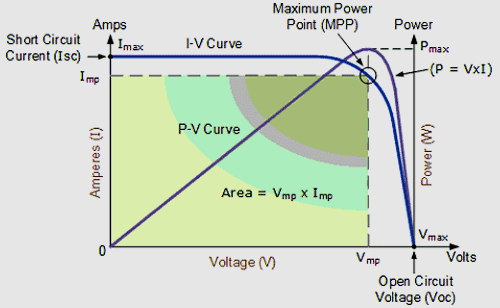
Let’s find the most common question about solar panels i.e.
What is the difference between nominal voltage, Voc, Vmp, short circuit current (Isc), and Imp in the case of a solar panel? Which parameters are important to check before the installation of solar panels?
Solar Panel Specifications
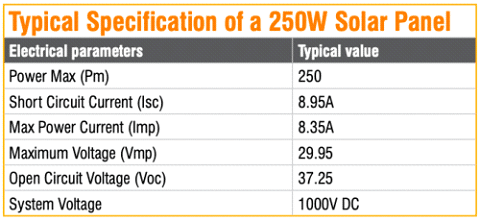
Let’s understand the difference between Nominal Voltage, Voc, Vmp, Isc, and Imp.
Nominal Voltage in Solar Cell
Used just for classification, it is not a real voltage you are going to measure. It is not a fixed voltage either and, normally, it is not mentioned in the specification sheet of a PV module. Some of the common parameters mentioned in the specification sheet are listed in the table.
Voltage at Open Circuit (Voc)
This voltage is checked with a voltmeter across the output terminals of the solar panel module, without connecting any load. This parameter is used to check/test the module during installation and later for system design. It is an important parameter under standard test conditions. Voc is used while determining the number of solar panels required for a particular load.
Voltage at Maximum Power (Vmp)
This is the voltage available when the panel is connected to a load and is operating at its maximum capacity under standard test conditions. Most solar panel manufacturers specify Vmp to be around 70 to 80% of the Voc.
Short Circuit Current (Isc)
This is the value of current obtained when the positive and negative terminals of the panel are connected to each other through an ammeter in series. This is the highest current the solar panel cell can deliver without any damage. Isc is used to determine how many amps a panel can handle when connected to a device like a solar charge controller or an inverter circuit.
Current at Maximum Power (Imp)
This current is obtained when the solar panels are producing their maximum power. It is the amperage you would want to see when connected to solar equipment.
Maximum Power Point of Solar Cell (Pm)
The maximum power point (Pm) of a solar cell denotes the maximum amount of power a cell can deliver during its standard test condition.
Efficiency of Solar Cell
The efficiency η of a solar cell is an important criterion for the selection of a solar cell. It helps compare the performance of a solar cell. It is defined as the ratio of energy produced by a solar cell to the energy it receives from the sun. The efficiency of solar panels depends on the efficiency of the solar cell. Most solar cells available in the market offer an efficiency of 17-19% and the highest efficiency of a commercial solar panel is about 23%.
Fill Factor (FF)
The fill factor (FF) denotes the efficiency of a solar cell. It is denoted by the ratio of maximum power point (MPP) to the product of short circuit current (Isc) and open circuit voltage (Voc). The fill factor can also be denoted as the largest square that can fit inside an IV curve.
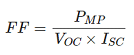
Below you can see the table for difference between these solar panel specifications-
| Specification | Definition | Additional Information |
|---|---|---|
| Nominal Voltage | Designed operating voltage under standard conditions | – Also known as “Rated Voltage”- Used as a reference for system design – May not reflect actual operating voltage |
| Voc (Open Circuit Voltage) | Maximum voltage with no load connected | – Occurs in bright sunlight when no current flows – Helps determine system safety margins |
| Vmp (Maximum Power Voltage) | Voltage at maximum power output | – Corresponds to the point where power output is highest – Used to optimize system performance |
| Isc (Short Circuit Current) | Maximum current with terminals shorted | – Occurs in full sunlight with zero voltage across the terminals – Indicates the panel’s current capacity |
| Imp (Maximum Power Current) | Current at maximum power output | – Corresponds to the point where power output is highest – Used to optimize system performance |
You can check the Solar Panel Installation Guide.









I have learnt a lot.
Thank you for your valuable feedback.
Good to have in understanding of terms of PV panels.
Thank you for your valuable feedback.
Thank you for the info
You are most welcome.
Thanks for the info but i have a little misunderstanding, i am doing an experiment on MATLAB and the PV system is connected with a boost converter and it is running. If i use a scope at the input of converter or you can say ouput of panel what will be that voltage called and if i use a scope at the output of converter what will that voltage be called? Some algos like P&O cant realy track MPP so what will be there converter output voltage called?