ARM (or Advanced RISC Machine) is a family of reduced instruction sets computing (RISC) architectures for computer processors. Arm Ltd, a UK based company, develops ARM architecture and licenses it to other companies. A typical ARM core block diagram is shown in Fig. 1.
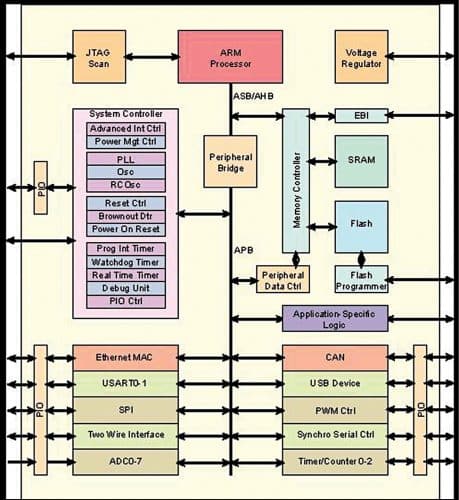
There are many generations of ARM processor designs, the recent one being the ARMv8.6-A processor. Currently, there are 32-bit and 64-bit ARM processors available in the market.
Particularly, the 32-bit ARM architecture, such as the ARMv7-A, was the most widely used architecture for mobile devices. The ARMv7 defines three architecture profiles:
A-profile
Application profile implemented by 32-bit cores in the Cortex-A series and by some non-ARM cores.
R-profile
Real-time profile implemented by cores in the Cortex-R series.
M-profile
Microcontroller profile implemented by most cores in the Cortex-M series.
The ARM Cortex-M family microprocessor cores are designed for use in microcontrollers, ASICs, ASSPs, FPGAs, and SoCs.
Most of the processors in mobile phones/smartphones are based on ARM processors. ARM processors are also used in personal computers, servers, and supercomputers.
STM32F103xx development board based on ARM Cortex-M3, 32-bit RISC core operating at 72MHz frequency is among popular and inexpensive boards used by hobbyists.
An example of practical application for interfacing an ARM processor with dot-matrix display is shown in Fig. 2. Due to space constraints we cannot include the source code and other information of this example here. However, the complete information including the circuit diagram and source code will be published in a coming months.






