While the Internet is now considered a necessary portal for the flow of information, sixty eight per cent of the population of our country still does not have access to it. Hence a change in this scenario requires undivided attention. From the founders’ perspective, the only way to solve this pain point was by introducing Astrome to the world.
The need for Astrome
“Terrestrial Internet requires infrastructure like laying a lot of cable to reach all locations and obtaining the necessary ‘right of way’ clearance to install the cable. This is not only slow and problematic but quite expensive, too (Fig. 1). For example, it costs about ` 210,000 to lay optical fibre cable for one kilometre in India,” says Dr Prasad Bhat, co-founder and chief technology officer, Astrome.
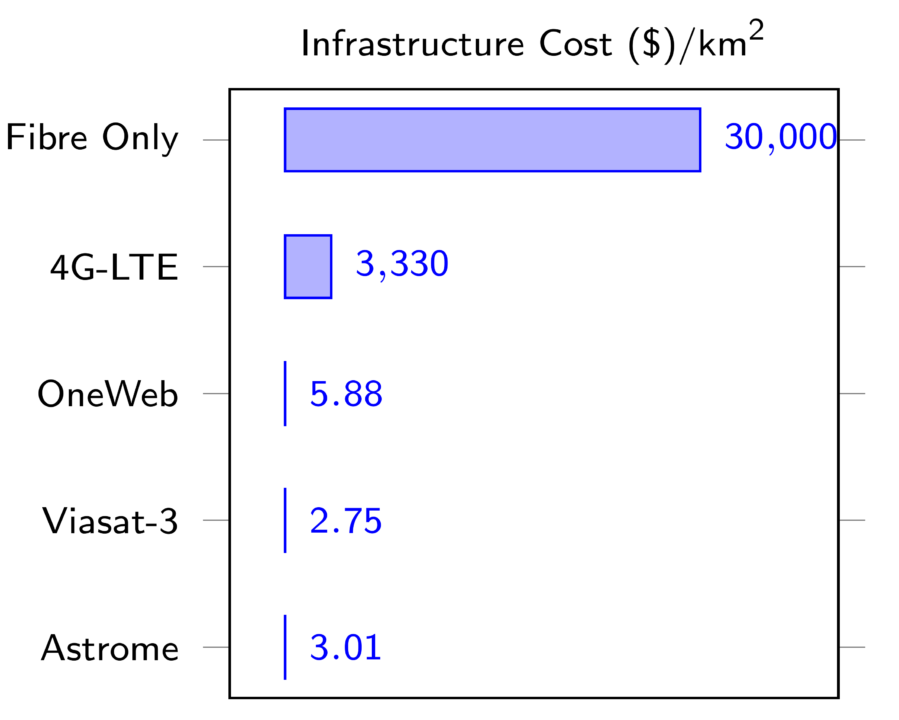
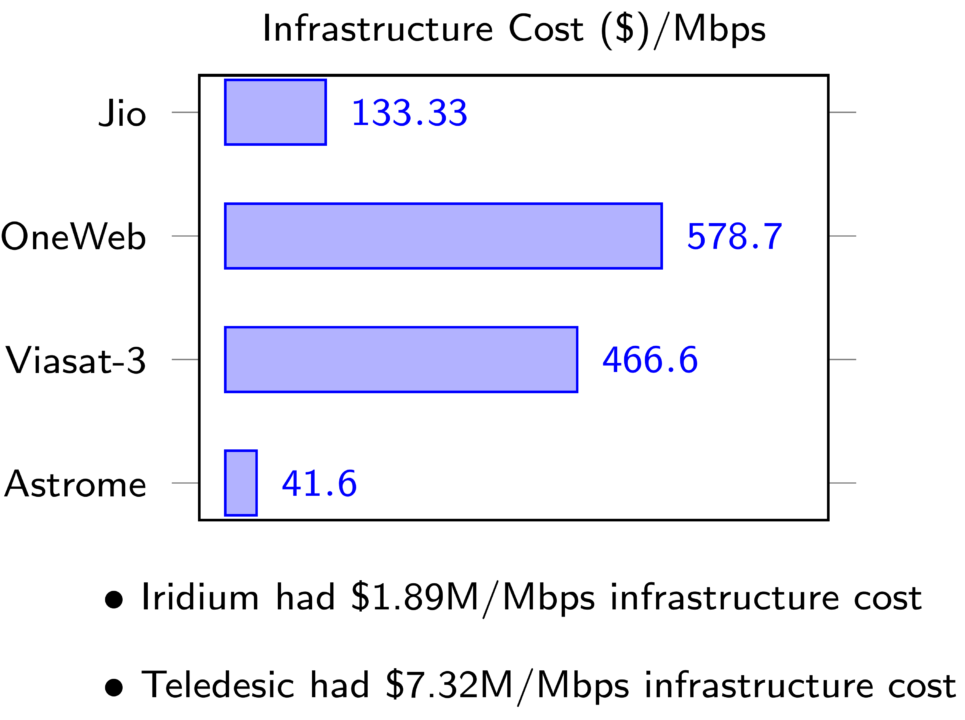
Reaching three thousand gram panchayats by laying only terrestrial cables is not an easy task. An initiative called BharatNet is trying to extend its fibre-optic connectivity but it has a very limited scope too, considering the terrain and geographic constraints.
“Satellite based Internet doesn’t require expensive ground infrastructure. Since we are not laying optical fibre cables, the cost of providing the Internet to semi-urban and rural locations is hundred times lower than that in terrestrial technology,” says Dr Neha Satak, chief executive officer, Astrome.
Though the Internet penetration rates are growing rapidly, the statistics provided on November 30, 2015 by the Broadband Commission showed that, more than half of the world population is not connected to the Internet yet.
Space based solutions are practically cost-effective in the long run compared to their terrestrial counterparts. Terrestrial technologies (cables, fibre optics) provide high capacity at high cost in a concentrated fashion, and could be customised where a large number of users are present. But space based solutions provide distributed capacity at lower cost. These are best suited for the businesses scattered across regions that are sparsely populated.
How Astrome works
The floating routers concept used by Astrome makes use of some low orbital satellites, which act as routers working similar to a DTH streaming system. The on-ground subscribers can get high-speed Internet using a simple dish antenna on a rooftop.
Over the next few years Astrome would send a constellation of hundred microsatellites in the low Earth orbit (LEO). LEO is preferred to the geosynchronous orbits, because geosynchronous orbits are too far to relay two-way communication with acceptable propagation delays. Propagation delay in a geosynchronous orbit is about forty times longer than in an LEO.
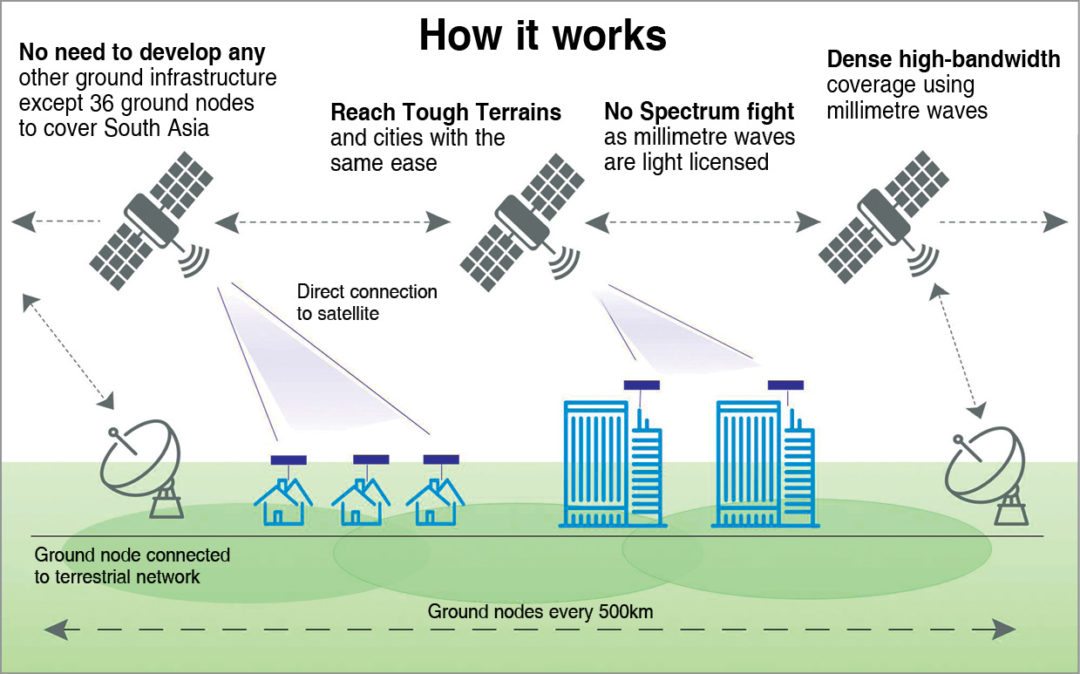
The satellites take up their positions on the lower orbits covering 1200-1800 kilometres in diameter. It is estimated that four to five satellites are enough to ensure broadband at one point of time all across the Indian geographical region.
Packed with a bandwidth of 100Gbps per satellite, the users on Earth can have up to 50Mbps and 400Mbps for business users. The beauty of it is that, this speed does not depend on the geographical location of the user. The speed at which the Internet streams for people accessing from a crowded city or a remote hamlet in the Himalayas remains the same.










