The induction cooking craze has been getting lots of buzz even though the technology has been around for about a century. Induction cooktop is quiet popular, both in domestic and commercial usage. They are considered as one of the advanced technological innovations in the field of cooking. Induction cooktops, are relatively new to many regions in emerging Asia-Pacific economies. The induction cooktops market is expected to see rise at a fast pace. This is due to growing awareness and rapid urbanization in Asia-Pacific and Eastern Europe regions.
Induction Cooking is a type of electric cooking that uses magnetic coils to heat cookware. The beauty of the induction cooking is that the cooking surface itself remain cool while heat is generated within the cookware. Cooking by means of induction cooktop is quick and highly energy efficient as compared to other conventional methods; on top of it lack of open flame makes them safer too.
How do they work?
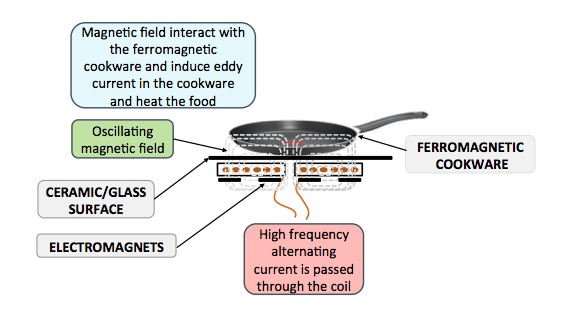
Induction Cooking is the process of generating heat directly in a ferromagnetic utensil/pot/cookware by means of electromagnetic induction and subsequent generation of eddy currents. Electromagnetic induction principle was discovered long back in 1831 by Michael Faraday. Electromagnetic induction refers to a phenomenon by which electric current is generated in a closed circuit by the fluctuation of current in another circuit placed next to it.
The ferromagnetic cookware is to be placed/positioned on top of an induction cooktop. Below ceramic or glass surface lies a resonant coil as shown in Figure 1. The induction cooktop and cookware can be considered as a transformer in which cookware act as shorted secondary (load). An alternating is made to flow through the resonant coil, which leads to generation of oscillating magnetic field. The magnetic field induces an electric currents inside the cookware.
The induction cooktop only works with cookware made of certain materials that have specific properties. In order to be heated by the magnetic field, the cookware has to be made of a ferromagnetic material, such as stainless steel or iron.
Inherent advantage of induction cooking:
“No Cookware, No Energy wastage” – The induction cooktop will consume power as long as the cookware is present on top of it. Unlike a gas burner or electrical stove, the induction cooktop is incapable of producing heat on its own. In case, the induction cooker is made to operate while no cookware present on top of it or the cookware is removed while induction cooktop is in operation then the resonant coil sees as if there is no load (open circuit) and there will be no energy transfer. In case of no cookware the induction cooktop enters into sleep mode to have minimum standby power consumption i.e. <1W.
Why and which resonant power conversion topology is used for induction cooking?
Generally, semiconductor devices are used as switching element in various power converters. Insulated gated bipolar transistor (IGBT) are used in induction cooking systems. For power conversion “soft switching” techniques are preferred over “hard switching” to have minimum switching losses. In soft switching the voltage or current is manipulated to become zero across the resonant switch, at the moment of switching. Soft switching can be further categorized in two methods i.e. Zero Voltage Switching (ZVS) and Zero Current Switching (ZCS).
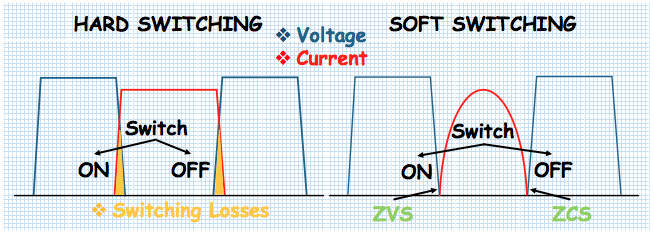
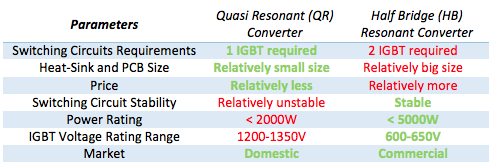
ZVS and ZCS switching technique methods has its pros and cons and also there use case is application specific. The voltage or current administered to the switching circuit can be made zero by using the resonance created by an L-C resonant circuit. This sorts of converter is known as “resonant converter” topology. The two main resonant power conversion topologies used in induction cooktop are:
• Quasi resonant converter.
• Half-bridge resonant converter.
Control Algorithms:
The induction cooktop works on the principle of a LC resonant converter. The resonant frequency not only depends on resonant tank circuit, but also on the size and material of the cookware/utensil. This causes the system to have an oscillating resonant frequency. In order to control the power delivery of the system i.e. (transferred to utensil/cookware) input mains voltage and current through IGBT are monitored by microcontroller and system switching frequency is made to adjust.
Quasi Resonant topology based Induction Cooker:
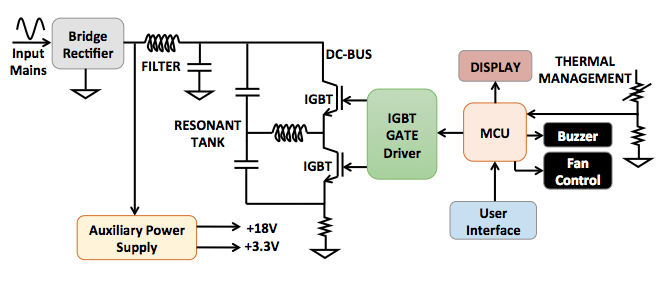
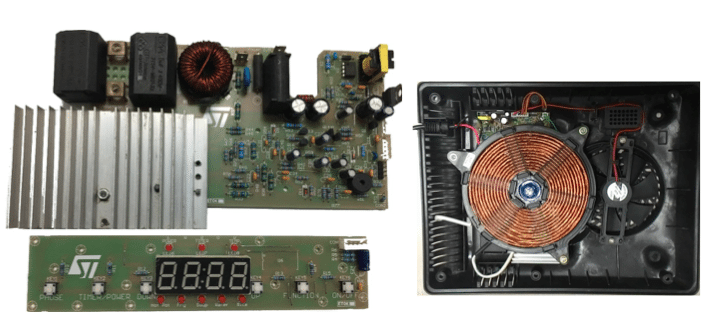
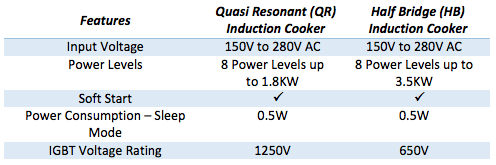
The quasi resonant induction cooktop system of “1.8KW” has been developed using STGWT20IH125DF – 1250V, 20A IH series trench gate field-stop IGBT and STM8S003F3 – value line 8-bit microcontroller from STMicroelectronics. Ready to manufacture is the maturity level. The system is incorporated with comprehensive safety mechanism to handle voltage transients and inconsistent cookware/utensil. The block diagram of the system developed is shown in Figure 2, while the actual system is shown in Figure 4.
Half Bridge Topology based Induction Cooker:
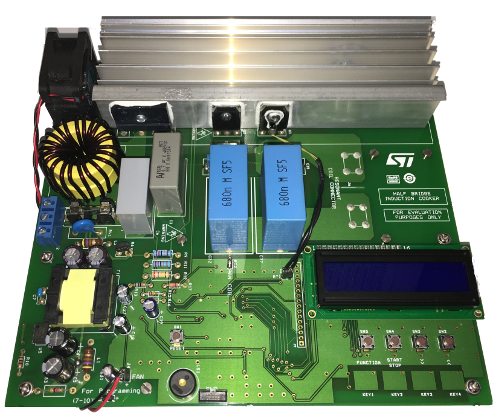
The Half bridge induction cooktop system evaluation board of “3.5KW” has been developed using STGW40H65DFB – HB series 650V, 40A high speed, Trench gate field-stop IGBT, L6491 High voltage high and low-side 4 A gate driver and STM32F072– 32-bit MCU from STMicroelectronics. The system is incorporated with comprehensive safety mechanism to handle voltage transients and inconsistent cookware/utensil. The block diagram of the system developed is shown in Figure 5, while the actual system is shown in Figure 6.


Conclusion:
Induction cooking is a promising technology for those seeking sustainability in the kitchens, hotels restaurants, and is clearly a better choice over standard electric or the expense and carbon footprint of installing a gas line.






Figure 3 and Figure 5 are swapped.
Nice
Let’s say I want to run the same ckt using DC. Can I just remove the rectifier part and do that? I am guessing I need to tinker the feed to the IGBTs but not sure exacly how.
Very Nice, though the component values could be really helpful