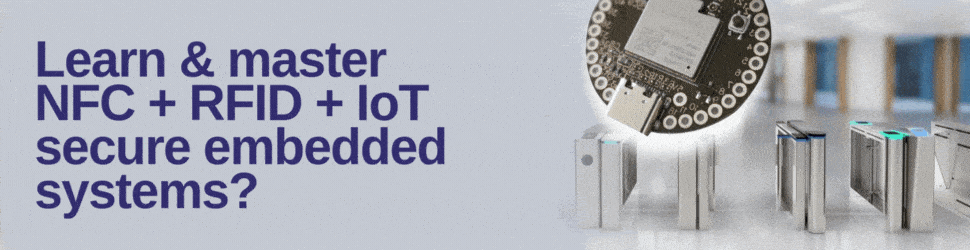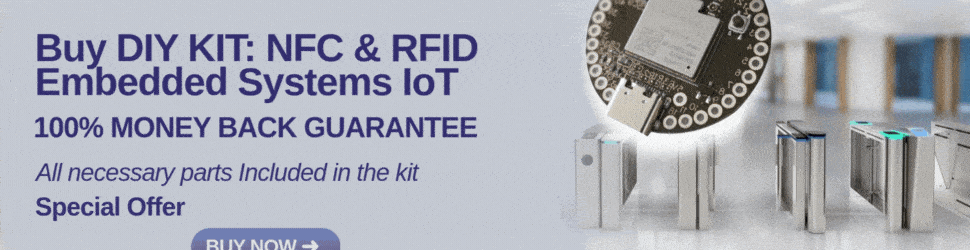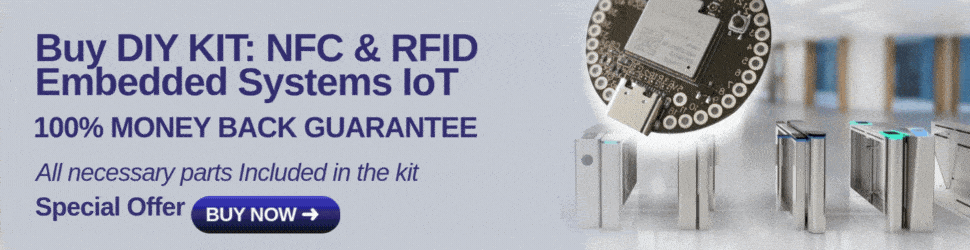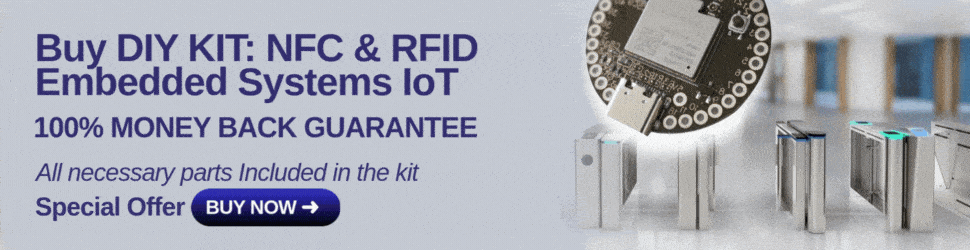
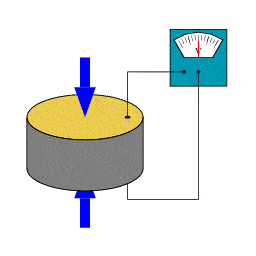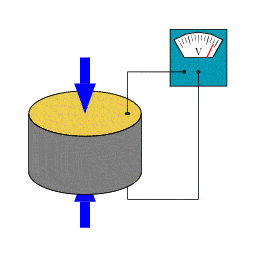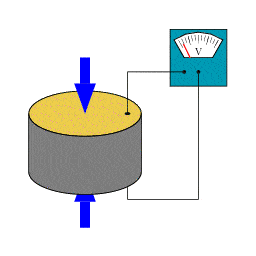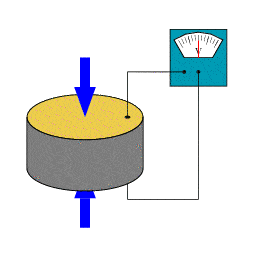
Piezoelectric sensors are devices that transform mechanical energy (such as pressure, force, or vibration) into electrical energy. It is based on the piezoelectric effect, a phenomenon in which some materials generate an electric charge when deformed.
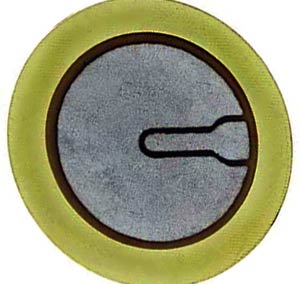
Since “piezo” means “press” or “squeeze” in Greek, a piezoelectric sensor monitors compression via the piezoelectric phenomenon.
A Piezoelectric Sensor does not require an external voltage or current source; it may generate an output signal based on the strain exerted.
This makes them a popular choice for a wide range of applications. They are becoming increasingly used in a variety of industries, and they are occasionally integrated into other sensors.
Table of Contents
Characteristics of Piezoelectric Sensors
Piezoelectric sensors are durable, lightweight, and made of flexible plastic, allowing them to be manufactured in a variety of sizes, shapes, and thicknesses. In many cases, they are moulded or bonded into positions within applications.
Piezoelectric sensors have particular characteristics:
- High strength: They can endure high pressures without permanent deformation.
- High Voltage Output: Minor impacts produce big electrical signals.
- Wide Frequency Range: Suitable for monitoring vibrations from low to high frequencies.
- Impact resistance: Can withstand mechanical shock.
- High mechanical strength: Able to withstand high physical conditions.
- High Stability: Ensures steady performance throughout time with low signal drift.
Functioning of Piezoelectric Sensors
When pressure or acceleration is applied to the PZT material, an equal quantity of electrical charge is created throughout the crystal faces.
The electrical charge will be proportionate to the applied pressure. The piezoelectric sensor cannot be used to measure static pressure.
At constant pressure, the output signal will be zero. The operation of a piezoelectric sensor can be indicated as:
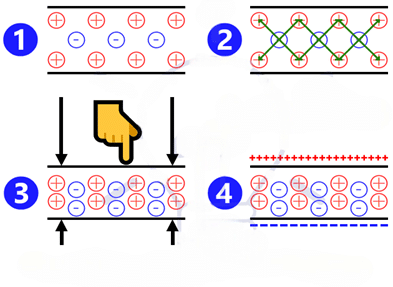
- Charges in a piezoelectric crystal are exactly balanced in both symmetric and asymmetric arrangements.
- The charges cancel out, therefore there will be no net charge on the crystal faces.
- When a crystal is compressed, its charge becomes imbalanced.
- As a result, the effect of the charge no longer cancels out, causing net positive and negative charges to appear on opposing faces of the crystal.
- Squeezing the crystal produces a voltage across the opposing face, which is known as piezoelectricity.
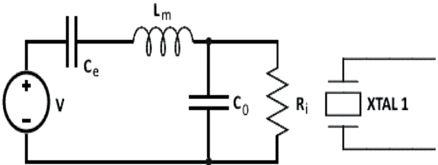
Piezoelectric Sensor Circuit
The piezoelectric sensor circuit is illustrated below. It is composed of internal resistance Ri, also known as insulator resistance. An inductor is connected, producing inductance due to the sensor’s inertia.
The capacitance Ce is inversely related to the elasticity of the sensor material. To acquire the sensor’s complete response, the load and leakage resistance should be large enough to maintain a low frequency.
Types of Piezoelectric Sensors
There are various types of piezoelectric sensors, including:
- Piezoelectric accelerometers
- Piezoelectric force sensors
- Piezoelectric pressure sensors
1. Piezoelectric Accelerometers
- Functions: These sensors detect acceleration, vibration, and shock by converting mechanical motion into an electrical signal using a piezoelectric substance.
- Applications: Common applications include OEM systems, machinery health monitoring, automotive systems, and aerospace. Their low power consumption and broad frequency response make them suitable for sensing dynamic motions.
2. Piezoelectric Force Sensors
- Function: These sensors detect and quantify force, tension, and compression. When a force is applied to the piezoelectric crystal, the sensor produces an analog voltage output.
- Applications: Applications include force monitoring and measurement in industrial equipment, robotic systems, and medical devices.
3. Piezoelectric Pressure Sensors:
- Function: These sensors detect pressure changes in gasses or liquids by turning them into an electrical charge.
- Applications: Used in automotive, aerospace, and industrial applications to monitor fluid and gas pressure changes.
Advantages of Pressure Sensors
- High Sensitivity: Capable of detecting even minute changes in pressure, force, or vibration.
- Broad Frequency Response: Ideal for dynamic applications with rapidly changing mechanical forces.
- Durability: Can withstand hostile conditions, high temperatures, and long-term use without substantial damage.
- Piezoelectric sensors have a small form factor and are lightweight, making them excellent for portable or limited-space applications.
Limitations of Pressure Sensors
- Not Recommended for Static Measurements: Because of charge leaking over time, piezoelectric sensors are not suitable for sensing constant forces or pressures.
- High impedance: Effective output measurement necessitates the use of specialized electronics such as charge amplifiers.
- Temperature Sensitivity: Because the output can alter depending on the temperature, thermal compensation may be necessary.
Applications of Pressure Sensors
- Automotive: knock sensors, vibration analysis, and pressure measurement in fuel systems.
- Medical: Medical applications include ultrasound imaging, pressure sensors in infusion pumps, and heart rate monitoring.
- Industrial: Industrial tasks include monitoring machinery, analyzing vibrations, controlling quality, and measuring dynamic forces.
- Consumer Electronics: Impact detection in touchscreens, microphones, and accelerometers.
- Aerospace and Defense: Include vibration monitoring in jet engines, structural health monitoring, and shock detection.
Also Check: First Piezoelectric Sensor for Automotive Interfaces
FAQs of Pressure Sensors
- What is a piezoelectric sensor?
- A piezoelectric sensor uses the piezoelectric phenomenon to transform mechanical stress into an electrical charge.
- How do piezoelectric sensors work?
- When mechanical stress, such as force, vibration, or pressure, is applied, they produce an electrical charge.
- What are the applications of piezoelectric sensors?
- They are mostly operated in automotive, industrial, medical, and aerospace applications to measure vibration, force, and pressure.
- Can piezoelectric sensors measure static forces?
- No, piezoelectric sensors are more suited to dynamic than static force measurements.
- What materials are used in piezoelectric sensors?
- Quartz, lead zirconate titanate (PZT), and polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) are all commonly used materials.
- How do piezoelectric accelerometers differ from other types of accelerometers?
- They outperform other varieties when it comes to measuring dynamic accelerations over a wide frequency range.







Peizoelectric by its prpoerty can be used to detect disturbances under earth that is to prredict earthquakes
I have an idea about vehicles
Kindly elaborate your query.