EEGLAB is a GNU general-public-licensed MATLAB toolbox for processing electrophysiological data from electroencephalography (EEG), magnetoencephalography (MEG) and others. Users can perform tasks like independent component analysis (ICA), time/frequency analysis (TFA), artefact rejection and several modes of data visualisation.
The toolbox, called ICA/EEG toolbox in 1997, has travelled a long way from its initial release on the Internet as a set of data-processing functions. This was done by Scott Makeig in Computational Neurobiology Laboratory under the direction of Terry Sejnowski at Salk Institute, USA. Graphical interface along with artefact-removal functions were added by Arnaud Delorme, and the first stable and fully-documented version of EEGLAB was made in 2003. A number of biomedical engineers and method developers worldwide have made effective use of the tool since then.
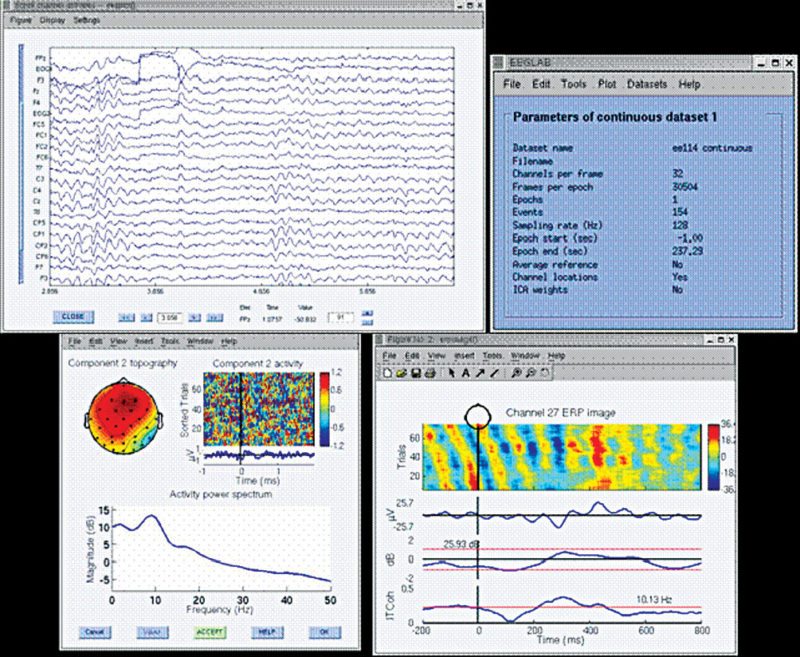
What the software is capable of
EEGLAB toolbox contains more than 380 stand-alone MATLAB functions, over 50,000 lines of code and about 20 user-contributed plugins.
Data analysis and processing. Users can input data in about 20 binary file formats and involve some amount of data pre-processing. There is an interactive graphical interface that allows processing of high-density biomedical data using techniques composed of ICA, TFA and other standard averaging methods. Artefactual ICA components can be eliminated from the data.
Detailed analysis and processing can be carried out on ICA components representing activities of the brain. Tutorial and Help windows along with command history function allow users to run batch or custom data-analysis scripts.
Data visualisation. If users try to model event-driven dynamics of the brain or visualise processed data for better analysis, the toolkit provides the necessary offerings. Analysis of data as an individual dataset or as a study-set containing multiple datasets could be done with the help of EEGLAB.
Who can make use of the toolkit
Hundreds of programming experts and researchers make use of EEGLAB for biomedical applications.
An expert MATLAB user. EEGLAB offers a well-structured programming environment, which enables an experienced MATLAB user to play around with EEG signals. The user can store, access, measure, manipulate and visualise event-related EEG data. He or she can find improved algorithms for artefact rejection, too. EEGLAB is a good starting point for those who are trying to master independent component analysis.
The toolkit provides a full structure for description of EEG data. This structure includes signal, trials, channel location, reaction time, type of trials and others. An expert programmer can make use of this structure either from MATLAB command line or in MATLAB scripts.
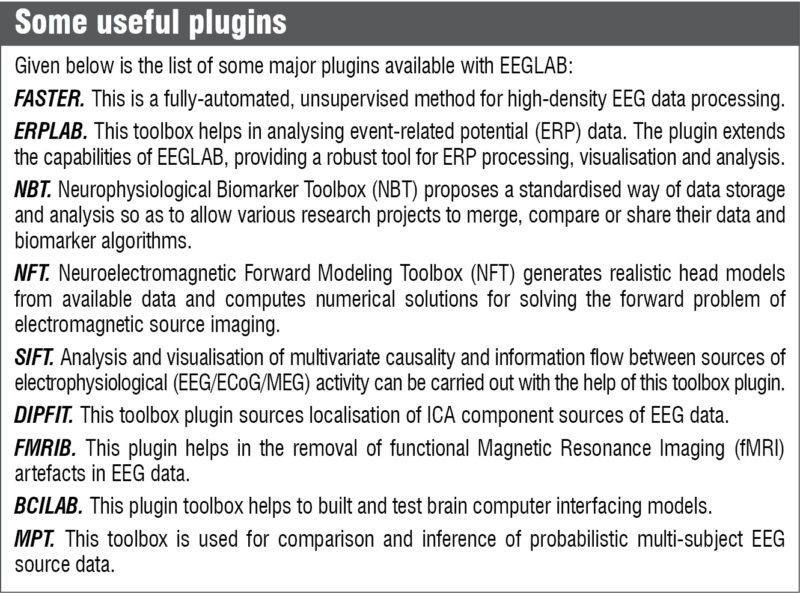
Research programmers and methods developers. They can share their newly-developed methods with the research community around the world as EEGLAB plugins, which automatically appear in EEGLAB menu and which users can download.
How efficient is EEGLAB in comparison with commercial EEG software
When it comes to making a decision of whether to move along with an open source solution like EEGLAB or rely on expensive proprietary ones, several parameters come into consideration. If you are willing to pay heavily for commercial software, you can expect expert support personnel willing to help you round the clock for your project.
For an open source project like EEGLAB there are no dedicated personnel for user support and the assistance delivered depends on availability and advancement on other projects.
Available features. Although some commercial toolboxes come with more methods for issues like source localisation, EEGLAB offers far more features than its commercial counterparts. As development is carried out by open source scientific research community, latest developments in the area are often first reflected in EEGLAB and later adopted by commercial software.
Scripting capabilities. EEGLAB makes use of flexibility and the range offered by MATLAB for its scripting. Commercial providers usually rely on their own proprietary language. Running MATLAB code within their scripts limits its capabilities.
Stability of code. Validation of the code is not always strictly carried out as per industry standards. Also, the software is always under constant development. Thus, in comparison with the most-reliable commercial counterpart, stability of the code cannot be guaranteed. If some stability issues are brought to the notice of developers, these are addressed in the future revisions of the software.
Graphical interface. The graphical user interface of EEGLAB may not be as refined as that of proprietary software. Processing is mainly done in EEGLAB using command line and the graphical user interface is used as just a tool to facilitate processing.
Within three years of its first stable release in 2003, there were around 25,000 downloads for the software from about 73 countries. Today, the toolbox is counted among the most-widely-used signal-processing environments by cognitive neuroscientists for EEG data processing.
Download: click here
The author is assistant professor, Department of ECE at SETCEM, Thrissur









very good!