FieldTrip is an open source MATLAB toolbox that helps in the analysis of non-invasive and invasive electrophysiological data including magnetoencephalography (MEG) and electroencephalogram (EEG) signals.
The software provides a common platform for both method developers as well as the scientific community who work on biomedical signals. Various signal-processing techniques including data pre-processing, event-related field/response analysis, parametric and non-parametric spectral analysis, forward and inverse source modelling, connectivity analysis, classification, real-time data processing, and statistical inference and distributed computing is possible with the help of FieldTrip toolbox. The software, consisting of more than 100,000 lines of code, defines more than 100 high-level functions and nearly 1000 low-level functions that are distributed freely under GNU public licence.
What Field Trip can offer

The research article titled ‘FieldTrip: Open Source Software for Advanced Analysis of MEG, EEG and Invasive Electrophysiological Data’ by Robert Oostenveld and others discusses the structure and main functionalities of the toolbox.
fileio. Main functions of this module include acquisition of electrophysiological data from various sensors, sorting information in received data into header information, events (such as triggers), actual recorded signals and the like.
Preproc. Various pre-processing tasks associated with raw data are accomplished with the help of this module. This includes time-domain filtering operations, re-referencing, base line correction and much more.
Specest. This module allows the user to implement various spectral analysis methods. Techniques like frequency decomposition and wavelets could be used for estimating the power and phase of oscillatory components.
Connectivity. FieldTrip connectivity module focuses on connectivity in the frequency domain. The widely-used connectivity matrices such as coherence, phase slope index and partial directed coherence are available in this module.
Forward. Various algorithms that provide solutions to the forward problem in MEG and EEG are implemented in this module.
Inverse. In order to estimate the location of neuronal activity and its strength, various source-reconstruction algorithms have been implemented in this module. These include dipole fitting based on non-linear optimisation, linear estimation of distributed source models and others.
Multivariate. The researcher could make use of various machine-learning classification algorithms in this module for offline single-trial analysis as well as online brain computer interface (BCI) applications.
Plotting. Functions that help in the visualisation of complex data including source reconstruction and multichannel decomposition of time and frequency are available in this module.
Real-time. The module facilitates construction of real-time BCI systems. This is accomplished with the help of a FieldTrip buffer that allows the acquisition client to stream data in small blocks and analyse it in parallel using MATLAB.
Peer. Analysis of electrophysiological data is often time consuming. Optimum utilisation of available resources by sharing computational resources among multiple users is the solution for this issue. Analysis could be done dynamically in various MATLAB sessions on a single computer or parallel in multiple computers in the network.

Some noteworthy features
Contrary to the signal-processing tools that have a graphical user interface (GUI), FieldTrip is designed to be used as a toolbox rather than an application. This gives the developer the flexibility not to stick to a specific GUI structure.
Let us take a look at some interesting features of this tool.
No dedicated GUI. Since FieldTrip lacks a dedicated GUI, users need to have direct interaction with MATLAB command-line functions or scripts. Obviously, they need to have some basic knowledge about MATLAB functions, but this allows them to have a combination of various functionalities that are very specific in nature for biomedical analysis.
The toolbox consists of both high-level and low-level functions. The former provides an easy programming structure allowing the user to have a step-by-step detailed analysis. The latter are intended for core functions that are not so user-friendly and cannot be easily used by a common neuroscience researcher. These functions are normally hidden from regular end users in private directories.
Handling data. Yet another important concept in this toolbox is that, data is handled completely in the hands of the users. As data passes through various functions, it gets transformed. So it is the duty of the user to explicitly manage data.
Users should assign meaningful names and save intermediate values as mat files, if they want to use those values again. In order to adapt to external software, users can also port the files to non-MATLAB file formats.
Batch processing. With a given set of parameters and a large number of subjects, if users need to analyse cognitive experiments, batch processing is the best choice. It allows them to have flexibility for further re-evaluation with a whole new set of parameter settings.
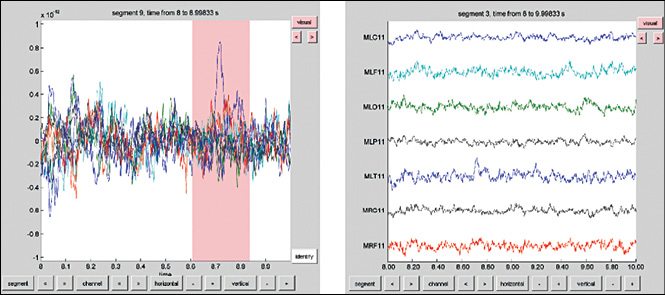
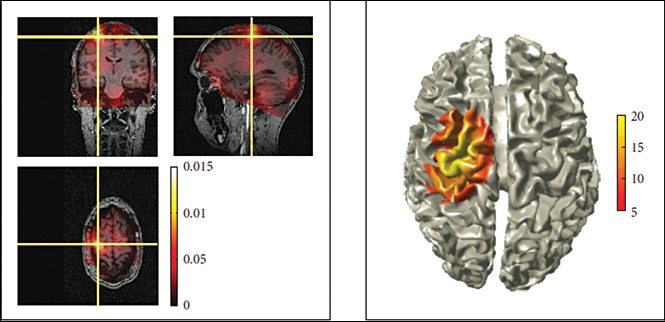
Result visualisation. MATLAB by itself has a variety of data visualisation and plotting tools. But when we are dealing with complex analysis or visualisation of multidimensional data, this could be difficult. In order to resolve this issue, FieldTrip comes with several high-level plotting functions.
For visualising sensor-level data, it is interpolated on a 2D projection of sensor positions.
Modular design. One major advantage of having a modular design is reusability of the code. fileio module that we discussed earlier is used in both SPM8 as well as FieldTrip software. Not only does this help in avoiding recurrence of work in rewriting the code, but also provides access to a comprehensive set of data formats. Other modules that are shared between these software are forward and Preproc modules.
While FieldTrip uses SPM for processing anatomical MRI data, SPM relies on FieldTrip for various algorithms on analysis of EEG and MEG data. The codes are also shared with software including EEGLAB, BESA and BCI2000.
Boosting experimental neuroscience
FieldTrip has brought significant contributions in the field of experimental neuroscience. The open source nature of the code has allowed active exchange of ideas between developers and users. The fact that experimental scientists and method developers have benefitted from this tool is exemplified by hundreds of research publications based on the tool. If you are a serious researcher in neuroscience, we suggest you give it a try.
For more information: click here
The author is an electronics enthusiast from Kerala






