 Presented here is an automatic switch-off battery charger based on a 555 timer IC. This smart charger automatically switches off when your rechargeable batteries reach the full charge.
Presented here is an automatic switch-off battery charger based on a 555 timer IC. This smart charger automatically switches off when your rechargeable batteries reach the full charge.
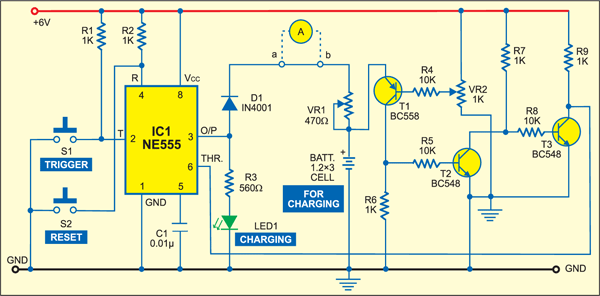
The circuit comprises a bistable multivibrator wired around timer IC 555. The bistable output is fed to an ammeter (via diode D1) and potmeter VR1 before it goes to three Ni-Cd batteries that are to be charged.
Automatic Switch-off Battery Charger
Circuit Operation
Normally, the full charge potential of an Ni-Cd cell is 1.2V. Trigger the bistable by pressing switch S1 and adjust potentiometer VR1 for 60mA current through the ammeter.
Now remove the ammeter and connect a jumper wire between its points ‘a’ and ‘b.’ Connect the positive output terminal of the batteries to the emitter of pnp transistor T1. The base of transistor T1 is held at 2.9V by adjusting potentiometer VR2. The output of transistor T1 is inverted twice by npn transistors T2 and T3.
Thus when the batteries are fully charged to 3×1.2V=3.6V, a voltage higher than this makes transistor T1 to conduct. Transistor T2 also conducts and transistor T3 goes off. The threshold level of timer 555 reaches 6V, which is more than 2/3×VCC = 2/ 3×6=4V, to turn off the timer.
During charging, the threshold level of the timer is held low. The green LED (LED1) glows during charging of the batteries and goes off at the attainment of full charge.
Note that this circuit can be used only for 1.2V, 600mAH Ni-Cd rechargeable batteries that require 60 mA of current for 15 hours to charge fully.
Adjustment Guidelines for Optimal Charging
- Charging Specificity: This circuit is intended for 1.2V, 600mAh Ni-Cd rechargeable batteries that require a 60mA charging current over 15 hours to fully charge.
- Modification Advice: For higher-capacity batteries or different battery chemistries, change VR1 and VR2 to account for various charging currents and voltage cut-off levels.
- Power Efficiency: To ensure steady charging circumstances, use a regulated 6V DC supply.
The article was first published in June 2005 and has recently been updated on 30 October 2024.








Thanks a lot for this project. My worry is can this circuit be adapted to charge a 12v 2.1A lead acid battery?
Please see the last line of this article. The circuit is meant for 1.2V, 600mAH Ni-Cd rechargeable batteries.
What are its benefits?
Is it suitable for 48x2V or 24x2V batteries?
Hi,
Can this circuit be powered by a USB Port?
This circuit can be powered using a 6V DC USB power supply. There are many variable USB DC power supply available in the market. Use a suitable power supply with USB connector.