The Automotive Buck-Boost DC-DC Converter reference design offers MOSFET options for optimal performance, ensuring stable output voltage and efficient power delivery in automotive applications.
USB Power Delivery (PD) charging has gained popularity for devices like smartphones, tablets, and laptops. To meet the increasing demand for power supply in vehicles, USB Type-C® connectors have been adopted, making USB PD charging popular even in cars. In USB PD, the receiving device determines the output voltage, requiring a buck-boost converter to adjust the voltage from the vehicle battery. This H-bridge type buck-boost DC-DC converter converter utilizes four switching elements. We’ve developed an efficient and space-saving automotive buck-boost DC-DC converter by employing our compact automotive MOSFETs as switches.
Toshiba’s Automotive Buck-Boost DC-DC Converter reference design offers two types of automotive MOSFETs for the H-bridge buck-boost DC-DC converter. Option 1 utilizes the XPN7R104NC, while Option 2 utilizes the SSM6K804R. Furthermore, our automotive MOSFET XPN3R804NC is a switching device in the reverse-connection protection circuit and shield short-circuit protection circuit.
The non-inverting buck-boost DC-DC converter circuit combines buck features and boosts DC-DC converters to achieve higher efficiency. Using synchronous rectification with MOSFETs instead of diodes further improves efficiency. This circuit, often referred to as an H-bridge buck-boost DC-DC converter, includes four MOSFETs positioned around the inductor. It is ideal for applications requiring seamless switching between step-up and step-down operations. This converter ensures a constant output voltage even when the input voltage fluctuates, making it suitable for use with batteries. Additionally, it can adjust the output voltage based on the load requirements, such as in USB Power Delivery devices.
In the automotive industry, designing efficient and reliable USB power chargers, DC-DC converters, and in-vehicle infotainment (IVI) systems requires careful consideration of factors such as power supply noise reduction, power consumption reduction, and circuit miniaturization. Toshiba offers a range of semiconductor products tailored for these applications, including circuits for cigar sockets or accessory circuits in USB power chargers, step-up or step-down DC-DC converter units, and components for display, audio output, video and voice input, and wireless communications sections in IVI systems. Additionally, Toshiba provides circuit configuration examples to aid designers in implementing these solutions effectively.
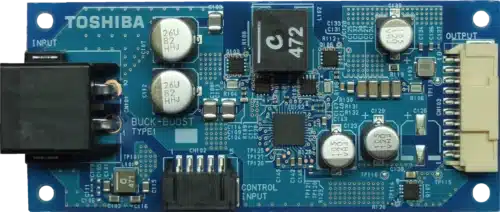
The design features include high efficiency, with Option 1 reaching a maximum efficiency of 96.4% and Option 2 achieving a maximum efficiency of 95.5% under the same conditions. The outline size is compact at 90 mm x 40 mm. Additionally, there are various MOSFET options available for this product.
The device features a wide input voltage range of DC 5 to 18 V, with a typical voltage of 12.6 V. It provides an output voltage range of DC 3.3 to 21 V, supporting an output power of up to 60 W. The circuit topology employed is an H-Bridge Buck-Boost Circuit.
Toshiba has tested this reference design. It comes with a Bill of Material (BOM), schematics, a Printed circuit board (PCB) layout, and other data. You can find additional data about the reference design on the company’s website. To read more about this reference design, click here.








