This article is a part of a Tech Expert Interview with Rei Tjoeng from Sharp Devices: The Market Is Now Shifting To Large-Size TFT Displays In The Automotive Segment
Wanting to select the right LCD screen for an automotive design? Here’s a list of parameters you need to consider:
High brightness and anti-glare
More brightness and higher contrast make the display clear even during bright sunlight conditions. Manufacturers have enormously brought down surface reflectivity with anti-reflective coatings, making the display easier to pursue during high-sunlight glare conditions. Progressive Super View Technology of Sharp, for example, gives an extremely crisp image under sunlight without pumping more power from the backlight, which helps in maintaining the life and quality of the product.

Screen size and resolution
Auto displays range from 3.8cm to more than 30cm. There’s a trend toward bigger display sizes (up to 61cm), with the reception of solid-state and advanced digital clusters. Thus, HD resolution is moving from wide VGA (800×480) to 720p and 1080p.
Form factor
In the automotive sector, the most common aspect ratio for display sizes between 17.8cm and 31.4cm are 16:9, 5:3, 16:9, and 16:6. From hatchback, sedan to SUV, the height varies a lot and, therefore, aspect ratio plays a vital role for display selection. Recent innovations like Free Form help automotive designers to break free from the rectangle to any size or any form factor of the display. The device may be shaped to fulfil a large range of user needs due to the incorporation of IGZO technology and proprietary circuit design methods.
Conventional displays are rectangular because they require a minimal width for the bezel so as to accommodate the drive circuit, called the gate driver, around the perimeter of the screen’s display area. With the morpheme display (using IGZO technology), the gate driver’s function is dispersed throughout the pixels on the display area. This enables the bezel to be shrunk considerably, and it gives the liberty to style the LCD to match whatever shape the display area of the screen has to be.
Interface
Low-voltage differential signalling (LVDS) could be a popular choice for giant LCDs and peripherals in need of high bandwidth, like high-definition graphics and fast frame rates. It is most ordinarily utilised in automotive TFT applications. It’s an excellent solution due to its high speed of data transmission while using low voltage.
Two wires carry the signal, with one wire carrying the precise inverse of its companion. The electrical field generated by one wire is neatly concealed by the opposite, creating much less interference to nearby wireless systems. At the receiver end, a circuit reads the difference (hence call Differential) in voltage between the wires. Therefore, this does not generate any noise or gets its signals scrambled by external noise. The interface consists of four, six, or eight pairs of wires, plus a pair carrying the clock and a few ground wires.
Wide viewing angle
Centre-stack displays should be visible to both driver and the passengers, including those on the rear seats. LCD display modules are designed to provide the best contrast and readability in one of the four directions, known as the Viewing Angle or Optimal Viewing Direction. These four directions are laid out in the shape of a clock. The top view is at 12:00pm and the bottom view is at 6:00pm.
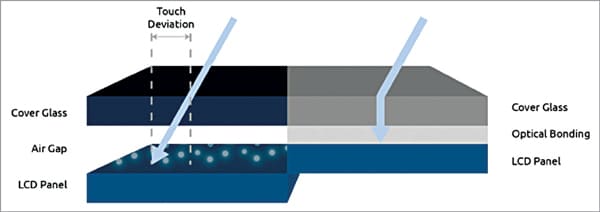
Touch and glass bonding
Optical bonding is the method involving overlaying touchscreens, glass, or plastic cover lenses, adding EMI filters and other display upgrades to an LCD. A layer of glue is incorporated between the cover layer and display to fill the air gap abandoned in a regular edge or gasket bonding. Optical bonding helps in enhancing clarity, viewability, reducing reflections, and making TFT more rugged, which are critical factors in automotive applications.
Wide temperature range
Temperature range can typically span from -40°C to 85°C. Such a high-temperature range is required because in summer ambient temperature adds up with the operational temperature of TFT, where normally in desert areas ambient temperature rises to 55°C in summer.
Colour depth
Higher-resolution displays might have to upgrade from 18-bit red, green, blue (RGB) to 24-bit RGB to attain a wider colour gamut.
Refresh rate and response time
Keeping away from slacks is basic for warning indicators and navigation functions like maps and traffic updates.
Power consumption
Low power consumption enables better fuel consumption and allows components to be placed in hot spots.
Lifetime and production support
Displays must support design and production cycles of a minimum of five years, extendable up to ten years because of vehicle warranties.








