Mechanical switches are one of the most common components used in electrical and electronics manual control circuits. When you press a mechanical switch, two metal parts come in contact with each other, and the current flows through the contacts. But sometimes the metal parts connect and disconnect several times before the actual stable connection is made. The same thing happens while releasing the switch button. The mechanical switch bounce or contact bounce, sometimes called chatter, is a common problem associated with mechanical switches and relays.
Note that each switch has its own characteristics regarding the bounce. For example, you may have two similar switches, but there is a high chance that each will bounce differently. These problems are very common in digital and microcontroller circuits associated with the mechanical switch. These chattering inputs are electrically cleansed with a switch debouncer circuit to prevent or reduce false triggering or multiple triggering.
One of the simplest solutions is adding a resistor and capacitor (RC) across the switch, as shown in Fig. 1. Here, the RC circuit acts as a filter to smooth out the output glitches. When the switch is open, the voltage across the capacitor remains zero. Initially, the capacitor charges through the resistors (Rp and Rd).
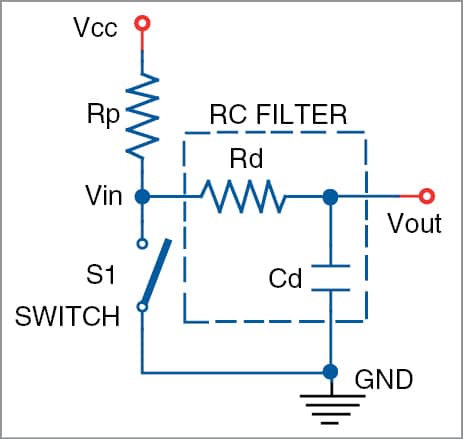
When the switch is closed, the capacitor starts discharging through Rd, and hence the voltage output (Vout) becomes high. In the bouncing condition, the capacitor stops the voltage at the input voltage (Vin) until it reaches Vcc or ground, preventing false triggering.






Your explanation is wrong, unfortunately!
Hi Prinz, can you help us improve this article? Please share the correct information so that we can check on our side and update the article
When the switch is open, the capacitor charges through the two resistors until Vout becomes high. When the switch is closed the capacitor discharges through Rd until Vout becomes low. While the switch is bouncing (either while closing or opening) the capacitor is rapidly charged and discharged small amounts and Vout stays at approximately the state it was in (high or low) until the bouncing stop.
Thank You, Gord. We will review your comment and update the article as soon as possible.