Life seems to find its ways in highly irrelevant nonliving spaces. Little did the barbaric clans of World War II ever imagine that a 180 steps descent old, suffocating, deserted tunnel meant to shelter thousands of people during war could inspire a documentary film maker, Ballard (of the Ballard-Dring led Growing Underground fame) to target vertical farming using LEDs. From 33 meters below the streets of London, at a growth stage of 2 weeks old, microgreens are the new “fast-foods”- Carbon Neutral and B Corp Accredited Salad to reach your plates and palates via the mainstream UK supermarkets. They use HYDROPONICs.
What we know today as Hydroponics blooming around the busy Israeli urban zones- Tel Aviv and Jerusalem, had its first roots floating through the hanging gardens of Babylon (present day Iraq) way back in 500 BC, an estimated twelve hundred km away. Other countries who lead the global market in hydroponics today are driven either by the natural atmospheric factors or the dearth of it. UK, India, Australia, Japan, South Africa, Moon and Space are motivated by one or more of the factors – Windchills, Heat waves, Overpopulation, Scanty rainfalls, infected soil micro-organisms, water crisis and/or transportation costs to opt for alternate sources of farming and agriculture.
Thus, developing a controlled micro climate zone under the roof of a chaotic world using Climate-Land-Energy-Water (CLEW) mapping techniques are the popular alternatives. It also targets to support the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) proposed by UN in 2015. Increased analytical modeling and computational capacity further supported by bilateral linkages across borders have led to better socioeconomic outcomes.
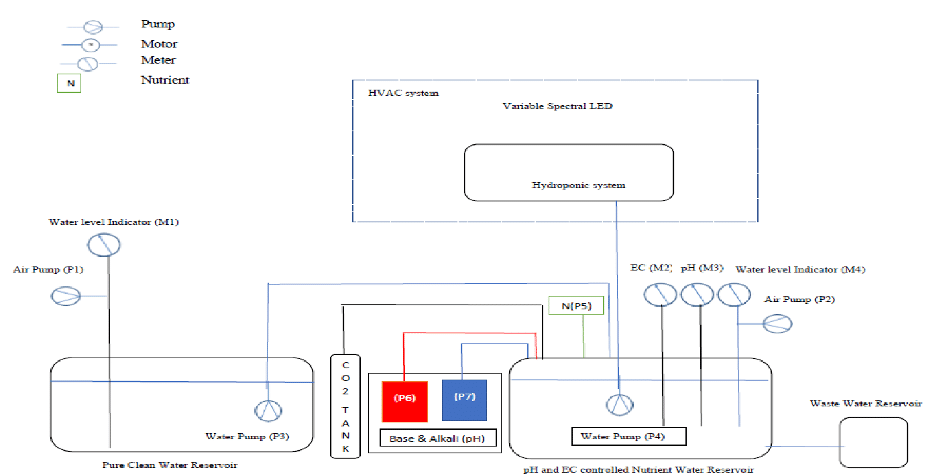
Fig 1 clearly indicates the dominance of electronic devices, monitoring setups, programming nutrient flows, maintenance of desired conditions for growth of a typical Hydroponic plant as food moves from seed to plate.
In the early 20th century, botanists experimented with the nutritional requirements and the techniques to enhance their delivery to the plant. Through experiments, it was deduced that instead of soil, it is the minerals present in the soil and the corresponding spaces in between (for oxygen) that was necessary for growth. Dr. Victor Tiedjens, in the 1920s, with experimentation concluded that nutrients when dissolved in water was best absorbed by plants. This was the beginning of liquid fertilizer.
In 1929, W. F. Gericke successfully converted his nutriculture laboratory into a commercial crop production unit using hydroponics thus confirming optimal results and faster growth. A water solution containing salts of Nitrogen (N), Phosphorous (P), Sulphur (S), Potassium (K), Calcium (Ca) and Magnesium (Mg) together with elements Hydrogen (H), Oxygen (O), and Carbon (C ) derived from air and water make up the macronutrients. Iron (Fe), Chlorine (Cl), Manganese (Mn), Boron (B), Zinc (Zn), Copper (Cu), and Molybdenum (Mo) are the micronutrients. Every plant has a different need of nutrition at various stages of development and their continuous monitoring in Controlled Environment Agriculture (CEA) is possible only through various electronic sensors and interfaces.
LED technology came up during the 1960s – a working option provided by Nick Holonyak Jr-a 33-year-old General Electric (GE) scientist. LED or any kind of supplemental lights contributes by increasing photon accessibility to our plants. Moreover, they don’t radiate much heat- so the requirement of high-power coolers can be waived away. Also, they can be easily operated on renewable sources of energy. Just like our regular plants respond to spectrum variation in the sunlight in terms of growing leaves, growing tall, flowering or fruiting throughout the days, months and years, Spectrum variable LEDs do the same by feeding the indoor plants the correct wavelength. This allows producers to manipulate growth in specific parts of the plant- thereby making your food more sweet, tangy, mild, fragrant and/or color vibrant.
Two types of pumps are required for a hydroponic system-a water pump for water and nutrients while an air pump – to infuse oxygen into the water system. A submersible water pump can be placed underwater. It is cheap but heat generative. Its performance is measured in GPH-Gallons Per Hour, the liters of water it can displace to variable head heights. An inline pump is essentially placed outside the system but is associated with high power delivery and durability. The origin of pumps began with the shadoof in the 2000 BC in Egypt. In today’s world, Integral VSDs-Variable Speed Drives, SCADA systems and Condition Monitoring equipment dominate the markets thanks to parallel progress in CAD-Computer Aided Design and CFD-Computational Fluid Dynamics based design understanding and implementation.
HVAC-Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning system is the heart of a Hydroponic setup. It essentially ensures a smooth balance between the inside and the outside atmosphere and also provides compression, blowing and filtering using ducts. In the 1800s, Dr. John Gorrie proposed cooling cities during summer months, patented it and planned automatic humidity and temperature control. In 1932 H.H. Schultz and J.Q. Sherman offered a portable unit that could fit in a window like space and this is how large-scale HVAC units developed through the years.
Media bed acts as a medium to support the root system of plants and also doubles up as a mechanical and biological filter. The medium is expected to be chemically inert, permeable to air and water. A bell siphon is a device used to efficiently regulate the flow of water in a media -based aquaponics system automatically with minimum human intervention. The bell siphon maintains a minimum water level in the grow bed as it drains the excess water. The media can also be used as a platform to fit electronic sensors (communicable using wired or wireless networks) to monitor the overall health and growth of the crops.
The concentration of salts (Nutrients generally dissolve in water) is measured by an EC or ppm meter. The positively charged ions conduct electricity that is measured in ppm. Electro-Conductivity (EC) or Conductivity Factor (cF) can be expressed as either milliSiemens (mS), cF, or parts per million (ppm) where 1 mS = 10cF = 700ppm.
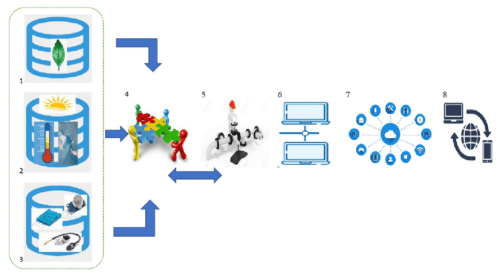
A typical hydroponics structure has the following components-
- Plant Database
- Atmospheric/ Surrounding database
- Sensor database
- Integration/Decision-making Unit
- Automated Control of valves, flow of water & nutrients
- Data storage
- IoT interface
- Remote Access
A hydroponic system is expected to interface existing conditions and based on the monitored samples, input of water, nutrients, pH enhancers can be altered. It is generally aimed to be self-sufficient in terms of energy requirements mostly using renewable sources of energy. The power of Hydroponics- reduced water intake, reduced land occupation, insect free zone when coupled with the contribution of electronic devices, sensors, pumps and interfaces ensure that all nutrients are kept within the closed-loop removing any risk of agricultural run-off.
Aquaponics is a specialized branch of hydroponics, wherein the nutrition need is fulfilled by fish waste. Water usage is highly limited and it is a closed loop symbiotic relationship through establishment of artificial food chain linkages.
Crops
One crop that has continued to be grown hydroponically since 5000 BC when it was first known to evolve till date is Rice, or Paddy- a water intensive crop that happens to be the staple diet of approximately half of the world population, followed by wheat and maize. Today also, one of the biggest challenges to the Agricultural, Biotechnological and Climatic sector is to cultivate Paddy. The minimum water requirement to grow 1 Kilogram of rice still happens to be in the range of 4000-5000 liters. As the amount of irrigable water is limited, sea water (66% constituent of the Earth’s surface) is under investigation to provide a solution to this persistent query.
The list of crops that can be hydroponically grown are definitely more than what is quoted here
- Flowers – Orchids, Iris, Daffodils, Chrysanthemums, Gerbera, Carnations, Peace Lily.
- Fruits – Blueberries, Strawberries, Melon, Watermelon,
- Vegetables – Tomato, Peppers, Beans, Cucumber, Pea
- Herbs – Thyme, Parsley, Mint, Chive, Lemongrass, Celery
- Fungi – Mushrooms
A comparative of the harvests per season is charted for few common crops in the following table.
| Crop | Traditional medium | Alternate medium | pH value | EC | ppm |
| Vegetables | |||||
| Tomato | 10-12 tons/acre | 180-200 tons/acre | 5.5-6.5 | 2-5 | 1400-3500 |
| Peppers | 10-12 tons/acre | 120-140 tons/acre | 5.8-6.3 | 2-3 | 1400-2100 |
| Cucumber | 15-20 tons/acre | 200-220 tons/acre | 5.5-6.0 | 1.7-2.5 | 1190-1750 |
| Green leafy vegetables | |||||
| Lettuce | 9-10 tons /acre | 300-400 tons/acre | 6.0-7.0 | 0.8-1.2 | 560-840 |
| Cabbage | 6-7 tons/acre | 10-12 tons/acre | 6.5-7.0 | 2.5-3 | 1750-2100 |
| Pakchoi | 10-12 tons/acre | 280-320 tons/acre | 7 | 1.5-2 | 1050-1400 |
| Fruits | |||||
| Strawberries | 20-25 tons/acre | 50 tons/acre | 6 | 1.8-2.2 | 1260-1540 |
| Blueberries | 20-25 tons/acre | 55 tons/acre | 4.5-6.0 | 1.8-2.0 | 1260-1400 |
Various designs are proposed for hydroponics and its choice is driven by factors like sustainability, scalable solution, reduced water use, ability to use recycled water and impressive efficiency. Following are the techniques commonly used – Wick System, Water Culture, Ebb and Flow, Drip, Nutrient Film Technology and Aeroponics out of which the below-mentioned techniques find wide acceptance in the commercial domain.
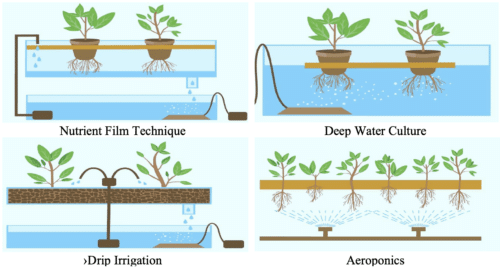
The following table provides a view about the various techniques used for hydroponics and the major attributes associated with each.
| Technique | Root exposure to nutrients | Pumped Water supply | Water demand | Disease |
| Nutrient Film Technique | Partial thin film of exposure to nutrient solution | 24 X 7 pumping through a sloped channel | More than Drip Irrigation | Root Rot |
| Deep water Culture | Throughout dipped in water nutrient solution | Filled container | Maximum | Insufficient oxygen content |
| Drip Irrigation | On and Off exposure | Pipe supply and drip emitter | Normal | Fungi/Bacteria infection in media bed |
| Aeroponics | Exposure in bursts | Sprinkler with mist nozzles | Minimum | Healthy roots |
Development
Hydroponics is no longer confined to water as the medium for cultivation. Other techniques are gradually germinating, growing, flowering and resulting into fruitful ventures thanks to the support provided by the parallelly growing electronic components, interfacing possibilities and government as well as NGO initiatives and support system. Even the lockdown has actually provided options to learn and grow. Consider the contribution by Ex. Navy personnel, Alumnus of the National Defence Academy, India, C V Prakash (CV Hydro Training Centre, Bengaluru) who in his experimental setup substituted regular soil by cocopeat in grow bags and converted a gift of rhizomes of the Tiger Claw Salem turmeric variety into a whopping crop harvest success story. Eurofin labs, Bengaluru have confirmed the curcumin content (known for its cancer fighting properties) of 5.91% (almost double of the regular 3% generally seen in the Salem variety) and no trace of heavy metals contributed largely by the precision irrigation, correct leaching fraction and the use of beneficial microbes. Mission Turmeric 2021 is his new venture which is also fondly called the Orange revolution embarking upon a commercial pilot run in May 2022. And this would not have been possible without the sensors, the stabilizing setup arrangements, the microprocessor program-based monitoring, feedback and HVAC- all gifts of the advances in the Electronics industry.
References:
- https://growing-underground.com/about/
- https://californialightworks.com/
- https://www.trees.com/gardening-and-landscaping/hydroponic-plants
- https://growguru.co.za/
- https://www.thebetterindia.com/260107/navy-cv-prakash-how-to-grow-bags-turmeric-hydroponics-soil-less-farming-yield/
This contribution is a follow up to a talk “Automation of an existing Hydroponics System” delivered by Dr. Geetali Saha during the ITW-TWC Talks during December 2020.






