A smart plug that works as a power meter and wirelessly transmits data to an Android device via Bluetooth interface.
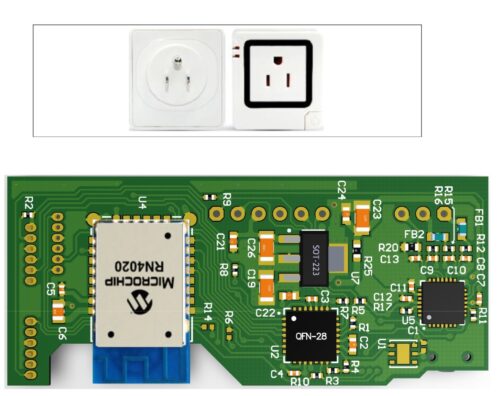
A smart plug can remotely control and monitor plugged-in electrical devices over Wi-Fi or Bluetooth. Microchip has launched a smart plug reference design that functions as a power meter and can transmit its data wirelessly to an Android device via Bluetooth. The design computes real-time Root-Mean-Square (RMS) current, RMS voltage, frequency, active, reactive, and apparent power, power factor, and energy consumption. The smart plug enables remote power control, helping users save energy by turning off unused devices instead of leaving them in standby mode. Additionally, it provides a simple method to monitor the electrical performance of household devices and appliances, facilitating early detection of malfunctions in case of overpowering or overcurrent situations. The smart plug can be placed between the electrical outlet and the electronic device the user wishes to monitor and control from a distance.
The MCP39F511 Smart Plug consists of three PCBs, with the North American plug board as the base for the other two boards: the power board and the Bluetooth Low Energy (BTLE) microcontroller unit (MCU) board, which are mounted vertically. The design is based on the BTLE MCU board, an affordable and versatile microcontroller with two UART modules and an internal oscillator. The MCU is the system’s core, extending power monitoring capabilities through wireless connectivity. The plug uses a latching type relay that consumes power only during state transition, not in ON or OFF, to allow remote turn on and off. Two status LEDs are included in def=sign to show the on and off status of the relay. The power board houses the AC-to-DC converter, providing power for the whole system.
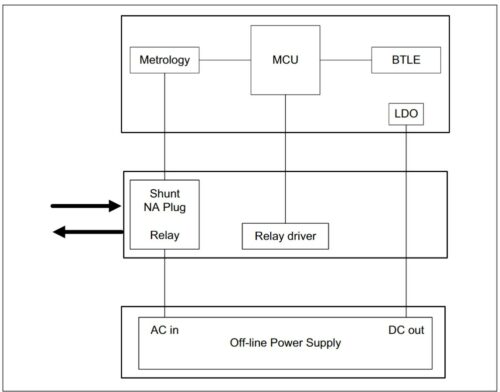
The smart Plug design runs on the nominal input voltage of 120V/230V. The design works at the nominal frequency range of 50Hz to 60Hz. The Bluetooth range of the smart plug is up to 100m. The reference design includes the wireless reporting of all power and energy quantities and a button for turning the wireless module OFF. The MCU obtains the wireless request and communicates with the power monitoring IC by sending a read command frame through the universal asynchronous receiver-transmitter 1 (UART1) interface. The power-monitoring IC sends the values of internal registers containing calculation results in response. The MCU transmits the data requested to the BTLE module via the UART2 interface, which wirelessly transmits the data, and displays it in real time on the screen.
Microchip has tested this reference design. It comes with a Bill of Material (BOM), schematics, Printed circuit board (PCB) layout, etc. You can find additional data about the reference design on the company’s website. To read more about this reference design, click here.






