A secure, low-power sensor network design with encrypted data, NFC authentication, and cloud integration. Learn more!
The MAXREFDES9001 is an IoT security reference design from Analog Devices (ADI) that provides a solution for design engineers looking to implement secure, low-power sensor networks.
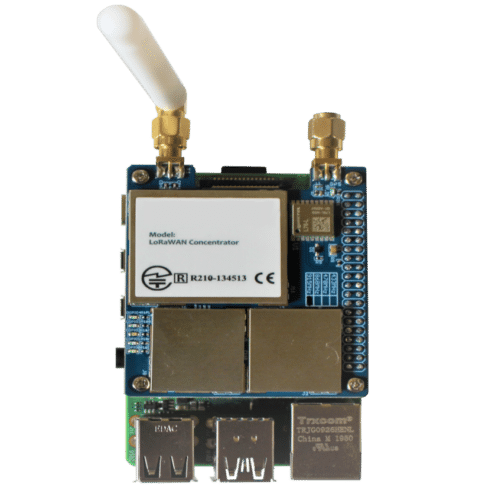
It features a LoRa-based temperature sensor node, secured by the DS28S60 cryptographic coprocessor, and includes a LoRa gateway and a cloud application hosted on AWS infrastructure.
This reference design provides an end-to-end security framework with authentication and confidentiality independent of the transmission protocol—in this case, the LoRaWAN protocol.
It is intended for engineers seeking to integrate communication and data integrity into embedded systems.
Design engineers can use this reference design to develop and deploy a sensor node that measures ambient temperature with the DS7505 temperature sensor.
The node uses the Cortex-M4-based MAX32660 microcontroller to manage communication between the components and encrypts the temperature data via AES-GCM encryption with the DS28S60 secure coprocessor.
The encrypted data is transmitted through the LoRaWAN network to the cloud via a Raspberry Pi-powered gateway.
Engineers can implement NFC-based authentication for sensor nodes to ensure security.
Before transmitting data, the sensor node must be authenticated via an NFC-enabled Android device using the MAX66242 Secure Authenticator.
This process verifies the node’s authenticity and prevents unauthorized devices from joining the network.
Once the sensor node is authenticated, the Android device interacts with the cloud application to provision the node. This involves generating a certificate for the sensor node and performing an AES-GCM key exchange with AWS infrastructure using the Elliptic Curve Diffie-Hellman (ECDH) protocol.
The certificate and key exchange are stored in the DS28S60 coprocessor, ensuring the node can securely transmit temperature data to the cloud.
The cloud application can further authenticate the sensor node using ECDSA, confirming the validity of the node’s certificate and key pair.
This reference design is useful for engineers who want to secure data transmission, regardless of the underlying communication protocols.
While the process also joins the device to the LoRaWAN network via AWS IoT Core, the main advantage is securing data transmission and ensuring integrity, confidentiality, and authentication.
Key components in this reference design include the DS28S60 cryptographic coprocessor, which encrypts data using AES-GCM through an SPI interface; the DS7505 temperature sensor, which provides temperature readings via I2C; the MAX66242, which enables NFC communication between the Android device and the sensor node; the MAX32660 microcontroller, which manages communication across the modules; and the SX1262, which modulates and transmits the encrypted data via the LoRa protocol. These components offer a solution for IoT designs.
ADI has tested this reference design. It comes with a bill of materials (BOM), schematics, assembly drawing, printed circuit board (PCB) layout, and more. The company’s website has additional data about the reference design. To read more about this reference design, click here.






