 This touch based doorbell makes use of enhancement-mode MOSFETs forming part of CMOS quad NAND gate CD4007B in conjunction with a detector and Darlington driver stage.
This touch based doorbell makes use of enhancement-mode MOSFETs forming part of CMOS quad NAND gate CD4007B in conjunction with a detector and Darlington driver stage.
Touch based doorbell circuit
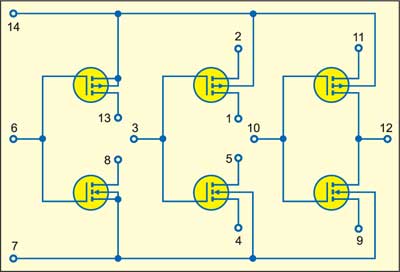
IC CD4007B comprises a dual complementary pair and an inverter. It has three p-channel and three n-channel enhancement-mode MOSFETs as shown in Fig. 1. The devices can be individually accessed for use as very high-input op-amps besides their use as linear amplifiers, current sinks/sources and crystal oscillators.
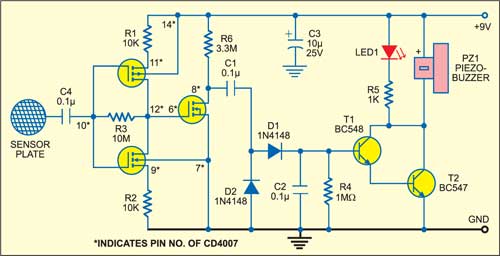
The circuit of the touch plate doorbell is shown in Fig. 2. Here, we have used the complementary pair comprising common gate (pin 10), individual drains (pins 9 and 11) and common output (pin 12) as a very high input micropower linear amplifier capable of amplifying the hand/finger induced AC voltages by a factor of ‘40.’
The output of this complementary stage is further amplified by a single-stage n-channel MOSFET (gate=pin 6, source=pin 7 and drain=pin 8). The output of this stage is detected by the detector circuit comprising diodes D1 and D2, with R4 acting as a bleeder resistance across C2. The detected voltage is amplified by the Darlington stage comprising transistors T1 and T2, which drive an LED-buzzer combination of LED1-PZ1 when a person touches the metallic sensor plate.
Construction & testing
The sensor plate can be suitably mounted on the entry door. For power supply, you can use either a 9V battery or a battery eliminator.
We have also designed the touchless doorbell using Arduino that only rings when hands are sanitized.
The article was first published in August 2006 and has recently been updated.







