The battery gives an electric vehicle the power to traverse long distances smoothly. When upgraded with a next-gen technology such as IoT and AI, then the entire system is bound to become even more enhanced.
As you all know, an electric vehicle or an autonomous vehicle consists of many mechanical and electrical parts. One of the crucial parts is the Battery Management System (BMS).
If you look at a simple electric vehicle, it has a battery, a converter and a motor. But that’s not all. We need to monitor and take care of the whole system continuously to prevent any anomaly. If you are driving a vehicle at high speed on a highway, you would not like anything to go wrong due to a significant load on the battery.
Basics Of IoT
Speaking of IoT, the term is not new. It’s a name given to a technology that has existed for decades. Internet of Things (IoT) describes the network of physical objects – ‘things’ – that are embedded with sensors, software and other technologies to connect and exchange data with other devices and systems over the internet.
The term IoT was coined in 1999, referring to the interconnection of sensors and software on a network. Also, it is where we can control the connected devices, and relevant data can be collected and visualised with the help of a user interface.

The lifecycle of IoT is as follows:-
- Collect: Data is collected from sensors and various other devices. They can be associated with a home, vehicle or manufacturing plant.
- Communication: We use a communication gateway to send data to a destination (cloud platform). WiFi, 4G and 5G can be a communication medium. Google Cloud, AWS, Azure or a personal data centre are some examples of cloud platforms.
- Analysis: Data is nothing without information. Therefore, information should be generated or created from this raw data. The cooked data is then visualised, reports are built and can be used to make predictions.
- Action: Based on the extracted data, further actions can be described. We can communicate with other devices through machine-to-machine (M2M) protocols or send notifications (SMS, email, etc.) to the concerned person for rectifying any errors.
About Electric Vehicles (EVs)
In literary language, we can say, “An electric vehicle (EV) is defined as a vehicle that uses one or more electric motors or traction motors for propulsion.” An EV may be powered through a collector system by electricity from off-vehicle sources, a self-contained battery, solar panels, fuel cells or an electric generator to convert fuel to electricity.
Most people think that smart cars such as Tesla can only be classified as EVs. But that’s not the case. We have had EVs here in India for a long time. I am talking about trains; they are also EVs. Their engines are traction motor-based. Therefore, the central part of an EV can be a traction motor, a BLDC motor or an AC induction motor.
Some advantages of EV are:
- Reduced dependency on petrol, diesel or any other fossil fuels
- Ensures environment is free from pollution and noise
- Comes with recyclable batteries (Li-Ion)
- Lowers maintenance and operation cost involved
For travel up to 100kms in a petrol-based or diesel-based car, you need to fill around Rs 2000 worth of fuel. But you can travel the same distance in an EV by charging for 3-4 hours. Comparatively, this costs less and does not hurt your pockets.
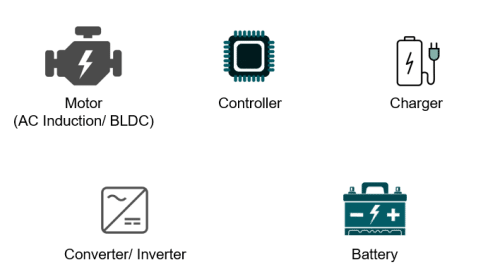
- Motor: It can be an AC induction motor or a brushless DC (BLDC) motor. Although there is a massive debate on which one is the best, they both have their advantages and disadvantages. Different companies use different types of motors. For instance, Toyota uses an AC induction motor whereas Volkswagen prefers a BLDC motor. Tesla Model S has an AC induction motor while Tesla Model 3 has a BLDC motor.
- Controller: It is a piece of electronic equipment used for controlling everything in a car – from the power deliverance of a battery to the power requirements of a motor.
- Charger: There are two types of chargers; one is like a travel charger and can be plugged into a house electrical socket. It is generally slow. The other is the super fast DC charging station, setup on highways or fueling stations.
- Converter/Inverter: It can be DC-DC or DC-AC, depending on the type of motor (AC or DC).
- Battery: Li-Ion or Li-Po batteries are generally used in EVs due to low-maintenance and high-power delivery characteristics.
EV System Configuration
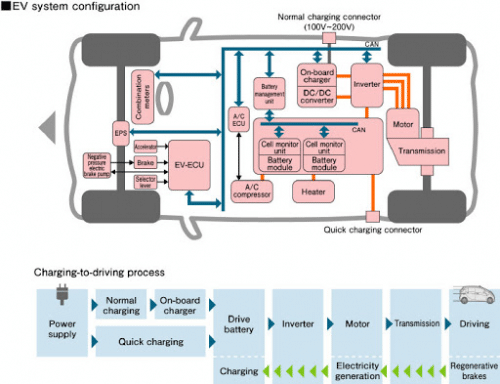
Starting with the power supply, the battery is charged. It can be regular charging i.e. onboard charging or fast charging, which most companies install on the highways. Regular charging takes around 7-8 hours to charge from 0% to 100%. But fast chargers installed in petrol pumps or highways can charge from 0% to 100% within 1-3 hours.
After the battery is charged, an inverter performs DC to AC or DC to DC charge conversion (depending on the voltage or current required by the motor).
The transmission consists of a gearbox and related components. And after that, you can drive.
Another thing to note is that there are regenerative brakes in most EVs. They generate electricity with the help of friction whenever brakes are applied in an EV. This generated electricity is used for charging the battery while driving.
Most EVs have batteries in the car’s base (due to safety reasons) instead of the boot or the front. If anything goes wrong with the battery or it blasts, the car and the drivers will be safe. This is where BMS plays a critical role.
Battery Management System (BMS) With IoT
Until now, we have discussed the basics of IoT and EVs. Here we will learn the role of BMS in an EV, and by integrating IoT and AI into BMS, how we have achieved another technological advancement.
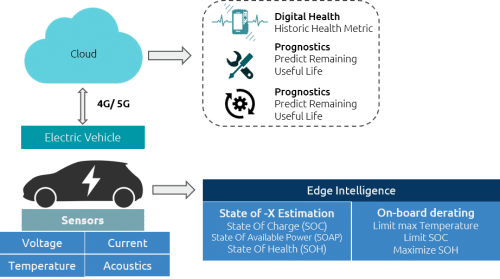
Multiple sensors are installed in a BMS of an EV to monitor voltage, current, temperature and acoustics/vibration in the given figures. These parameters are collected every split second. In intelligent vehicles and EVs, we use an edge intelligence system, which reduces our dependency on the cloud. Most of the EVs have embedded computing systems that work in real-time, allowing the performance of basic operations by itself. For example, the State of X-Estimation, where X stands for the state of charge (SOC), State of Available Power (SOAP) and the State of Health (SOH).
On the other hand, the actions taken by the edge intelligence can help limit certain anomalies, such as limiting the maximum temperature by lowering the power consumption by the motor. Although this can make the EV slightly slower, the motor won’t draw excessive power and heat the battery. Edge Intelligence can also control the State of charge (SOC) to maximise the State of Health (SOH).
With the help of 4G/5G, the data can be sent to the cloud. GPUs with huge computing power can calculate the digital health or predict the remaining useful life on the cloud. If an anomaly occurs in the BMS, then a notification can be sent to our mobile phone or on any dashboard application installed in the EV.
Basically, a digital twin of an EV or every part of it (such as battery, motor, controller) is created. And data from different sensors are analysed to deliver safety of the driver, passenger and the vehicle itself.
The benefits of using BMS with IoT include:
- A mirrored framework of process and functions of a car on the cloud or edge
- Sends updates and maintenance notifications remotely from the car to the maintenance engineer or the car owner/company so that they can guide you through the complex servicing requirements
- Initiate system warning in case of any anomaly
- Management of energy stored in a battery and the amount of charge required (smart charging)
- SOX estimation
- Battery diagnostics
- Cell balancing
- Data collection and processing
Big car companies like Tesla and MG have already installed different kinds of sensors in the car. So on swapping a battery, you will receive a notification that the battery has been uninstalled/installed in a car. Also, these batteries come with an ECU, which has its digital properties and identity.
On the topic of data privacy, it doesn’t matter which company provides the battery. Generally, the data-sharing policies of a car manufacturer play a decisive role. Suppose a particular car company wants to share data with the battery manufacturer. In that case, it’s advantageous for the latter as they can optimise their production according to battery usage and save a lot of time and cost.
Takeaway
Electric vehicles are poised to be the trendsetters of the future. And a highly efficient BMS will play a critical role in accomplishing that. Therefore it is essential to consider various aspects of battery requirements and what benefits the integration of technologies such as IoT and AI can offer.
The article is based on the talk The Combination Of BMS And IoT In EVs by Arqum Ahmad, Scientist (Digital Twin) at Leonardo S.p.A, Italy, presented at the February edition of Tech World Congress 2021. He is also the co-founder and former CEO of Antrax Labs, India.