- The industrial Internet of Things integrates wireless technology but demands robust networks for battery-powered devices.
- Boosted Energy, Spectral Efficiency, and Extended Battery Life – A Game-Changer for Smart Devices Everywhere.
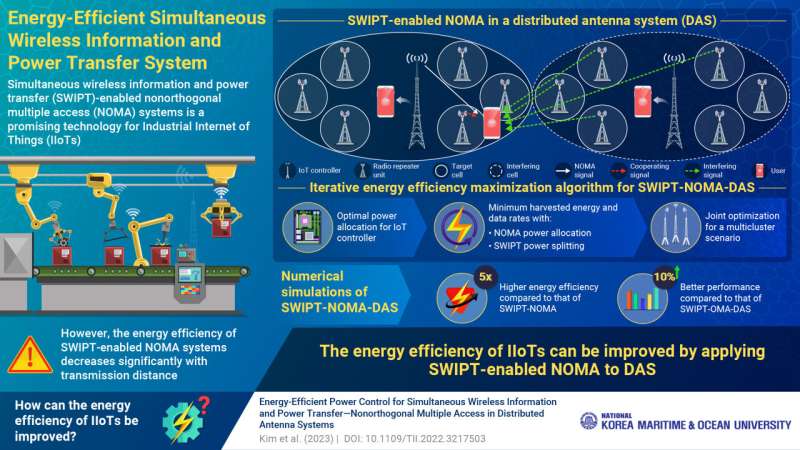
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) merges wireless sensors, controllers, and mobile tech to boost industrial efficiency. Due to its reliance on small battery-powered devices, it demands a robust network for data and power distribution. Wireless power transfer is promising, using radio signals for low-power devices. Simultaneous Wireless Information and Power Transfer (SWIPT) is vital for extended battery life in IIoT, integrated with the nonorthogonal multiple access (NOMA) system. However, energy efficiency decreases with distance from the central controller.
A group of researchers based in South Korea, under the leadership of Associate Professor Dong-Wook Seo from the Division of Electronics and Electrical Information Engineering at Korea Maritime and Ocean University, has introduced an innovative approach. They have successfully incorporated SWIPT-supported NOMA into a distributed antenna system (DAS), resulting in a notable enhancement of energy and spectral efficiencies for IIoTs. Dr. Seo elaborates, “The strategic deployment of a DAS, with closely positioned supporting antennas near edge users in conjunction with a central base station, effectively mitigates the diminishing performance of SWIPT-NOMA over extended distances. This results in enhancing both information decoding and energy harvesting capabilities.”
The research team devised a three-step iterative algorithm to optimise the SWIPT-NOMA-DAS system’s energy efficiency. Their approach involved an initial phase dedicated to fine-tuning the power allocation for the central IoT controller. They jointly optimised the power allocation for NOMA signalling and power splitting (PS) assignment while minimising data rates and the energy-harvested prerequisites. They assessed an outage scenario wherein the system couldn’t deliver adequate energy and data rates. They expanded the joint power allocation and power splitting (PS) assignment optimisation approach to encompass multi-cluster scenarios. Through comprehensive numerical simulations, they verified the effectiveness of their algorithm.
Their findings revealed that the suggested SWIPT-NOMA-DAS system boasts a fivefold increase in energy efficiency compared to SWIPT-NOMA without DAS. It demonstrated over a 10% enhancement in performance when compared to SWIPT-OMA-DAS. This technology efficient energy utilisation, providing numerous benefits such as convenience, minimal power requirements, and extended battery life. It finds applications in smartphones, laptops, wearable devices, and electric vehicles. SWIPT-NOMA-DAS system optimises resource allocation and proficiently handles wireless charging and information transmission for IoT users.






