An innovative bimanual robot demonstrates tactile precision nearly matching human skill, guided by artificial intelligence (AI) in its movements.
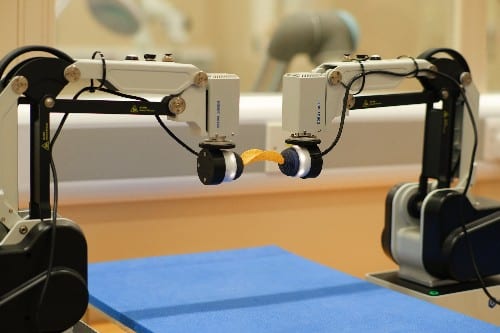
Tactile feedback in bimanual manipulation is crucial for achieving robot skills on par with humans. Yet, this area is less investigated than single-arm scenarios, partly because of the lack of appropriate hardware and the challenges in creating efficient controllers for tasks with expansive state-action spaces.
Scientists at the University of Bristol, based at the Bristol Robotics Laboratory, have designed the Bi-Touch system, which enables robots to perform manual tasks by receiving guidance from a digital assistant. The system demonstrates an AI agent utilizing tactile and proprioceptive feedback to guide robot actions for accurate sensing and practical task completion. This innovation could revolutionise sectors like fruit picking domestic aid and even emulate touch in artificial limbs.
The researchers have created a virtual simulation featuring two robot arms outfitted with tactile sensors. They designed reward functions and a goal-update mechanism to motivate the robot agents to master the bimanual tasks. Subsequently, they developed a real-world tactile dual-arm robot system where the trained agent could be directly applied. This robot acquires bimanual skills using Deep Reinforcement Learning (Deep-RL), a leading-edge technique in robotic learning. Like training a dog with rewards and punishments, Deep-RL is structured to teach robots through trial and error.
In robotic manipulation, the robot learns decision-making by trying various actions to complete specific tasks, such as lifting objects without dropping or damaging them. It receives a reward for successful attempts and learns from failures, determining optimal methods over time. The AI agent operates without visual input and relies solely on proprioceptive feedback, which is the body’s innate ability to sense its movement, action, position, and tactile sensations. Through this approach, the researchers equipped the dual-arm robot to adeptly lift delicate items, even as fragile as a single Pringle crisp.
The Bi-Touch system uses affordable software and hardware to simulate bimanual touch behaviours, transferable to real-world applications. The tactile dual-arm simulation, being open-source, facilitates further research and task development.
Reference: Yijiong Lin et al, Bi-Touch: Bimanual Tactile Manipulation With Sim-to-Real Deep Reinforcement Learning, IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters (2023). DOI: 10.1109/LRA.2023.3295991








