From small innovations like fitness bands to larger, more complex technologies like artificial organs and robotic prosthetic limbs, technology is laying the path for accurate health treatments. Technology helps doctors make sure the right patient receives the right treatment at the right time.
Technologies like augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), artificial intelligence (AI), blockchain, sensors and the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) will shape the future of the medical world in the coming years. Technologies will boost the capabilities of doctors and researchers, whereas patients will get the benefits of new treatments, better healthcare devices and medicines. With advancements in medical technology, patients will be able to make more informed decisions by considering online reviews from apps, social media or friends.
Digital tools and software will help healthcare services to evolve to create unprecedented levels of transparency and transform the way patients interact with their doctors. These will fulfil the demand for instant response and feedback with online scheduling to book, change or cancel appointments. Demand for notifications and reminders about appointments, annual checkups, test results and price promotions will also grow.
Role of digital technology
Mobile technology links patients and healthcare professionals through smartphone apps and wearable tech products. It helps users record data, which could be further communicated. Digital technology has the potential to increase the number of patients seen daily by doctors, promote patient independence and increase focus on prevention.
A mobile working solution reduces paper work, hospital admissions, hospital bed use and cost. Today’s patients can use digital technology to research information online, share experiences and identify treatment options. Digital communication promotes e-visits, e-prescriptions and remote monitoring of changes in the health status of patients. Some applications can even keep track of medications and provide alerts for when to take medicine and automating refilling at the chemist. Whereas, other applications can monitor health parameters like blood pressure and share it with a doctor.
Connected equipment like X-ray machines can notify the monitoring system when an RFID tag worn by a patient is placed under the machine. IoMT identifiers can track the location of every doctor, nurse, patient and other medical equipment staff within a medical facility at any time. AI can predict which patient is most likely to be readmitted based on analyses over 100,000 data points. Predictive analytics can do other things like suggesting treatments, detecting diseases and identifying genetic factors affecting the patient. IoMT sensors can not only monitor but can immediately report when predefined criteria are exceeded.
3D training tools like 3D Medical help doctors learn about human anatomy without an actual dissection. These tools improve the doctors’ understanding of patients by taking them through each stage of a disease. Tools like EchoPixel render patient-specific anatomy in an interactive VR format to increase knowledge, leading to faster and better care. EchoPixel takes data from CT and MRI scans, and transforms it into 3D holographic images to view and interact with patient tissues and organs as if these are real physical objects.
The IoMT, the emergence of distance health
The IoMT refers to a connected system of medical devices and software applications. It includes remote monitoring of patient health and hospital asset management, followed by data analysis of applications for clinicians and patients. Everything from hospital beds to scanners can now be connected using technologies such as Bluetooth tags. Hospitals can track patients and treatments by accessing data via apps on their phones from connected devices like implantable glucose monitoring systems and others.
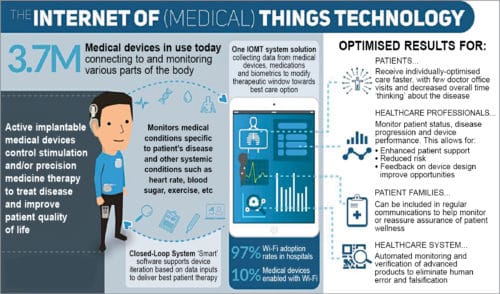
Wireless health monitoring
This offers a quality life for users and provides critical physical, biochemical and genomic data to healthcare professionals. Wireless and mobile cellular networking are increasing the demand for mobile-based solutions, both in general-ward hospital environments and home-care scenarios.
Wireless monitoring has shown unprecedented levels of analysis and understanding into disease progression, diagnosis and therapies. The idea is to allow patients to become responsible individuals in the matters of their own health.
This technology allows continuous, intelligent monitoring of multiple vital signs such as ECG heart rate, body temperature, respiration and activity level in real time, allowing earlier detection and prediction of adverse events such as heart attacks, falls or hypoglycaemia, with the help of appropriate external sensors, such as three-axis accelerometer, digital thermometers, pressure gauges, strain gauges and so on. This allows patients to monitor vital signs, be aware of what they should do in a distress condition and learn to take preventive actions against chronic illnesses.
Benefits of health monitoring apps.
Healthcare apps can be used to monitor health, track activity, adhere medication or notify care providers in case of a health emergency. Patients can immediately get e-consultations through apps like Push Doctor. This increases accessibility, particularly for patients who may be house-bound, bed-ridden or physically unable to go to a doctor.
Role of data analytics
Data managed by medical organisations includes medical insurance claims, hospital asset records, patient health records, pharmacies’ medicine records, data collected from IoT devices or monitoring systems. This data helps in tracking patients and their progress. Healthcare systems can be transformed by deploying technologies like AI, machine learning, blockchain and cloud computing to restructure the way healthcare is delivered, measured and paid for.

The ability to interpret and analyse data inputs has the potential to transform many aspects of the healthcare industry. Key applications for Big Data in healthcare include the IoMT, predictive analysis and patient monitoring in real time. AI and machine learning provide clinical decision support, re-admissions, mediclaim processing and image recognition for diagnosis. These can help schedule doctor appointments based on the severity of symptoms, thus minimising staffing challenges.
Blockchain-based solutions
It is easy to detect fraudulent drug dealers with blockchain-maintained transactions. Blockchain ensures authenticity and high quality of registered medicines. It creates transparency by recording operational data when a drug is produced and moved from the manufacturer to retailer. This makes it easy to prove the authenticity of any registered document, verify the whole path of the drug movement and determine all chain links at any time.
Blockchain allows recording, storing and sharing of results from clinical tests in a secure way. It makes it impossible to modify data as it generates a unique hash every time a modification is made to the data. A patient can decide whom to provide access and whether this access will be full or partial. A few blockchain healthcare startups that have made this technology the base of their operational structure are Guardtime, Gem Health, Cyph, MedRec and Blockchain Health.
Electronics to transform the medical industry
Complete diagnostic tool
DxtER by Basil Leaf is a diagnostic tool that can identify 34 illnesses, including pneumonia, diabetes and atrial fibrillation. It uses a suite of Bluetooth sensors to connect to an app on the tablet. The app informs about the health status through sensors applied on the chest patch, finger probe, spirometer and a combination of thermometer-stethoscope using automated dialogue. Basil Leaf is working on DxtER upgrades that will enable it to use the same hardware to diagnose as many as 75 conditions, including respiratory illnesses and a wider range of cardiac ailments.
Neuromodulation to treat obstructive sleep apnea
Sleep apnea can lead to high blood pressure, heart diseases and stroke. A continuous positive airway pressure device used for treatment is an implant that delivers stimulation to open key airway muscles during sleep. It can be controlled by a remote or wearable patch, the technology acting as a pacemaker. It helps synchronise the intake of air with the action of the tongue with the help of a breathing sensor and a stimulation lead powered by a small battery.
Centralised monitoring of hospital patients
This includes sensors and high-definition cameras around a patient to monitor blood pressure, respiration, heart rate and more. An alert is generated for doctors or on-site personnel that help is needed.
Smart inhalers
A Bluetooth-enabled smart inhaler has been designed to detect need for inhaler use, remind patients to take medicine, encourage proper use of the device and gather data about inhaler use that can help take proper care. A smart inhaler is effective when it is used correctly, so each time it is used, it records the date, time, place and whether the dose was correctly administered. It can also send data to a connected smartphone app.
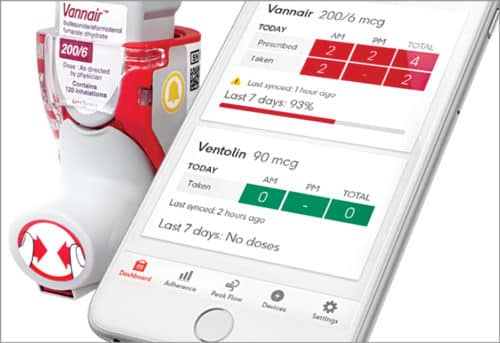
Propeller Health has designed a GPS-enabled inhaler that has a Bluetooth transmitter to communicate with an asthma patient’s caretaker’s smartphone. This sensor activates when the inhaler is pressed and records the exact time and location of a patient’s asthma attack on a smartphone app.
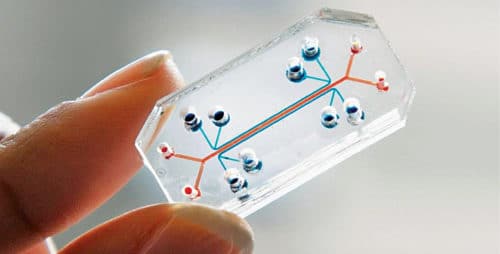
Organs on a chip
Wyss Institute has created organs on a chip by making advancements in DNA sequencing and through in-depth stem cell research. These are electronic sensors that are used to test different kinds of treatment possibilities to choose the best, and apply the same to the patient. These chips mimic different human organs like lungs, kidney, heart, gut, bone marrow and so on. Cells on the chip grow and respond exactly like real cells found in human organs. Now, drugs can be tested safely before being tried on humans. This technology will also prevent killing of several animals due to medical tests being conducted on them.
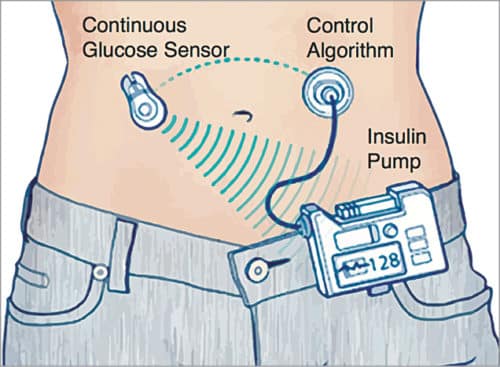
Artificial pancreas
This is a fully-automated, closed-loop insulin delivery system that connects a continuous glucose monitor with an insulin pump to test and manage insulin levels. MiniMed 670G is the first insulin pump to win FDA approval. It is designed to automate blood sugar management by monitoring glucose levels continuously and providing insulin that can stabilise blood sugar levels when required. All of this is managed by an algorithm, or computer model, that connects the insulin pump to the smartphone.
Laws for using healthcare electronic equipment
There are millions of electronic products manufactured every day to provide the healthcare industry with greater efficiency and convenience. However, equipment and computers containing toxic materials, if disposed improperly, can be a threat to public health and the environment. To avoid this, there are three important federal laws that must be followed by healthcare providers:
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)
It requires confidentiality and security of health data stored on computers and other electronic equipment.
Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA)
It manages hazardous waste disposal of computers and other electronic equipment so that these do no end up in landfills.
Comprehensive Environmental Response Compensation and Liability Act (CERCLA)
This states that the creator of a product containing hazardous substances is liable for its proper disposal throughout its life, even if the product is sold to someone else.
Healthcare facilities can address this issue through the purchase of equipment with fewer toxic components, in addition to extending the life of equipment and purchasing products that incorporate recyclability and reusability into their designs.
To sum up
Some patients become victims of misdiagnoses or flawed medical procedures, medical staff’s failure to track medications or wrong medication. The future of healthcare will change with advancements in medical technology. Technology and healthcare will go hand in hand to uplift patient care levels. From small innovations like fitness bands to larger, more complex technologies like artificial organs and robotic prosthetic limbs, technology is laying the path for accurate health treatments. Technology helps doctors make sure the right patient receives the right treatment at the right time.






