Enables simultaneous USB PD and wireless charging utilizing the latest standards
 ROHM has recently announced the availability of dual-input boost-buck charging ICs that support 1 to 4 battery cells for notebook PCs, smartphones, and power banks that utilize the latest charging technologies such as wireless and USB Power Delivery (USBPD).
ROHM has recently announced the availability of dual-input boost-buck charging ICs that support 1 to 4 battery cells for notebook PCs, smartphones, and power banks that utilize the latest charging technologies such as wireless and USB Power Delivery (USBPD).
The BD99954GW/MUV generates a charging voltage from 3.07 to 19.2V for 1 to 4 cells through boost-buck control for USBPD. In addition, the industry’s first dual-input charging system automatically switches charging operation without an MCU using an original built-in charging adapter function. And support is provided for both USBPD and USB BC 1.2. This facilitates configuration of dual-mode systems capable of simultaneous charging via USBPD, wirelessly, or from an AC adapter.
A growing number of portable devices, including notebook PCs, are adopting the USB Type-C PD standard that can charge up to 100W, providing a common charging platform. At the same time wireless charging is gaining traction, increasing the demand to support both charging methods. However, in order to deliver a wide power supply range required by USBPD, a boost function must be added to the system to charge 2-cell (~8.4V) batteries from conventional 5V chargers. Also, enabling two different charging methods to operate at the same time requires mounting charge ICs along with peripheral components as well as an MCU to control charge switching, presenting a significant barrier to introduction.
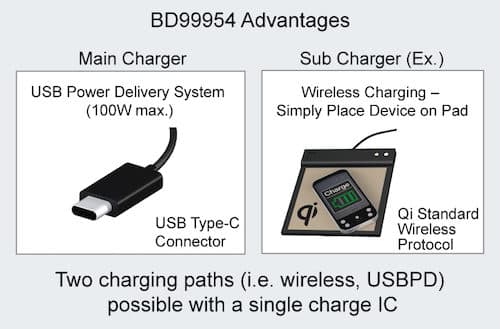
In response, combining its USBPD IC with proprietary semiconductor technologies allowed ROHM to meet these needs and develop dual-input charging ICs that support both USBPD and wireless protocols in a single package.
Key Features
The BD99954GW and BD99954MWV provide the following 2 features that make it easy to configure a wireless charging environment
1. Facilitates configuration of the industry’s first simultaneous dual-mode charging system
To support the 2 predominant charging methods for the latest portable devices, ROHM developed the industry’s first 2-input charging system. A built-in charging adapter discrimination function enables automatic switching between modes without an MCU. This eliminates the need to mount and adjust external peripheral components such as transistors and resistors typically necessary for each charging system (for charge path switching and backflow prevention), significantly reducing both mounting area and design load.
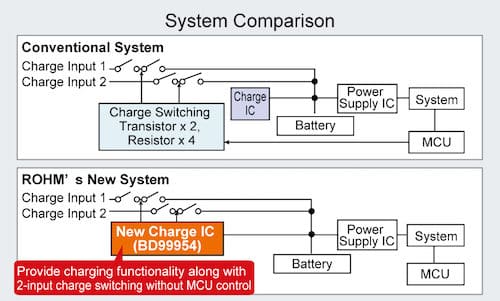
2. Supports the latest USBPD standards through boost-buck control
Step-up/down control makes it possible to generate the charging voltages necessary for USBPD operation (5V to 20V). For example, when charging a 2-cell battery (~8.4V), boost-buck control enables step-down operation from 20V to 8.4V as well as step-up from 5V to 8.4V.
Lineup

In addition, compliance with the popular USB BC1.2 and USBPD standards provides support for both conventional USB and the newest USB PD charging protocols.
Applications
- Notebook PCs
- Tablets PCs
- Smartphones
- Portable Batteries
- Wireless Audio
- <100W Portable Battery-Equipped Devices
Terminology
USB Power Delivery (USBPD), USB BC1.2
Power standards established and promoted by the USB Implementer Forum, Inc. (USB-IF). USBPD is the newest standard that enables power supply up to 100W (20V/5A), whereas USB BC 1.2 is the conventional standard specifying power supply up to 7.5W (5V/1.5A). ROHM offers control ICs for USBPD.
Wireless Charging
Technology that is quickly attracting attention due to the ability to charge without the need for a power cord, improving device connector resistance to water and dust while providing greater convenience by enabling a single power supply to charge multiple different devices. Portable devices that support wireless charging can be charged by simply placing the device on a charging stand/pad (or moving it close to the charger).






