It acts as a suitable replacement for Raspberry Pi Pico and offers compactness with flexibility while developing embedded projects

Measuring just 21mm x 21mm x 3mm (LxWxH) and approximately the size of a postage stamp, this compact RP2040 board known as PGA2040 offers flexibility while developing embedded projects. This is achieved by the presence of only necessary components on-board such as crystal, flash, regulator and essential support circuits. There are no LEDs, buttons and USB connectors (a separate USB connector is required).
Features
- Dual ARM Cortex M0+ running at up to 133Mhz
- 264kB of SRAM
- 8MB of QSPI flash supporting XiP
- Crystal oscillator
- On-board 3V3 regulator (max regulator current output 300mA)
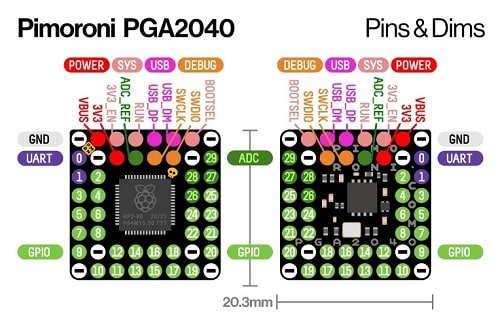
- 48 pins, arranged with 2.54mm (0.1″) spacing in a Pin Grid Array
- 30 multi-function General Purpose IO (4 for ADC)
- 8 GND pins
- Input voltage range 3V – 5.5V (on VB pin only)
The PGA2040 is programmable with C++ or MicroPython just like the Raspberry Pi Pico. You can also use CircuitPython on PGA2040! CircuitPython provides an easy to use ecosystem with lots of example code and drivers for interfacing with different kinds of hardware.
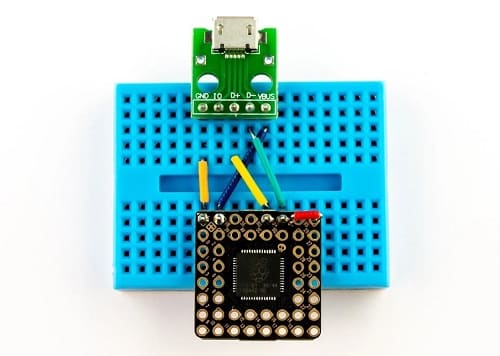
With respect to programming the PGA2040 via USB, you will need to hook wires up to VB, GND, U+ and U-. Make sure that the only 5V goes to VB on PGA2040, else you will get an unfavourable outcome. A USB breakout board is a convenient way of getting at the wires in your USB cable.
To get into BOOTSEL mode so you can flash firmware to your PGA2040, connect the BS pin to the ground whilst plugging the USB into your computer.
A bit about RP2040
Raspberry Pi’s RP2040 microcontroller is a dual-core ARM Cortex M0+ running at up to 133Mhz. It bundles in 264kB of SRAM, 30 multifunction GPIO pins (including a four-channel 12-bit ADC), several standard peripherals (I2C, SPI, UART, PWM, clocks, etc.), and USB support.
The RP2040 has programmable IOs, which allow you to execute custom programs for manipulating GPIO pins and transfer data between peripherals – they can offload tasks that require high data transfer rates or precise timing (that traditionally would have required a lot of heavy lifting from the CPU).






