Jiangnan University researchers developed a scalable, customizable method to create textile actuators for healthcare and robotics.
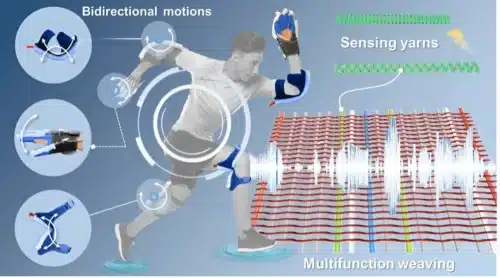
In recent years, electronics engineers have made significant strides in creating devices that are more adaptable, multifunctional, and efficient, catering to various practical uses. Among their innovations are smart and sensing textiles designed for applications such as flexible robotics, medical equipment, and wearable technology.
Researchers from Jiangnan University have developed a novel textile engineering method to produce woven and soft actuators for health care technologies and robotic systems. Their fabrication technique is scalable and customizable, which may facilitate its widespread adoption in the future.
The method used by the team organizes warp and weft yarns—the fundamental elements for transforming threads into fabrics—into a precise planar configuration during the weaving process. This approach allows for the customization of woven actuators by meticulously programming the placement and composition of the yarns.
When the yarn in the actuators is stretched, it leads to the separation of the conductive yarns’ helices, effectively interrupting the pathways for electrical current. This structural change alters the electrical signals traveling through the yarn, thereby enabling strain detection.
A distinctive feature of the sensing yarns created with the team’s technique is their complete integration into fabrics. As a result, they do not increase the weight, stiffness, or bulkiness of the textiles, ensuring that actuators can track their movements while maintaining their flexibility and adaptability.
Additionally, our weaving approach provides a flexible and scalable method for producing multi-morphing soft actuators. These actuators are capable of bilateral bending, twisting, and spiraling with just one air supply. Adjustments to yarn tension, density, and woven structure allow for these diverse functionalities.
The researchers showcased the potential of their yarn in creating bilateral bending actuators, suitable for use as soft robotic grippers. These grippers could imitate animal movements, such as extending octopus tentacles to draw objects nearer and securely grasp them.






