The vision sensor offers a broader field of view and higher precision, paving the way for smarter autonomous systems in robotics and drones.
Recent technological advances have led to the development of increasingly sophisticated sensors, enhancing the sensing capabilities of robots, drones, autonomous vehicles, and other smart systems. However, many of these sensors rely on individual cameras, and their measurement accuracy is limited by the cameras’ field of view (FOV).
Researchers at Beihang University in China have developed a new multi-camera differential binocular vision sensor with a wider field of view that could collect more accurate measurements.
The main goal of the team’s recent study was to develop a sensor with a wider field of view. By arranging multiple cameras strategically, they aimed to create a coordinated system that would collect more precise measurements than conventional, single-camera-based sensors.
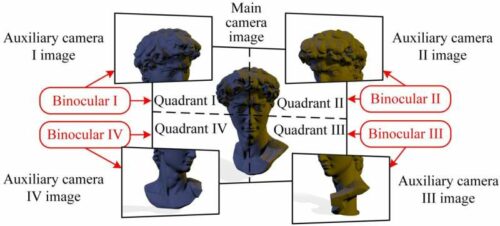
The team’s multi-camera differential binocular vision sensor comprises a central main camera and four peripheral auxiliary cameras. The researchers explained that the four quadrant images of the main camera form four pairs of binoculars with the four auxiliary camera images. The sensor’s structure parameters are optimized from the spatial arrangement, measurement range, and accuracy to collect high-precision three-dimensional measurements.
In a series of experiments, the team tested the sensor they developed and found that its field of view was significantly broader than that of conventional binocular cameras. By combining the field of view of multiple cameras, the sensor could collect more precise measurements of its surroundings.
The sensor developed by the research team could be integrated into various systems, such as semi-autonomous or autonomous vehicles, robots, and motion-sensing devices. This integration will enable the researchers to validate its performance in real-world settings and further adapt their design to facilitate its commercialization.
Based on the proposed principle and idea, high-precision vision perception with a large field of view is realized. With the combination of small industrial cameras and structure design to further realize miniaturization and lightweight, this sensor may become a standard configuration similar to LiDAR in future intelligent unmanned systems.
Reference: Lemiao Yang et al, A novel multi-camera differential binocular vision sensor, Optics & Laser Technology (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.optlastec.2024.110624.






