Researchers design 3D printed plasma sensors to predict weather and study climate change.
Researchers at MIT have designed the world’s first completely digitally manufactured plasma sensor for satellite application. These plasma sensors, which are also known as retarding potential analyzers(RPAs), are used in satellites to determine the chemical composition and ion energy distribution in the atmosphere.
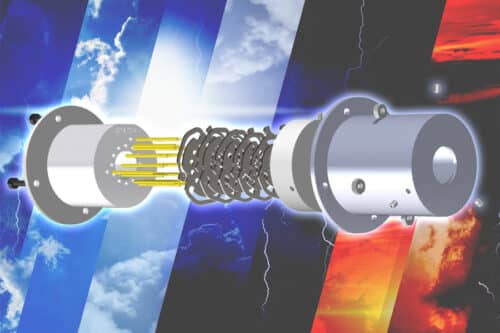
These 3D-printed sensors are manufactured in a cleanroom, which makes them inexpensive and easy to manufacture, therefore making them ideal for CubeSats. These RPAs are developed using a glass-ceramic material making them more durable than the traditional sensors which are generally made of materials like silicon and thin-films. Using glass-ceramic as 3D printing material allowed formation of complex shapes and the ability to withstand temperature variations of lower Earth orbit.
The sensors contain a series of electrically charged meshes dotted with tiny holes that allow ions present in plasma to pass through them. These ions create an electric current that the sensor measures and analyzes. This data is recorded by scientists for predicting the atmospheric changes.
Therefore the material used must possess electrically inductive property as well as must be able to withstand drastic changes in temperature. The researchers used a printable, glass-ceramic material that displays these properties, known as Vitrolite. Vitrolite tends to withstand up to 800 degree Celsius whereas its polymer can withstand not more than 400 degree Celsius of temperature.
The manufacturing process is based on vat polymerization, where the structure is created in layers. Each layer is 100 microns thick enabling creation of complex shapes. According to Velásquez-García, this high precision work could enable 3D-printed sensors for applications in fusion energy research or supersonic flight. The rapid prototyping process could also enable cutting edge innovation in space technology and enhance fabrication technology. Velásquez-García also aims to explore the use of AI to optimize designing and enhancing products.






