This device reduces the timing jitter to 56ps, improving distance resolution to 8mm.
The Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) has developed a new single-photon avalanche diode (SPAD) to advance LiDAR technology. The innovation aims to improve the accuracy of short- and mid-range LiDAR systems used in applications like advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS), autonomous driving, and AR/VR devices.
LiDAR, which relies on measuring the time it takes for photons to reflect off objects and return to the sensor, benefits greatly from improvements in timing jitter performance—the variability in detection time—which this new SPAD addresses by reducing the timing jitter to 56ps and improving distance resolution to approximately 8mm.
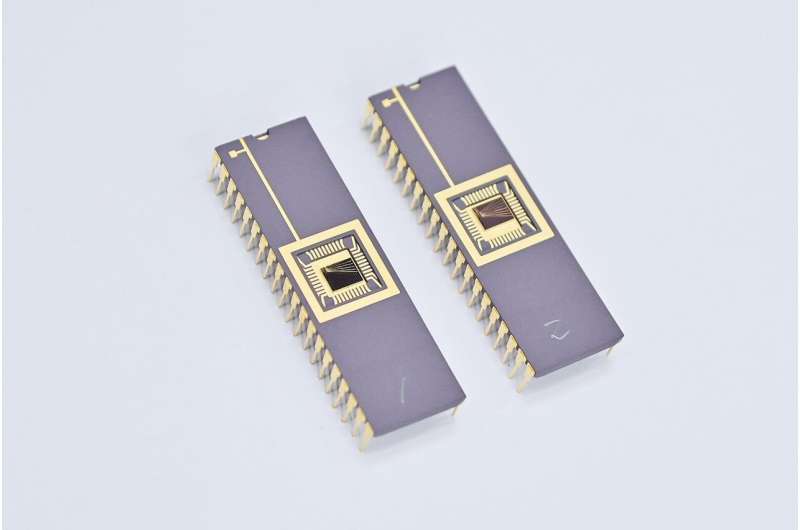

Unlike existing SPAD technologies, which have struggled to achieve the timing jitter performance necessary for precise user discrimination, gesture recognition, and accurate object shape recognition, the KIST-developed SPAD marks a notable improvement. Developed based on a 40nm back-illuminated CMOS image sensor process in collaboration with SK hynix, this technology not only performs better but is also ready for mass production and commercialisation.
Sony has previously led in commercialising SPAD-based LiDAR for Apple products with its 90nm process, offering efficient but not sufficiently precise timing jitter performance for short- and mid-range LiDAR applications. The advancement by KIST, therefore, represents a significant step forward, potentially boosting Korea’s competitiveness in the strategic industries of semiconductor LiDAR and 3D image sensors.