Imagine a world without screens. No more scrolling through social media, no more watching your favourite shows, no more gaming. This is a difficult concept to grasp in today’s digital era. But decades ago, this was the reality. A big part of our modern world revolves around these visual interfaces, and at the heart of most of them is the LCD liquid crystal display.
Table of Contents
A Brief History
The origins of the LCD started in the 19th century, when researchers found that some crystal varieties could alter their characteristics in response to an electric field. The electro-optic effect, a phenomena, served as a drive for LCD development.
How Does an LCD Work?
LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) is a flat panel display technology that uses Liquid crystals to regulate light. The fundamental concept is the control of light waves via liquid crystal materials positioned between two polarized screens.
- Consists of an array of tiny segments known as pixels that may be adjusted to display different types of content.
- Using light polarization to show objects.
- To illuminate the display, solely use ambient light.
An LCD is essentially a sandwich of two glass plates with a layer of liquid crystals between them. The liquid crystals are arranged in a specific pattern, and when an electric current is applied to them, they can twist and rotate. This twisting and rotating affects how light passes through the LCD, allowing it to create images.
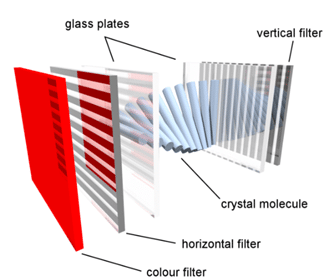
Also Check: LCD 16×2
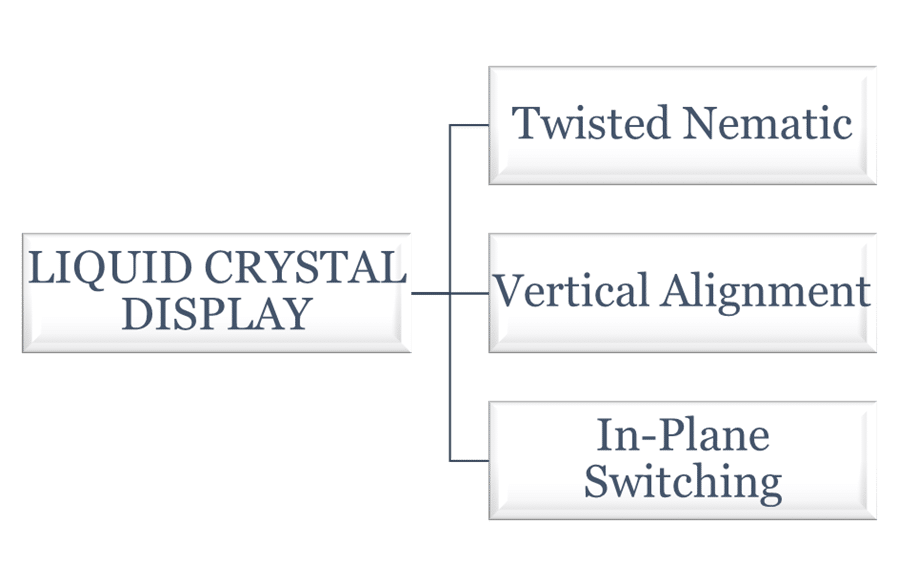
Types of Liquid Crystal Displays (LCDs)
Three types of LCD screens can be distinguished: TN (twisted nematic), IPS (in-plane switching), and VA (vertical alignment).
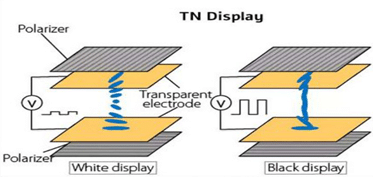
TN (Twisted Nematic)
TN (Twisted Nematic): Nematic liquid crystal is positioned between two glass plates in this technique. The liquid crystals twist at 90° when electricity is applied to the electrodes. The most common kind of LCD screens are TN (Twisted Nematic) screens. They provide modest viewing angles and full-color visuals.
TN LCD Characteristics

- Cost-Effective: Traditionally, the least expensive LCD alternative has been twisted nematic panels.
- Highest Rates of Refresh: The fastest refresh rates and response times are found in TN LCD displays.
- Restricted Viewing Angles: The typical viewing angle of TN LCD displays is between 45 and 65 degrees.
- Restricted Brightness: TN LCD screens lack sufficient brightness to be viewed outside or in direct sunlight.
VA (Vertical Alignment)
VA (Vertical Alignment): Displays with VA, or Multi-Domain Vertical Alignment, (MVA), offer characteristics present in both TN and IPS screens. Light can pass through VA displays because when voltage is applied, the pixels align vertically with the glass substrate.
VA LCD Characteristics

- Broad Viewing Angles: Compared to TN LCDs, VA panels provide wider viewing angles.
- Contrast and Colors: When it comes to color and contrast, VA LCD panels prevail over TN TFTs.
- Backlight Intensity: In general, VA LCD displays are less bright than comparable TN type TFTs.
- Power Usage: Standard LCD screens tend to use less energy than sunlight-readable LCDs.
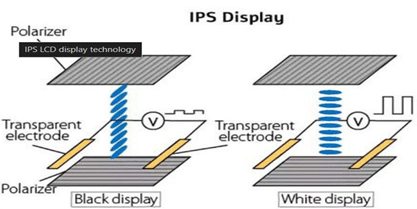
IPS (In-Plane Switching)
IPS (In-Plane Switching): IPS (In-Plane Switching) technology works on the liquid crystal within the display screen to enhance image quality. In order to let light through, the crystals rotate parallel, or “in-plane,” when voltage is applied. The image quality of these screens is significantly enhanced by this behaviour in multiple ways.
IPS LCD Characteristics

- Price Point: Compared to TN LCDs, IPS displays are now more affordable.
- Average Refresh Rates: Refresh rates and response times are slower on IPS screens than on TN LCD screens.
- Broadest Angles of Viewing: Of all TFT LCDs, IPS LCD screens offer the largest viewing angles.
- Ideal Shades: Out of all TFT LCDs, IPS LCD panels generate the most accurate and vibrant colors.
- Maximum Radiance: High brightness backlights on IPS LCD screens enable reading in harsh sunlight.
TN vs VA vs IPS Comparison Table
| Parameters | TN | VA | IPS |
| Viewing Angles | Narrow | Wider than TN, but narrower than IPS | Wide |
| Contrast Ratio | High | Very high | Good |
| Response Time | Fast | Faster than TN | Slower than TN and VA |
| Color Accuracy | Average | Good | Excellent |
| Black Levels | Good | Excellent | Good |
| Energy Efficiency | High | High | Lower |
| Price | Lowest | Moderate | Highest |
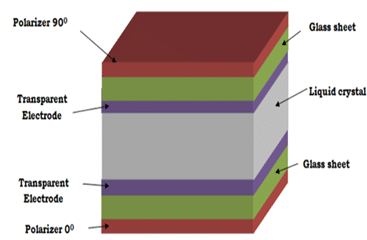
Construction of Liquid Crystal Display
The LCD is constructed from two pieces of polarized glass. There are two electrodes used: a positive electrode and a negative electrode.
External voltage is applied to the LCD to LCD using these electrodes and it is made up of indium-tin-oxide. A 10–20 µm liquid crystal layer is sandwiched between two sheets of glass.
By altering the polarization, light can be transmitted through or prevented.
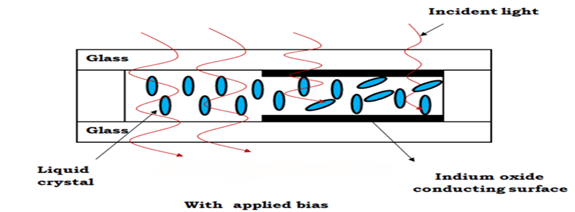
Working Principle
The basic working principle of LCD is obstruction of light. It cannot generate light by itself. Thus, an external light source is required. When external light moves from one polarizer to the next, a liquid crystal receives an external supply, and the polarized light aligns itself to form an image on the screen.
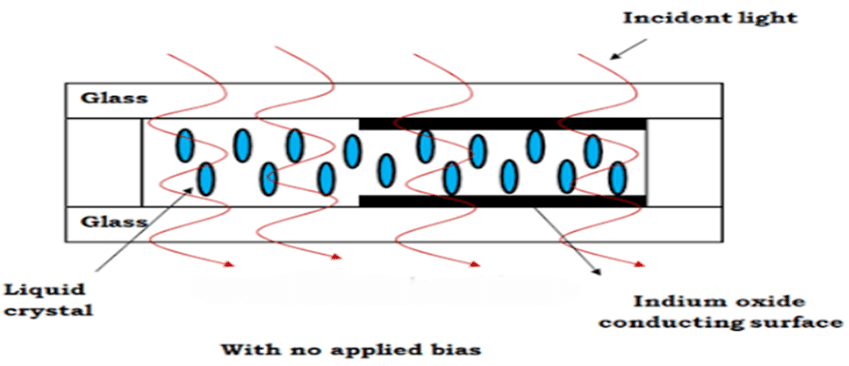
The transparent layer on each side of the sealed thick layer of liquid crystal is the indium oxide conducting surface. The molecular arrangement is unaffected in the absence of any external bias.
The molecular arrangement changes when an external bias occurs, making one area appear dark and the other area appear clear.
Positive and Negative LCDs
In a positive LCD panel, the polarizers are positioned perpendicular to one another, and the segments have dark backgrounds. Whereas the polarizers are lined up with each other, the segments in the negative LCD display appear white against a dark backdrop.
Advantages of LCD
- Low power consumption
- Thin and lightweight
- No geometric distortion
- Sharp images with good color reproduction
Disadvantages of LCD
- Limited viewing angles
- Slower response times
- Lower contrast ratios compared to OLED
- Prone to dead pixels
Applications of LCD
- Mobile phones and tablets
- Televisions and monitors
- Digital watches and calculators
- Instrument panels and displays in vehicles
Check out this video to explore the building of the Liquid Crystal Display.
Difference between CRT, LCD, OLED and QLED
CRT
CRTs or Cathode Ray Tubes are bulky and very thick. They employ vacuum glass tubes, electron guns and deflection plates and consume very high-power during operation.
LCD
LCDs or Liquid Crystal Displays are flat, thin and lightweight, making them more usable and user friendly compared to CRTs. It uses liquid crystals and layers of polarised glass to produce images while consuming less power than CRT.
OLED
OLEDs or Organic Light Emitting Displays use a single glass with plastic panel and need no external light to work. Every pixel of this display is an LED light, and an image is formed by controlling each of these LEDs. It is much thinner and lighter but expensive as compared to a Liquid Crystal Displays.
QLED
QLEDs or Quantum Light Emitting Displays are an advanced form of OLEDs in which nanometre size light particles known as quantum dots produce different colours of light that form an image. The technology helps in creating richer and stunning picture quality.
FAQs on LCDs
- What does LCD stand for?
LCD stands for Liquid Crystal Display.
- How does an LCD work?
LCDs use liquid crystals that align to either block or allow light to pass through, forming images.
- What are the types of LCDs?
Types include Twisted Nematic (TN), In-Plane Switching (IPS), and Vertical Alignment (VA) panels.
- Why do LCDs have poor viewing angles?
The liquid crystal arrangement can limit the clarity and brightness when viewed from the sides.
- Are LCDs energy efficient?
Yes, LCDs consume less power compared to older display technologies like CRT.
- What’s the difference between LCD and OLED?
LCDs use backlights, while OLEDs have self-illuminating pixels, leading to better contrast and thinner designs in OLEDs.