Since the government’s move to demonetise old ₹ 500 and ₹ 1000 notes last year, usage of digital money has drastically increased in the country. As India takes the cashless route and emerges as the biggest digital economy in the world, it also opens up many opportunities for cyber criminals.
According to Norton Cyber Security insight report 2016, those who were not careful have experienced negative consequences including identity theft, money stolen from bank accounts, credit cards issued in their names and unauthorised apps installed on their devices.
Data from Ministry of Finance in India shows that about 50 leading banks in India have lost around ₹ 4.85 billion between April 2013 and November 2016 because of cyber frauds. Fifty six per cent of this money was lost due to net banking thefts and credit/debit card cloning. Discussed in this article are some possible security threats and what you can do to avoid these.
Debit/credit card fraud
A debit or credit card fraud occurs when a criminal gains access to your debit/credit card details and the PIN to make purchases or withdraw money from your account. To safeguard your card, follow the steps given below.
Sign up for banking alerts.
Signing up for banking alerts that are delivered as SMSes to your registered mobile number or email ID can help you keep track of your account transactions.
Safeguard your PIN.
Never write down your PIN or save it on your mobile phone. And, while entering your PIN at an ATM or while paying for stuff at a shop/restaurant, cover it using your hand or body so that no one else can view it. Also, change your PIN regularly.
Use credit cards instead.
For purchases, use credit cards instead of debit cards, because the former offer greater protection. You can also block credit cards at any time.
Stick to own bank ATM.
It is preferable to use your own bank’s ATMs instead of a different bank’s. This also saves you from paying transactions fees that you might have to pay after a certain number of transactions.
Avoid saving card data.
Most online vendors offer card saving options for easier and faster transactions in the future. Avoid doing so wherever you can.
Do not let anyone else use you card.
At shops or restaurants, always swipe your card yourself or have it swiped in front of your eyes. This is a good way for criminals to otherwise get access to all your details.

Digital wallets
Online wallets are easy targets. Many a time these do not have very advanced security measurements. This makes these vulnerable to attack. Many wallets need only one-time login to carry out the transactions, and these keep you signed in. This helps hackers to access your account easily.
Wallets usually have a simple one-click feature for easy operation. So if you lose your phone, anyone who lays hands on it can control your mobile wallet. Let us see what you can do to protect your digital wallet.
1. Install a basic antivirus and malware scanner on you mobile phone.
2. Check for the rating and credibility of the app before installing it.
3. Use a one-time password (OTP) instead of a regular password.
4. Log out of the mobile wallet after the transaction is complete.
5. Make sure the wallet provider has a customer support wing that can help in case of fraud.
6. Do not use the same password for all accounts.
7. Avoid installing third-party software shown on pop-up advertisements while using apps.
8. Double-check the details while transferring money. Even if the wallet has a possibility of threat, it is still safer than using a credit/debit card for online transactions.
Threats in Internet banking
Even though banks provide a lot of security measures, online banking services (NEFT/RTGS) are not free from the menace. Security threats include phishing, spyware and adware, viruses, trojans and key-loggers, among others.
Phishing and spam emails look like these have been sent from the bank itself, and ask for personal details such as usernames and passwords.
Spyware and adware are a special type of software created by hackers to collect sensitive information. These track your Internet habits and interests, and provide the same to marketing companies. This is how you end up with spam in your inboxes.
A virus attaches itself to a program by clubbing with another program in the computer by using different resources of the computer. An email virus is a special type of virus that gets embedded in an email and when you open the email, it replicates your information and distributes it.
A trojan can also be categorised as virus but it does not replicate itself and does not need any particular program to attack. It is a destructive program that acts as a harmless application, such as as helpful software claiming to get rid of unwanted software or virus. Instead, it attacks your information and makes it vulnerable.Key-loggers log all user activities on the computer by capturing every keystroke. The sensitive information is then captured and accessed by fraudsters to attack users.
Some security measures that you can take while using Internet banking are:
1. Always access the registered website of the bank. Do not follow any links sent in emails.
2. Beware of phishing attacks. Do not reply or disclose any sensitive information like username and password in response to emails claiming to be from your bank. Banks never ask for sensitive details.
3. Protect your password, and do not write it down. Always use strong passwords that are difficult to hack. Change your password regularly—at least once a month.
4. Install a good antivirus on your system for protection from virus and spyware.
5. Check for https:// instead of http:// in your browser address while using Internet banking.
6. Avoid using public computers or Internet café computers for accessing bank accounts. If you need to do so, use the onscreen keyboard for typing out the username and password, check for unnecessary background programs, clear history and cache after logging out, and hide the password while typing it out.
7. Do not click on unwanted ads on emails or other websites.
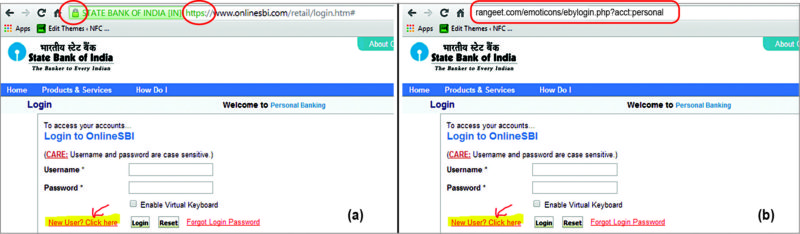
Mobile security
A lot of us use phone banking these days, but most of us do not check the permissions we give while installing apps on our mobiles. Our mobile phones contain very sensitive information, and giving permission to access these means making it easier for criminals to hack our systems. Always be careful while accessing bank or financial data through mobile phones.
1. Do not use the same password for wallets and bank accounts.
2. Use dynamic password-generation apps for creating passwords for bank accounts.
3. Check while granting permissions when installing apps.
4. Avoid third-party software that pop up while using other apps.
5. Always log out after accessing your account.
6. Do not save usernames and passwords on the app.






