Buildings are getting smarter with IoT, Sensors and Artificial Intelligence, those technologies combined are offering new opportunities to help the users to simplify their daily life.
With the growing demand on accessibility, flexibility and user friendliness, Sensor/Actuator Networks with cable or radio are becoming more and more important, also with regard to energy efficiency and IT security in Buildings.
KNX has established itself as the global standard for communication and automation in buildings for many years. The origin can be found as early as 1990 under the name EIB (European Installation Bus).
After consolidating with other standards like BATIBUS (France) and European Home System Association (the Netherlands), the KNX association was created in 2006.
With KNX a decentralized bus system, all KNX certified products from many different providers and manufacturers can be networked and configured with one another.
An engineering tool software (ETS) is used for the design, the configuration and diagnosis
on all KNX networks.

The most common media used on the physical level are T/P (Twisted Pair), Ethernet (IP: Internet Protocol) and Radio Communication (KNX-RF on 868MHz).
STMicroelectronics now offer a complete KNX certified chipset for all transmission media and further the possibility of integrating mobile devices such as Bluetooth5 compatible Smart Phones or Tablets.
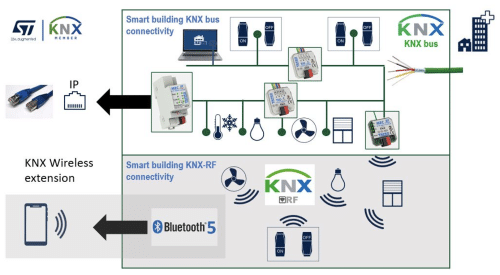
STKNX is a KNX Transceiver for Twisted Pair cables with 2 integrated voltage regulators on the KNX Bus for wired communication which today protects the largest market share in building automation.
KNX-RF now uses radio technology in the range of 868 MHz.
KNX devices can easily be integrated into the wired infrastructure of KNX with the help of ETS.
The chipset is open to a KNX-RF Stack implementation from KNX certified partners.
TAPKO Technologies GmbH www.tapko.de already offers certified KNX Stacks (KAIStack) for the ST platform.
Figure 4 shows the Software Layer integration of the KNX-RF and the BLE Stack into the
BlueNRG-2 Host, which is connected through SPI to the SubGHz KNX-RF Transceiver.
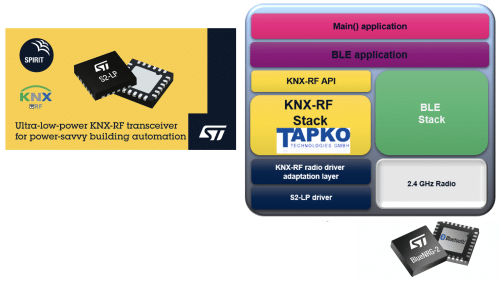
The 32-Bit Cortex M0 ARM based BlueNRG SoC therefore represents the Host for the S2-LP as well as the Controller for the BLE communication e.g. with mobile devices for IOS or Android.
Figure 5 shows the ST development environment with Evaluation boards for KNX and BLE. For Bluetooth implementation, also BLE certified ST-Modules (BlueNRG-M0/M2) are available.
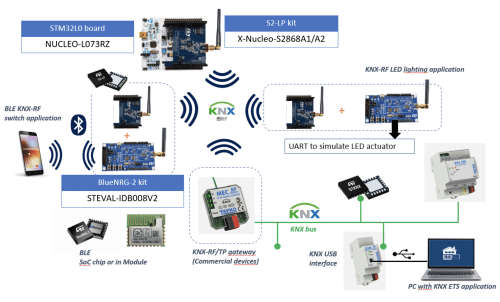
If no BLE functionality is required a STM32 Microcontroller can be used as Host for KNX-RF as well.
Conclusion
The area of application for KNX certified components in buildings is growing all the time.
Room management, Lighting control, home & building monitoring, remote- and automatic- control systems for shutters, blinds, heating, ventilation and air conditioning, enable intelligent solutions for the Smart Building.
Various Sensors from ST based on MEMS or Imaging Technologies are available for movement, environmental or optical sensing in Building Networks.
Bluetooth Low Energy expansions in the KNX infrastructure enable easier configuration and can be used as Human Machine Interfaces controlled by mobile Devices.
The use of KNX in Buildings also helps to reduce energy consumption and the radio communication allows modernization or retrofitting of existing Infrastructures without having to lay new cables.
Further, on the current topic of smart grid solutions with electronic meter systems for energy, water or electricity, and heat cost allocators, interfaces to those devices can be developed to communicate with other wireless subGHz standards such as wireless M-BUS / OMS used in modern Metering Systems.
Michael Muenkel studied communication engineering at the Esslingen University of Applied Sciences and since 1987 has worked for several companies in the field of development, application consulting and marketing.
Since 1999 he has been working for STMicroelectronics and is responsible for radio and sensor components as Technical Marketing Manager