This Parallel and Series Resistor Calculator is designed to help you quickly calculate the equivalent resistance of resistors connected in parallel and series. To use it, just specify how many resistors there are and the resistance value for each one.
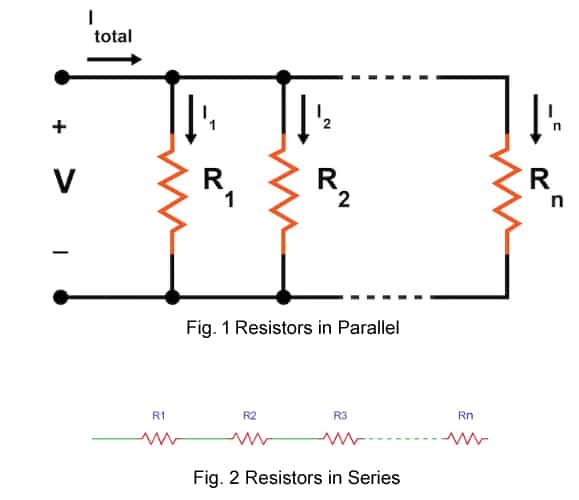
Calculating Resistance in Parallel Using Ohm’s Law
The voltage (V) across all of the resistors in a parallel circuit is identical. This can be seen by observing that the parallel resistors share the same nodes. The current through each individual resistor, Rx, can be calculated using Ohm’s law:
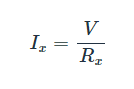
The total current through the parallel resistors is the sum of the individual currents:
Itotal=I1+I2+I3+…+In
The current through each individual resistor does not change when you add resistors in parallel because adding resistors in parallel does not affect the voltage across the resistors’ terminals. What changes in the total current delivered by the power supply, not the current through one particular resistor.
From the total current equation, we can then derive an equation for the equivalent parallel resistance:
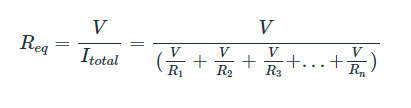
This is often expressed as:
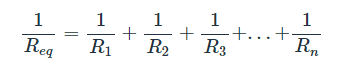
When you have only two resistors in parallel, the equivalent resistance can be easily calculated using this equation:
Req=(R1×R2)/(R1+R2)
Calculating Resistance in Series Using Ohm’s Law
In a series circuit, resistors are connected end-to-end, creating a single pathway for the flow of current. Unlike parallel circuits, where the voltage across each resistor remains the same, in a series circuit, the total voltage (V) is equal to the sum of the voltage drops across each resistor.
The current (I) flowing through each resistor in a series circuit is identical, as it experiences no branching. Ohm’s law can be applied to calculate the current through each resistor:
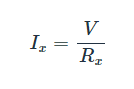
To find the total resistance (Req) in a series circuit, you simply sum up the individual resistances:
𝑅𝑒𝑞 = 𝑅1+𝑅2+𝑅3+…+𝑅𝑛
This equation shows that in a series circuit, the total resistance is the sum of all the individual resistances.
When dealing with only two resistors in series, you can use a simpler formula to calculate the equivalent resistance:
𝑅𝑒𝑞 = 𝑅1+𝑅2
This is because in a series circuit with only two resistors, the equivalent resistance is just the sum of the two resistances.
Also try Resistor Color Code Calculator that is free to use.
FAQS
- How does adding more resistors in series affect the total resistance?
- Ans: Adding more resistors in series increases the total resistance. The equivalent resistance is simply the sum of all individual resistances, so adding additional resistors will increase the overall resistance in the circuit.
- What is the difference between resistors in series and resistors in parallel?
- Ans: In a series circuit, resistors are connected end-to-end, and the same current flows through each resistor. The total voltage across the circuit is the sum of the voltage drops across each resistor. In a parallel circuit, resistors are connected across the same voltage source, and the voltage across each resistor is the same, while the total current is the sum of the currents through each resistor.
- Why does the equivalent resistance decrease when resistors are added in parallel?
- Ans: In parallel circuits, adding more resistors provides additional pathways for current to flow. This results in an increase in total current for a given voltage, which lowers the overall equivalent resistance of the circuit. Mathematically, since each additional path decreases the overall opposition to current, the equivalent resistance decreases.
- What is the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance in series and parallel circuits?
- Ans: In a series circuit, the same current flows through all components, and the total voltage is the sum of the voltage drops. In a parallel circuit, the voltage across each component is the same, while the total current is the sum of the currents through each branch.









