This calculator helps you determine the values of the resistors R1 and R2 to be used for a Pi Attenuator.
Inputs
Outputs
A Pi Attenuator is a passive network composed of resistors arranged in a “pi” configuration (three resistors in total). It is commonly used to reduce the amplitude of a signal while ensuring proper impedance matching between components in a system. This type of attenuator is widely used in both RF (radio frequency) and audio applications where precise signal attenuation is necessary.
The Free Online Pi Attenuator Calculator allows users to quickly calculate the resistor values needed for a Pi attenuator based on the desired level of attenuation and impedance requirements, making it a valuable tool for engineers and designers.
Why Use This Calculator?
The Pi Attenuator Calculator provides several advantages for circuit designers:
- Efficient and Accurate Calculations: Instantly calculates the required resistor values for the Pi attenuator, helping you achieve the desired attenuation level.
- Easy to Use: The interface is intuitive, allowing users to input attenuation and impedance values, and receive results in just a few clicks.
- Versatile: Applicable for both RF and audio systems, making it a flexible tool for a wide range of industries.
- Maintains Impedance Matching: The calculator ensures that the input and output impedance are matched, which is crucial for preventing power loss and signal reflection.
- Free and Accessible: It’s available online for free, with no installation needed, making it a convenient tool for quick calculations.
How to Use the Pi Attenuator Calculator
The Free Online Pi Attenuator Calculator is simple to use. Here’s how to get started:
- Enter the Desired Attenuation (in dB): Specify how much you want to attenuate the signal.
- Input the Impedance Values: Provide the input and output impedance values (typically 50 ohms for RF systems, or other values based on your application).
- Click Calculate: Once you input the values, click on “Calculate” to instantly get the required resistor values (R1, R2, and R3) for the Pi attenuator.
The Pi attenuator consists of:
- R1: The series resistor placed between the input and the load.
- R2: The shunt resistor placed between the input and output.
- R3: The series resistor placed between the output and the load.
Formula:
The resistor values for a Pi Attenuator are derived from the following formulas:
- R1: The series resistor that connects the input to the load, contributing to the attenuation.
- R2: The shunt resistor, placed between the input and the output, which directly affects the level of signal reduction.
- R3: The second series resistor that ensures impedance matching between the output and the load.
The formulas used for calculation are as follows:
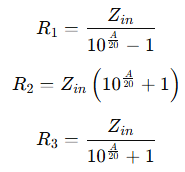
Where:
- A is the attenuation in dB.
- Zin is the input impedance of the system.
These formulas help determine the correct resistor values to achieve the desired attenuation while maintaining proper impedance matching.
Applications of the Pi Attenuator Calculator
The Pi Attenuator Calculator is useful in a variety of applications:
- Signal Level Adjustment: Commonly used in RF and audio systems to reduce signal strength without distorting the signal quality, ensuring that the output signal remains clean.
- Impedance Matching: It helps match the impedance between different components, such as amplifiers and antennas, to avoid signal reflections and power loss.
- RF Network Design: Essential in designing RF circuits, such as transmitters, receivers, and communication systems, where precise signal attenuation is needed.
- Audio Systems: Used to balance signal levels between components like mixers, amplifiers, and other audio equipment.
- Test Equipment: Useful in calibration and testing systems where precise attenuation of signals is necessary for accurate measurements.













