This calculator determines the resistance of a microstrip trace.
Inputs
Outputs
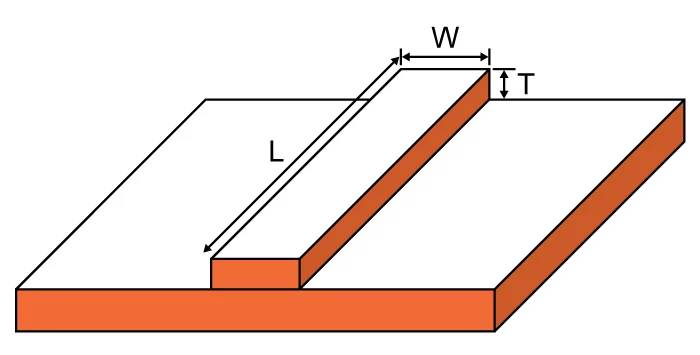
The Trace Resistance Calculator is a valuable tool for PCB designers and electronics engineers who need to determine the resistance of copper traces on a printed circuit board (PCB). The resistance of a PCB trace affects the overall performance and efficiency of electronic circuits, influencing factors such as voltage drop, heat dissipation, and signal integrity.
This calculator helps you quickly estimate the resistance of a trace based on its length, width, thickness, and temperature, providing a reliable reference for designing efficient and low-resistance PCB layouts.
Why Use This Calculator?
The Trace Resistance Calculator offers several features that make it an essential tool for electronics design:
- Quick and Accurate Calculations: Provides precise resistance values, reducing the risk of design errors.
- User-Friendly Interface: Simple and intuitive input fields for easy use, even for beginners.
- Temperature Adjustment: Allows you to factor in temperature changes, which can significantly affect trace resistance.
- Design Optimization: Helps in selecting appropriate trace dimensions to minimize resistance and power losses in high-current applications.
- Free to Use: Available online for free, making it a convenient and accessible tool for anyone working on PCB design.
How to Use the Trace Resistance Calculator
To use the Trace Resistance Calculator, follow these steps:
- Input Trace Length: Enter the length of the copper trace in millimeters (mm) or inches.
- Input Trace Width: Specify the width of the trace in millimeters (mm) or inches.
- Input Copper Thickness: Select the copper thickness, typically in ounces per square foot (oz/ft²) or micrometers (µm).
- Input Operating Temperature: Enter the temperature in degrees Celsius (°C) to account for temperature variations.
- Click Calculate: The tool will instantly provide the trace resistance value in ohms (Ω).
Formula
The resistance (RRR) of a PCB trace is calculated using the formula:
R=(ρ×L)/A
Where:
- R is the trace resistance (in ohms, Ω),
- ρ is the resistivity of copper (typically 1.68×10−8 Ω⋅m),
- L is the length of the trace (in meters, m),
- A is the cross-sectional area of the trace (in square meters, m²).
The cross-sectional area (A) is calculated as:
A=Width×Thickness
Temperature correction can be applied using:
RT=R0×[1+α(T−T0)]
Where:
- RT is the resistance at temperature T,
- R0 is the resistance at reference temperature T0 (usually 20°C),
- α is the temperature coefficient of copper (≈0.00393/°C).
Applications of the Trace Resistance Calculator
The Trace Resistance Calculator is useful in various PCB design and electronics applications:
- Power Electronics: Helps in designing traces that can handle high currents with minimal voltage drop and heat generation.
- Signal Integrity: Assists in optimizing trace width and length for high-speed signal transmission with reduced resistance and loss.
- Thermal Management: Aids in minimizing heat buildup due to trace resistance, crucial for maintaining circuit reliability.
- PCB Prototyping: Facilitates quick checks of trace resistance during the PCB layout phase, ensuring optimal trace dimensions.