Off-air testing of ‘ground station’ equipment has come a long way since the technology of geostationary satellite communications began nearly half a century ago.
In those early days, the term ‘ground station’ meant a large parabolic antenna along with the large and massive structure upon which it is kept to transmit and receive signals.
Each element of the ground station was individually tested before being assembled into a system. At that point, an occasional test on a transponder might be the final set up check before going live. Makeshift loopback tests using a basic RF mixer and microwave signal generator were also started as the technology advanced.
Scope, Roles and Responsibilities
Today, the term ‘ground station’ has grown significantly .Due to the electronics miniaturisation revolution, mobile satellite ground stations started emerging. SATCOM-On-The-Move (SOTM) is a reality – platforms which now includes ships, aircraft, road vehicles, trains .
After a communications satellite is in its target orbit, several tests need to be performed in order to ensure proper performance of the transponders in the ground station. The on-orbit measurements are a vital part of the maintenance of a live satellite as well. Operating a satellite channel for an on-orbit measurement rather than the intended application comes with significant opportunity cost and hence test duration needs to be minimised as much as possible.
Likewise, newer testing methods for SATCOM systems have started evolving to meet the needs of the modern user and the manufacturers. Such equipment is now mass produced and on-satellite testing is disliked due to the large range of test parameters . As a result ‘good old’ mixer/LO testing is becoming outmoded.
For the major terrestrial teleports, the rack mounted loop test translator still provides a cost-effective and easy-to-use option. However, attempting to use these tests and measurements , where the whole ground station is both compact and mobile would be quite cumbersome.
Long distance group delay test , gain transfer ( or conversion loss) measurement also equally plays a critical role in RF simulation testing.
Real time spectrum analysis greatly helps with monitoring against double illumination , while the generic vector signal analysis helps in monitoring satellite carriers. Time taken for on -orbit measurement needs to be minimised without sacrificing reliability.
Drone based RF testing – Trigger for innovation
This method of testing vehicular ground stations greatly increases measurement accuracy and speed of measurement. Testing cost and time can be minimised using drones.

Modern Satellite simulation – How does it work?
Ground station test and measurement , sometimes called satellite simulation, is carried out to analyse the performance of ground stations and to improve the quality of satellite signals.
Equivalent Isotropic Radiated Power measurement helps to verify the satellite antenna to be properly directed at the ground station during antenna pattern mapping. The antenna pattern tests are used to ensure the beam patterns are correctly oriented on the earth.
During operation of a satellite , one common problem faced is interference or double illumination. It occurs when an earth station directs an uplink to the wrong satellite .This further drives the satellite transponder into saturation. Real time spectrum monitoring helps to eliminate this problem by identifying faulty carrier signals.
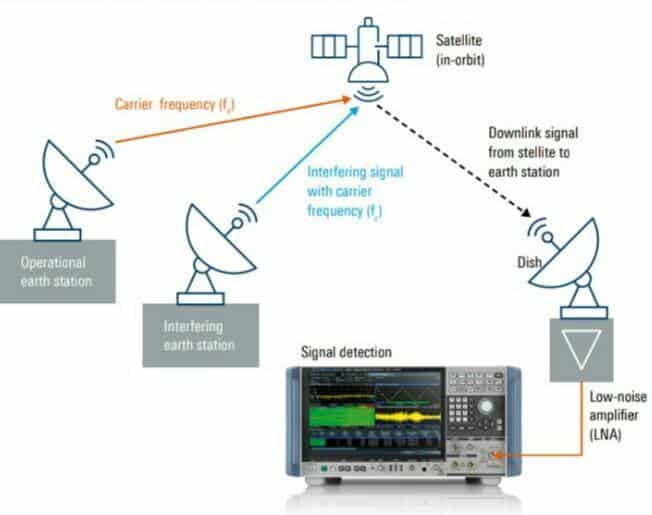
If the satellite signals arrive at an earth station with sufficient field strength , this may cause serious problems. The Bit Error Ratio (BER) if increases rapidly , the communication link may be treated as useless.
Various atmospheric factors such as fog, clouds etc. increase noise especially at higher frequency bands like Ku band and particularly Ka band.
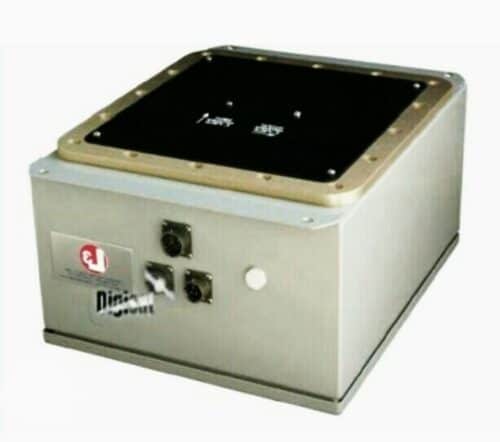

Digisat’s satellite simulation system (Fig. 2) instead of satellite tests and measures signal acquisition by the earth terminal, antenna position, uplink power adjustment, signal reception , link closure and communication system adjustment to establish acceptable bit error rates with very low satellite terminal transmit power.
Many satellite antennas are installed in open atmospheres i.e. they have to withstand humidity , extreme temperature and mechanical stress caused by wind load. They all play a negative role on signal quality.
Reliability is always a king
Needless to say, RF investigations play a vital role in enhancing performance of ground stations. Satellite engineers are always under pressure to develop reliable and economical designs for satellite play loads . Further economical designs of ground stations for different environmental conditions , in turn necessitates strong performance of test and measurement tools used.
The need of the hour is to predict the behaviour of satellite antennas to a very high degree of reliability .This has resulted in advanced drone based satellite simulation methods to predict behaviour of mobile vehicular ground station designs. Due to the increase in flow of satellite signals as a result of the information technology revolution , better satellite communication devices design and T&M tools are necessary to gain useful information benefits.
References:
- Article on Satcom RF testing and drone based RF testing of ground stations by atlanticmicrowave.com
- Articles on RF testing of satellite ground stations by rohde- Schwarz.com
- Some other web pages are also referred to.