Terahertz (THz) radiation is also known as submillimeter radiation. It has wavelengths that lie between those of microwaves and visible light. It can penetrate many nonmetallic materials and detect signatures of certain molecules. These qualities of terahertz waves could lend themselves to a wide amount of applications. THz imaging methods have considerably developed over the past decade.
Working Principle
Now, a new kind of camera that can detect terahertz pulses rapidly, with high sensitivity, and at room temperature and pressure has been developed by researchers at MIT, the University of Minnesota, and Samsung. This camera can simultaneously capture information about the orientation, or “polarisation,” of the waves in real-time, which existing cameras cannot. This information can be used to characterise materials that have asymmetrical molecules or to determine the surface topography of materials.
The new system uses particles called “quantum dots” . Quantum dots have recently been found to have the ability to emit visible light when stimulated by terahertz waves. The visible light can then be recorded by a device that is similar to a standard electronic camera’s detector and can even be seen with the naked eye.
The new “camera” consists of several layers, made with standard manufacturing techniques like those used for microchips. It includes an array of nanoscale parallel lines of gold, separated by narrow slits, lying on the substrate. Above that is a layer of the light-emitting quantum dot material. Further above that is a CMOS chip used to form an image. The polarisation detector, called a polarimeter, uses a similar structure, but with nanoscale ring-shaped slits, which allows it to detect the polarisation of the incoming light.
This new camera is able to detect terahertz pulses at low intensity levels that can make today’s large and expensive cameras outmoded.
The camera consists of patch sheets made from carbon nanotubes ( CNT) films. Moreover the patch sheet can be attached to the surface of the test object for better coverage.
Technology And Ecosystem Involved
Lying between microwaves and infrared in the electromagnetic spectrum, THz radiation easily penetrates materials like paper, clothes, and plastic in the same way X-rays do, but without being harmful. It is safe to use with even the most delicate biological samples. THz imaging makes it possible to ‘see’ the molecular composition of objects and distinguish between different materials – such as sugar and cocaine, for – example.

Advantages
- High penetration.
- High resolution.
- High sensibility.
- Flexible and free standing THz sensor arrays can be used to determine irregularly shaped objects.
Limitations Need To Be Resolved
Sources of THz radiation are very faint and as such hyperspectral imaging had until now limitations. To overcome this, The Sussex team shone a standard laser onto a unique non-linear material capable of converting visible light to THz. The prototype camera creates THz electromagnetic waves very close to the sample. This is similar to how a microscope works. As THz waves can travel right through an object without affecting it, the resulting images reveal the shape and composition of objects in three dimensions.
Applications
- Airport security.
- Intelligent car sensors.
- Quality control in manufacturing such as Non Destructive Testing ( NDT).
- As scanners to detect health problems like skin cancer.
- Astrophysical observations.
- Wireless communications with higher bandwidth than current cell phone bands.
- In pharmaceutical industries.
- Checking illicit drugs using spectral fingerprints.
- Food quality inspection.
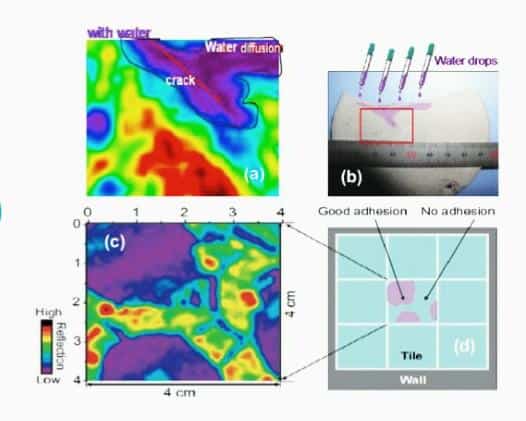
Figure illustrates how THz camera can be used in NDT ( Detecting holes inside concrete blocks in the above figure).( Image credit : https://www.researchgate.net/.. ) 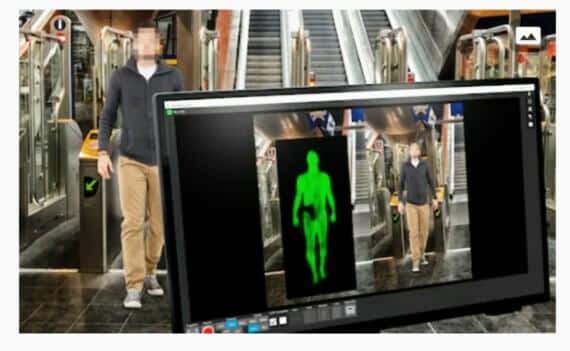
Figure illustrates how THz cameras can be used in Airport security scanning.( Image credit :https://www.laserfocusworld.com/… ) 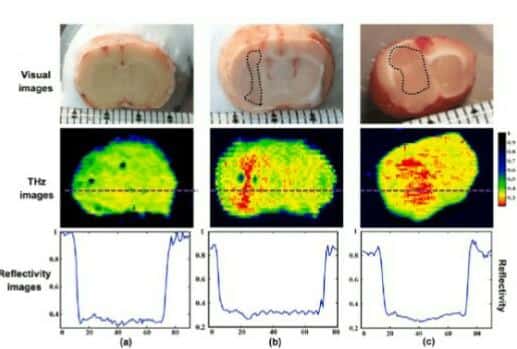
Figure. THz cameras can be used in medical diagnosis. Figure shows various images captured by THz cameras for the normal and glioma brain tissues. Glioblastoma is a kind of malignant tumour that results in glioma brain tissue.( Image credit : https://www.researchgate.net/..)
Components Of THz Camera
THz camera is mainly based on an uncooled microbolometer array. The components which work or are used for terahertz frequencies are called terahertz components. These are THz windows, THz lenses, THz Prisms, THz mirrors, THz waveplates, THz spectral splitters, THz beam splitters etc.
The Terahertz components used in wireless communication systems are THz antennas, THz sources or generators, THz detectors, THz modulators/demodulators, THz oscillators, THz filters, THz attenuators, THz amplifiers THz dielectric materials and so on. Terahertz optics production requires use of crystals such as quartz, silicon and sapphire etc.
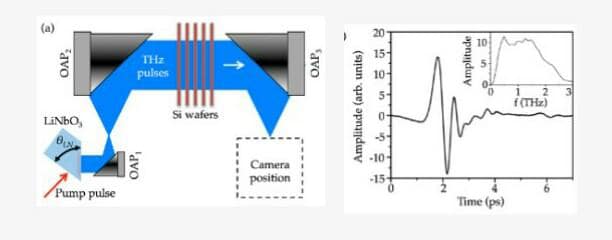
Figure (b) shows the THz pulse with its Fourier transformation in inset.( Image credit : https://www.mdpi.com/2076-3417/9/12/2531)
Road Ahead
During experiments, the present low cost THz camera detected terahertz pulses at low-intensity levels that crossed the capability of today’s large and expensive systems.
The terahertz source used in the new study is a large and complicated array of lasers and optical devices that cannot easily be scaled to practical applications. But new sources of innovations based on microelectronic and nano techniques are well under development. The cost of the present THz camera is expensive. Through well structured R and D efforts it is possible to make the system less bulky and inexpensive.
Presently efforts are on to fabricate GaAs high mobility heterostructure in standard semiconductor cycle to form a detector of the camera. Optical lithography process is used for this purpose. Further cameras require imaging sensors which are manufactured on single wafer. All such efforts are promising to make low cost quantum dots based THz cameras less bulky and less expensive.
Vinayak Ramachandra Adkoli is a B. E. in Industrial Production and served as lecturer in three different polytechnics for 10 years. I am also a freelance writer and cartoonist.