Hyper-convergence is the current and potentially future course of a journey that began years ago with server and storage virtualisation to optimise the traditional siloed approach to information technology.
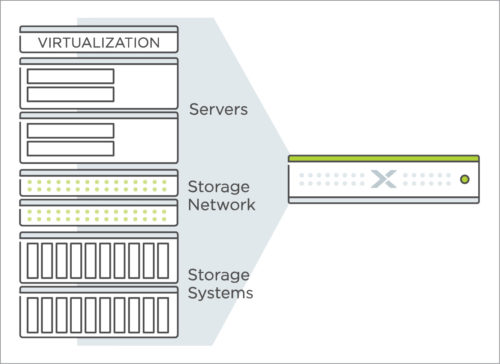
Hyper-convergence is basically an emerging technology in which the server, storage and networking equipment are all combined into one software-driven appliance. Hyper-converged infrastructure (HCI) can be managed comfortably through an easy-to-use software interface. Typically, a hyper-converged platform uses standard off-the-shelf servers and storage, and a virtualisation hypervisor that helps abstract and manage these resources conveniently. A simple operational structure makes this infrastructure flexible, easy to scale and manage.
HCI is gaining traction not just in enterprises but also with others who can benefit from heavy computing without complex management, such as professional racers! Training and racing is usually data-intensive. Racers need information like speed, acceleration and torque in real time to understand how they are performing and how they need to proceed. One mistake could cost not just a victory but a life too! Racing speed depends on the speed and reliability of the data processing and analytics that takes place behind the scenes. Last year, Formula One racing team Red Bull Racing replaced its legacy systems with HPE Simplivity hyper-converged infrastructure, achieving 4.5 times faster performance, increased agility and lower TCO through the move.
A few quick facts about HCI
At the outset, hyper-convergence might sound similar to all the virtualisation stuff you have read about in the past. So, let us first set out some facts about HCI before rounding up the latest updates:
1. Nutanix, a leader in HCI, defines that the technology streamlines deployment, management and scaling of data centre resources by combining x86-based server and storage resources with intelligent software in a turnkey software-defined solution.
2. HCI combines compute, storage and network together as a single appliance. It can be scaled out or expanded using additional nodes. That is, instead of scaling up the traditional way by adding more drives, memory or CPUs to the base system, you scale out by adding more nodes. Groups of such nodes are known as clusters.
3. Each node runs a hypervisor like Nutanix Acropolis, VMware ESXi, Microsoft Hyper-V or Kernel-based Virtual Machine (KVM), and the HCI control features run as a separate virtual machine on every node, forming a fully distributed fabric that can scale resources with addition of new nodes.
4. Since most modern HCI are entirely software-defined, there is no dependency on proprietary hardware.
5. HCI does not need a separate team as it can be managed by any IT professional. This makes it ideal for small and medium enterprises.
6. HCI is different from the traditional server and shared-storage architectures. It also differs from the previous generation of converged infrastructure.
7. HCI is not the same as cloud computing!
8. Scale-out and shared-core are two of the keywords you are bound to encounter when reading about HCI. Basically, most HCI implementations involve multiple servers or nodes in a cluster, with the storage resources distributed across the nodes. This provides resilience against any component or node failure. Plus, by placing storage at the nodes, the data is closer to compute than a traditional storage area network. So, you can actually get the most out of faster storage technologies like non-volatile memory express (NVMe) or non-volatile dual in-line memory module (NVDIMM).
The scale-out architecture also enables a company to add nodes as and when required rather than investing in everything upfront. Just add a node and connect it to the network, and you are ready to go. The resources are automatically rebalanced and ready to use.
A lot of hyper-converged implementations also have a shared core, that is, the storage and virtual machines compete for the same processors and memory. This reduces wastage and optimises resource usage. However, some experts feel that in some special cases, users might have to buy more equipment to run the same workloads.
9. It’s true that HCI is great for small enterprises as it can be used without fuss and hassles, but it can be used by really large data centres too. Leading companies have on record hyper-convergence case studies where more than a thousand HCI nodes are installed in a single data centre.
10. In a recent survey, research leader Forrester found that the most common workloads being run on hyper-converged systems are: database, such as Oracle or SQL server (cited by 50 per cent); file and print services (40 per cent); collaboration, such as Exchange or SharePoint (38 per cent); virtual desktop (34 per cent); commercial packaged software such as SAP and Oracle (33 per cent); analytics (25 per cent); and Web-facing workloads such as LAMP stack or web servers (17 per cent).11. During a recent talk, Dell EMC European chief technology officer for converged and hyper-converged infrastructure, Nigel Moulton, said that “mission-critical applications live best in converged infrastructures.” He justified his view by saying that many mission-critical applications such as ERP are architected to rely on the underlying hardware (in the storage area network) for encryption, replication and high availability. In HCI on the other hand, many of these things come from the software stack. Instead of looking at the move to HCI as all-or-none, he suggested that organisations take a practical look at it. If an application can work on HCI, companies must make the move as and when their existing hardware reaches end of life. The rest can remain on traditional hardware or converged systems. He also added that by the end of this year, feature-sets of traditional hardware, converged and hyper-converged will align and it will be difficult to even see the differences.

How HCI differs from traditional virtualisation, converged infrastructure and cloud computing
In the beginning, there was just IT infrastructure, no virtualisation. Enterprises spent a lot on buying the best IT components for each function and spent even more on people to implement and manage these silos of technology.
Then, there came virtualisation, which greatly optimised the way resources were shared and used without wastage by multiple departments or functions.
In the last decade, we have seen converged infrastructure (CI) emerging as a popular option. In CI, server, storage and networking hardware are delivered as a single rack, sold as a single product, pre-tested and validated by the vendor. The system may include software to easily manage hardware components and virtual machines (VMs), or support third-party hypervisors like VMware vSphere, Microsoft Hyper-V or KVM. As far as the customer is concerned, CI is convenient because there is just a single point of contact and a single bill. Chris Evans, a UK-based consultant in virtualisation and cloud technologies, describes it beautifully and humorously in one of his blogs, where he says that in CI there is just one throat to choke!
While this single product stack approach is ideal for most enterprises, there are some who want to do it themselves. This could be because they need heavy customisation or have some healthy legacy infrastructure that they do not want to discard. Given the required time and resources, one can also build a CI out of reference architectures. Here, the vendor gives you the reference architecture, which is something like an instruction manual that tells which supplier platforms can work together well and in what ways. So, the vendor tests, validates and certifies the interoperability of products and platforms, giving you more than one option to choose from. Thereafter you can procure the resources and put them together to work as a CI.
Enter HCI. What makes the latest technology ‘hyper-converged’ is that it brings together a variety of technologies without being vendor-agnostic. Here, multiple off-the-shelf data centre components are brought together below a hypervisor. Along with the hardware, HCI also packages the server and storage virtualisation features. Term ‘hyper’ also stems from the fact that the hypervisor is more tightly integrated into a hyper-converged infrastructure than a converged one. In a hyper-converged infrastructure, all key data centre functions run as software on the hypervisor.
The physical form of an HCI appliance is the server or node that includes a processor, memory and storage. Each node has individual storage resources, which improves resilience of the system. A hypervisor or a virtual machine running on the node delivers storage services seamlessly, hiding all complexity from the administrator. Much of the traffic between internal VMs also flows over software-based networking in the hypervisor. HCI systems usually come with features like data de-duplication, compression, data protection, snapshots, wide-area network optimisation, backup and disaster recovery options.
Deploying an HCI appliance is a simple plug-and-play procedure. You just add a node and start using it. There is no complex configuration involved. Scaling is also easy because you can add nodes on the go, as and when required. This makes it a good option for SMEs.
Broadly speaking, CI can be considered a hardware-focused approach, while HCI is largely or entirely software-defined. CI works better in some scenarios, while HCI works for others. Some enterprises might have a mix of traditional, converged and hyper-converged infrastructure. The common thumb rule today is that when organisations don’t have a big IT management team and want to invest only in a phased manner, HCI is an ideal option. They can add nodes gradually depending on their needs and manage the infrastructure with practically no knowledge of server, storage or network management. However, they lose the option of choosing specific storage or server products and have to settle for what their vendor offers. For organisations with more critical applications that require greater control over configuration, a converged system is better. CI offers more choice and control, but users might have to purchase the software themselves, which means more time, money and effort.Finally, even though HCI is a software-defined architecture that brings the convenience of cloud to your enterprise infrastructure, it is not a term that can be used synonymously with cloud computing. The two are quite different. Cloud is a service—it provides infrastructure, platform and software as a service to those who need it. It could be private, public or hybrid, and herein starts the confusion, as many people mistakenly think that hyper-convergence and private cloud are one and the same. Hyper-convergence is merely a technology that enables easy deployment of infrastructure-as-a-service in your private cloud by addressing many operational issues and improving cost-efficiency. It is an enabler, which prepares your organisation for the cloud era, and not the cloud itself!
The bring-your-own-hardware kind
According to a recent Gartner report, software-only “bring-your-own-hardware” hyper-converged systems have become significant and are increasingly competing with hyper-converged hardware appliances.
Gartner research director Jon MacArthur explained in a web report that “Most of the core technology is starting to shift to software. If you buy a vSAN ReadyNode from Lenovo or Cisco, or HPE, or your pick of server platform, they are all pretty much the same. Customers are evaluating vSAN and ReadyNode, not so much the hardware. Dell EMC VxRAIL is a popular deployment model for vSAN, but so is putting VMware on your own choice of hyper-converged hardware.”

Special needs like those of the military and the sophistication level of users are some of the factors that influence the decision in favour of implementing HCI as a software stack rather than a pre-packaged solution.
Major players
Gartner predicts that the market for hyper-converged integrated systems (HCIS) will reach nearly $5 billion (24 per cent of the overall market for integrated systems) by 2019 as the technology becomes mainstream.
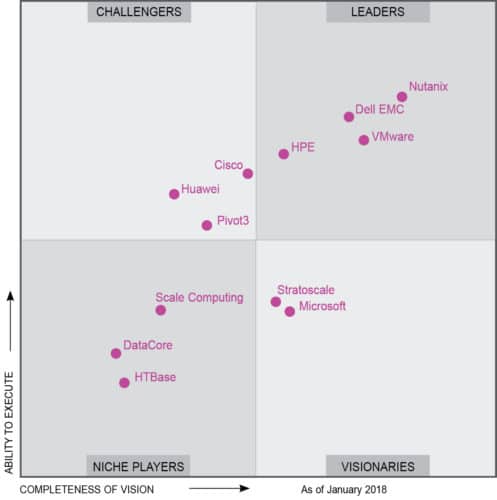
Nutanix, a pioneer in this space, offers a range of hardware systems with different numbers of nodes, capacities of memory and storage, different processors, etc. These can run VMware vSphere or Nutanix’s own hypervisor system called Acropolis. The company excels at supporting large clusters of HCI deployments—scaling up to 100 node clusters—which are easy to use and manage.
Nutanix tempts customers with the idea of a full-stack infrastructure and platform services through “One OS, One Click.” Prism is a comprehensive management solution, while Acropolis is a turnkey platform that combines server, storage, virtualisation and networking resources. Calm is for application automation and lifecycle management in Nutanix and public clouds, while Xpress is designed for smaller IT organisations. Xi Cloud Services help extend your data centre to an integrated public cloud environment. Nutanix also has a community edition that lets you evaluate the Nutanix Enterprise Cloud Platform at no cost!
Companies like Cisco and HPE are strengthening their foothold by acquiring start-ups in the space. Cisco bought Springpath, whose technology powers Hyperflex—Cisco’s fully-integrated hyper-convergence infrastructure system. HPE acquired Simplivity, one of the major competitors of Nutanix. HPE Simplivity products come with a strong, custom-designed platform called OmniStack, which includes a host of features like multi-site data management, global de-duplication, backup, snapshots, clones, multi-site data replication and disaster recovery and WAN optimisation.
Pivot3 also finds a place amongst the most popular HCI players. Last year, the company launched Acuity, which it claims to be the first priority-aware, performance-architected HCI solution with policy-based management. Acuity’s advanced quality of service (QoS) makes it possible to simply and predictably run multiple, mixed applications on a single platform.
Dell EMC offers VxRail and XC series of HCI solutions based on its PowerEdge servers powered by Intel processors. Last year, it released hyper-converged appliances that include Intel’s 14-nanometre Xeon SP processors, along with VMware’s vSAN and EMC’s ScaleIO. Dell EMC offers Nvidia GPU accelerators in both VxRail and XC solutions.
Apart from the regular HCI infrastructure, some start-ups are also coming up with innovative solutions, which some trend-watchers describe as HCI 2.0! NetApp, for example, has an option for those who want to keep their servers and storage separate—either to share the storage with non-HCI systems or to off-load certain tasks to dedicated servers. NetApp HCI uses SolidFire technology to deliver clusters with dedicated storage and compute nodes.
Companies like Pivot3, Atlantis Computing and Maxta also offer pure software HCI solutions.
AI and machine learning may create demand
It is interesting to note that Dell EMC is pushing NVIDIA GPU accelerators in its HCI solutions not just for video processing but also for running machine learning algorithms. Chad Dunn, who leads product management and marketing for Dell EMC’s HCI portfolio, explains in a media interview, “All the HCI solutions have a hypervisor and generally in HPC you’re going for a bare-metal performance and you want as close to real-time operations as you possibly can. Where that could start to change is in machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI). You typically think of the Internet-of-Things intelligent edge use cases. There’s so much data being generated by the IOT that the data itself is not valuable. The insight that the data provides you is exceptionally valuable, so it makes a lot of sense not to bring that data all the way back to the core. You want to put the data analytics and decision-making of that data as close to the devices as you can, and then take the valuable insight and leave the particularly worthless data out where it is. What becomes interesting is that the form factors that HCI can get to are relatively small. Where the machine learning piece comes in is what we expect to see and what we’re starting to see is people looking to leverage the graphical processor units in these platforms.”
Incidentally, in November 2017, Nutanix’s president Sudheesh Nair also spoke about how AI and machine learning are becoming extremely important for customers, at the company’s .Next user conference. He explained: “If we have a customer who is prototyping an autonomous car, that car generates almost 16TB of data per day, per city. An oil rig generates around 100TB per rig in the middle of an ocean with no connectivity. There is no way you can bring this data to the cloud—you have to take the cloud to the data, to where the data is being created. But moving information from the datacentre to the cloud creates manageability issues, and AI can be a better option. That’s where machine learning and artificial intelligence have a big part to play.”
Companies have to work out ways to store all that information such that you can easily access it and run analytical models to get predictive behaviour. This surge in demand for AI and machine learning provides a real opportunity for HCI.
Five good reasons why CIOs are moving to HCI and why IT guys should stay on top of the tech
Although hyper-convergence as a concept has been around for more than five years, it is obviously gaining a lot of momentum now with everybody talking about it and the spate of acquisitions. And it is not without real benefits as it:
1. Is ‘really’ quick and easy
2. Does not require a big team to manage it
3. Reduces cost of ownership
4. Makes it easy to launch and scale on-the-go
5. Improves reliability and flexibility of the data centre
As we mentioned earlier, HCI is not the panacea for all your infrastructure management problems. But if you need new infrastructure or have to replace an existing one, do ask yourself whether an HCI system can do the job. If it can, go for it because it can ease your admin and cost headaches quite a bit!






