IGBT vs MOSFET in power electronics: Both IGBTs (Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistors) and MOSFETs (Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistors) play crucial roles in switching applications. Though they share similar functions, each has unique characteristics, making them suitable for different power, speed, and efficiency requirements in various use cases
Table of Contents
Types of Transistors in Power Electronics
There are three major types of transistors available:
- Bipolar transistors
- Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor (MOSFETs)
- Insulated-Gate Bipolar Transistor (IGBTs)
The table above compares the performance and characteristics of these transistors.
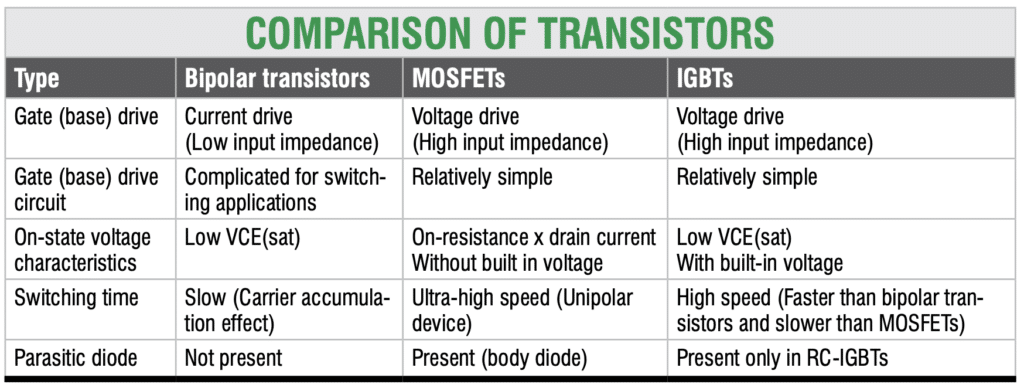
Note: While BJTs were once popular, they are now rarely used in high-power applications due to their slower switching speeds and complex circuitry needs. IGBTs and MOSFETs have largely replaced BJTs due to their improved efficiency and performance in power electronics.
Why MOSFETs and IGBTs are Common in Power Applications
- IGBTs are preferred for high-power applications due to their lower conduction losses and efficiency at higher currents. However, they are slower to switch compared to MOSFETs.
- MOSFETs are known for their faster switching speeds and simple drive circuitry, making them ideal for applications where speed is critical.
To know everything about MOSFET, check this article: MOSFET basics
In-Depth Characteristics of MOSFETs and IGBTs
On-State Voltage Performance
- MOSFETs tend to have a lower on-state voltage at low currents, leading to efficient performance at low power levels.
- IGBTs excel at high currents, where their lower on-state voltage drop reduces heat dissipation.
Switching Frequency Range
- MOSFETs can operate effectively at high frequencies (above 20kHz), making them the go-to for high-speed applications.
- IGBTs, with higher switching losses, are typically used at lower frequencies (below 20kHz), which is adequate for most high-power applications.
Common Applications of IGBTs and MOSFETs
- IGBT Applications: Electric vehicles, industrial motor drives, and HVAC systems where high current handling and efficiency are essential.
- MOSFET Applications: Switching power supplies, DC-DC converters, and low-power applications where rapid switching is a priority.
Also Read: High-Performance IGBT for EV Applications
Is It Possible to Use an IGBT In Place Of a Power MOSFET?
Yes, it is possible to use an IGBT (Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor) in place of a Power MOSFET in a project.
Both IGBTs and Power MOSFETs are used for switching applications in power electronics, and they have some similarities and differences. IGBTs are preferred in high-power applications because of their lower conduction losses, which allows for higher efficiency and lower heat dissipation. In contrast, Power MOSFETs are typically preferred for lower voltage and lower power applications because of their faster switching speeds and simpler drive circuitry requirements.
However, there are some design considerations that need to be taken into account when replacing a Power MOSFET with an IGBT. For example, IGBTs have a higher gate capacitance, which can affect switching times and require a more powerful gate driver circuit. IGBTs also have a higher voltage drop than Power MOSFETs, which can result in higher power dissipation and temperature rise.
Overall, the decision to use an IGBT or a Power MOSFET will depend on the specific requirements of the project, including voltage, current, switching speed, and efficiency. It is important to carefully evaluate the specifications of both devices and consider the trade-offs before making a decision.







