Blockchain consortia are creating a massive hype in the market. Many enterprises are highly interested in this type of network and willing to join consortia to gain optimal benefits of blockchain technology. However, there are still lots of unknown facts regarding how a consortium works and how it is governed, etc.

Till recently, the focus was mainly on governance solutions for public blockchain platforms like Hyperledger and Ethereum. Consortium blockchain governance, however, will become as or even more important to enterprises than public blockchain governances because these will work with this level of governance on daily basis.
It is important to understand that there is no universal sort of blockchain governance. It all depends on the type of blockchain solution that companies can use. There are three main types of blockchain systems: open or public, private or permissioned, and consortium or federated blockchains. Public and private blockchains are all known to the general audience, but consortium blockchain needs more understanding.
Blockchain consortium, is defined as a type of network where multiple organisations maintain the system. A group of companies thereby collaborates on advancing the state of blockchain technology adoption in the industry, establishing industry standards, drafting use cases, developing key infrastructure, and operating commercial blockchain platforms.
Consortium blockchains are termed as ‘Hybrid Solutions,’ in-between public and private, that is, between fully open decentralised systems and fully centrally controlled, thus taking the best of both the worlds. Rather than one organisation, multiple organisations take part in the consortium and every organisation gets similar treatment. So, there is no single entity ruling over the network.
During a small Deloitte survey of 1,386 global enterprises in 2019 regarding blockchain consortium impact of industry in world, the following percentage was observed in varied parameters:
- Cost savings: 57%
- Learning acceleration: 55%
- Risk sharing: 47%
- Mass adoption: 45%
- Lifespan maintenance: 42%
- Influencing standards: 42%
Blockchain consortium vs public and private platforms
Blockchain is based on peer-to-peer topology that allows data to be stored globally on millions of servers. It is also described as a P2P, decentralised, distributed ledger technology that works involving any third-party intermediary or central authority, unlike traditional banks that rely on intermediaries. Blockchain offers more security, transparency, immutability, which is why it is the most discussed technology at present. The technology is attracting blockchain developers and blockchain experts due to its potential to revolutionise the way industries and businesses work.
As per the Deloitte survey, at least 76 percent of enterprises that are using blockchain solutions are moving towards blockchain consortium, or willing to move in two to five years due to its increasing popularity and agility in architecture. In actual state, blockchain platforms are classified in order of usability growth as private blockchain, public blockchain, semi-private blockchain, and consortium blockchain.
In fact, semi-private blockchain is the early adoption of a hybrid blockchain platform where it offers enterprise-level public blockchain platform to address business-to-business users. It provides a closed set of service accessibility for an enterprise’s communication.
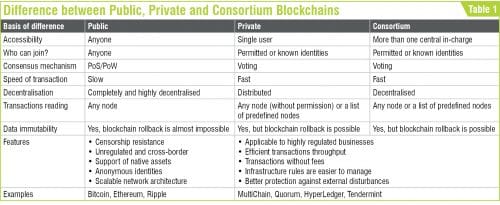
Depending on the use and requirements, blockchains have been categorised into three types: public, private, and consortium (also known as federated). Each of these blockchain networks serves its purpose and solves problems, and each blockchain has its own set of features and advantages over one another.
Public blockchain
Public blockchain is a permission-less, non-restrictive, distributed ledger system, which means anyone who is connected to the internet can join a blockchain network and become a part of it. The basic use of such a blockchain is in exchanging cryptocurrencies and mining. It maintains trust among the whole community of users as everyone in the network feels incentivised to work towards the improvement of the public network.
The first example of such a blockchain is Bitcoin that enabled everyone to perform transactions. Litcoin and Ethereum are also examples of a public blockchain.
Private blockchain
Unlike the public, a private blockchain is a permission-needing and a restrictive blockchain that operates in a closed network. Such a blockchain is mostly used within an organisation where only particular members are participants of the blockchain network.
The major difference between public and private blockchains is that the former is universally accessible, whereas the latter is confined to a particular group of people. Moreover, a private blockchain is more centralised as a single authority maintains the network. Corda, Hyperledger Fabric, Hyperledger Sawtooth, and Corda are some examples of the private blockchain.
Consortium blockchain
Consortium blockchain (also called federated blockchain) is best suited for organisations where there is a need for both types of blockchains, that is, public and private. In this type, there is more than one central in-charge, or we can say more than one organisation involved who provides access to pre-selected nodes for reading, writing, and auditing the blockchain. Since there is no single authority governing the control, it maintains a decentralised nature. Energy Web Foundation and IBM Food Trust are two examples of such a blockchain.
Table 1 highlights the differences between public, private, and consortium blockchains.
Types of blockchain consortium
There are three types of blockchain consortium:
- Technology-focused
- Business-focused
- Dual-Focused