Table of Contents
Solenoids drive innovation in various sectors. They convert electrical energy into mechanical motion. This enables precise control in applications. From fuel injectors to medical devices, solenoids optimize performance. Before diving deep into a solenoid’s principles, let’s get a basic understanding of what an electromagnet is.

An electric current flowing through a coiled wire creates a magnetic field. A magnet is known as an electromagnet when this wire is wound around a ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic material.
Since a magnetic field is produced as long as the current exits in the wire, the subsequent electromagnet has a temporary magnetic effect. When the current decreases to zero, there will be no magnetic effect.
Introduction
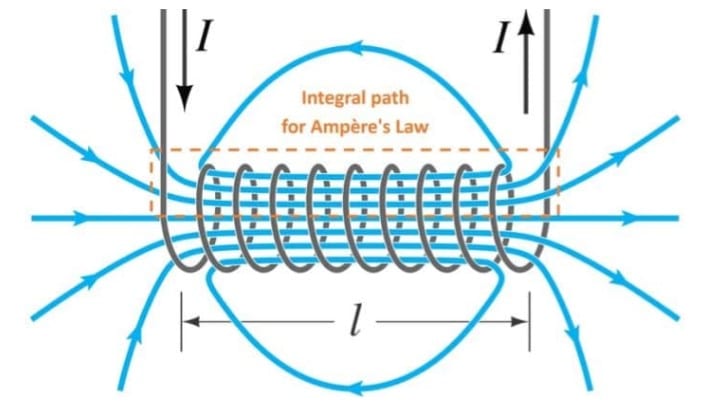
Derived from two Greek words: Solen (pipe) and Eidos (coil), the solenoid is a type of electromagnetic device that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. It is generally made by tightly wounding wires in a helix shape around a piece of metal.
Whenever an electric current passes through it, a magnetic field is created. As previously stated, the power of the magnetic field depends on the electric current. Therefore, by varying the current as per our need, we can easily magnetize and demagnetize the electromagnet, enabling us to control the magnetic fields for different requirements.
Working Principle
A solenoid works on electromagnetism and electromagnetic force. It consists of a round cylindrical coil with several wire turns and a metal rod inside the coil that is free to move. When an electric current is provided to the coil, a magnetic field is generated due to which the metal core or rod inside the coil gets attracted towards the direction where the magnetic flux is high.
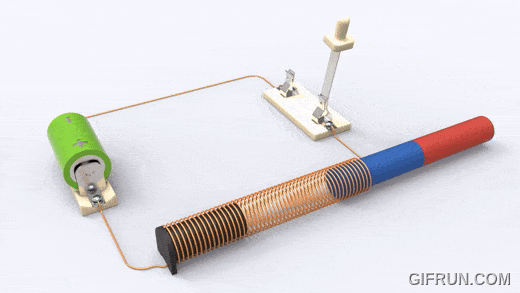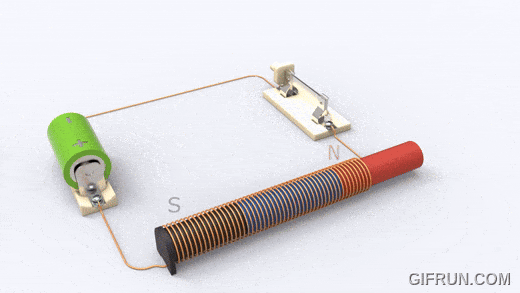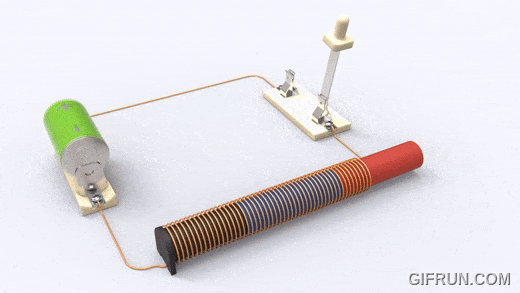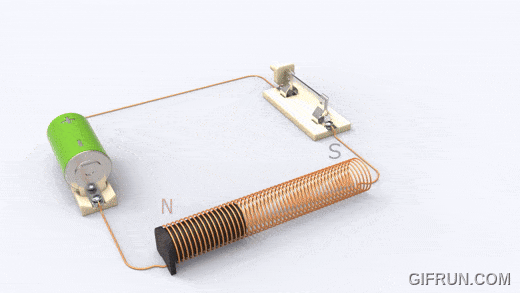
This electromagnetic effect in a solenoid enables any connected plunger or armature to move as per our needs. In this way, we can control the magnetic field of a coil by controlling and in turn use it for controlling the mechanical movement of metalcore.
The formula for the magnetic field in a solenoid is:
| B=µIN/L |
Where,
- B= Magnetic field
- µ= Permeability
- N = number of turns
- I = current of coil
- L= length of coil
| n= N/L |
Turns density (No. of turns per unit length)
So from this formula, we can see that to increase the magnetic force produced in a solenoid coil, we will have to increase the number of turns, N and the current, I.
Types of Solenoid
| Solenoid Types | Definition | Working Principle | Application |
| AC Laminated Solenoid | A solenoid that operates on alternating current & has laminated steel frames to reduce energy losses. | The function of the laminated core is to minimize the eddy current that is generated by the AC. This increases the efficiency of the device. The working principle is similar to a linear solenoid but with additional damping due to the AC. | This type of solenoid is perfect for applications that require quicker response such as in relays, circuit breakers, etc. |
| DC-C Frame Solenoid | As the name itself suggests, a solenoid operated by DC, with a framed coil to increase the magnetic strength is known as a DC-C frame solenoid | As its name states, this solenoid is constructed in such a way that it has a letter ‘C’ like frame cover around the coil. DC solenoids produce a steady magnetic field that pulls a plunger into the coil upon energization. | Ideal for applications that need reliable, sustained power without the vibration typical of AC solenoids, such as in automotive applications, industrial equipment, etc. |
| Linear Solenoid | A solenoid that produces linear motion when energized. | When an electric current passes through the coil, it creates a magnetic field that attracts a ferromagnetic plunger, causing it to move in a linear direction. Releasing the current allows the plunger to return to its original position, often with a spring. It has a very high initial attracting force and a very short closing time. | Mainly used in open-close motion applications such as control valves, electrically operated doors, vending machines, etc. |
| Rotary Solenoid | A solenoid designed to produce rotary or rotational motion when powered. | It is a special type of solenoid where the magnetic force is converted into a rotational force or a rotary motion. It consists of an armature core mounted on a flat disk. When a current is provided, the armature gets attracted toward the stator and the flat disk rotates (Typically 30 to 90 degrees). | Commonly used for twisting or turning applications such as shutter mechanisms in cameras, gaming, robotics, etc |
Applications
Solenoid Valve

The solenoid valve is a simple device in which a solenoid is used to control and regulate fluid flow. It has a coil with a free movable plunger or an iron rod with a spring inside it.
When we energize the coil, the plunger moves from its position due to magnetic attraction and when we cut the power to the coil, the plunger comes back to its original position with the help of a spring. As soon as the plunger comes in the path of the flowing fluid, its flow stops.
Solenoid Lock
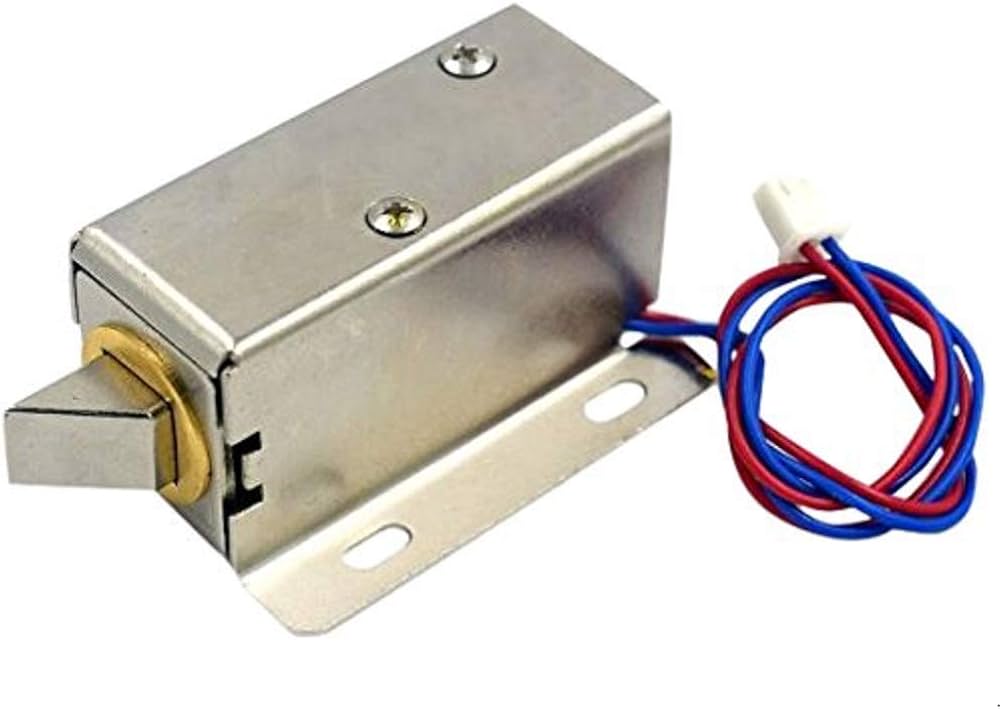

Here we use the movement of the solenoid plunger for the locking and unlocking mechanism. These solenoid locks are widely used in electronic and biometric password-based locks.
It consists of a movable strong metal plunger. When the coil gets magnetized due to an electric field, the plunger moves to perform the lock and unlock mechanism.
Circuit Breakers
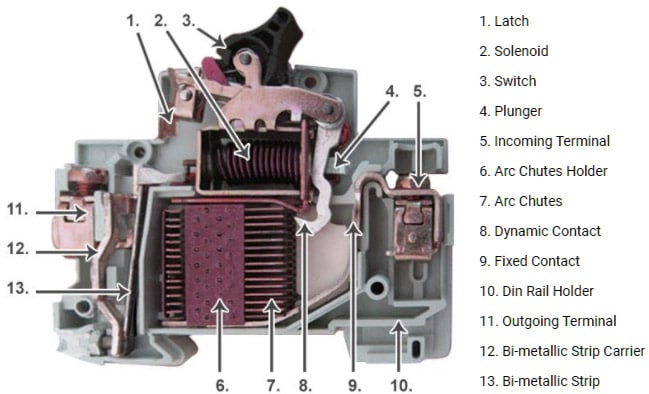
Solenoids trip circuit breakers by moving a lever that disconnects electrical flow when an overload is detected. The solenoid is powered by the current and opens the circuit to prevent damage to electrical systems.
Haptic-Actuators

Solenoids can also play a role in haptic feedback systems. By converting electrical energy into mechanical movement, solenoids can simulate tactile sensations through physical movement, adding a layer of touch-based feedback to electronic devices.
Advantages and Disadvantages
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Energy-efficient and cost-effective | Limited Range of Motion |
| Faster response time | Voltage fluctuation sensitivity |
| Durable for repetitive tasks | Sensitive towards magnetic interference |
| Provides precise control | Susceptible to Wear and Tear |
| Compatible with both AC & DC | Fluid flow significantly affects valve performance, influencing pressure, wear, noise, and lifespan. |
Design Consideration and Selection
When designing and selecting solenoids for specific applications, several factors must be considered to ensure optimal performance and efficiency. Some key factors include:
- Type of solenoid based on the application
- Force and Stroke Requirements
- Power consumption & Voltage requirement
- Duty cycle
- Response time
- Size and space constraints
- Cost & mounting options
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Maintenance Checklist
| 1. Regularly check for any signs of wear on the plunger, springs, coil, etc. Look for bent or damaged components that may affect performance. 2. Lubricate the moving parts as and when required 3. Use a multimeter to verify whether the solenoid is receiving the correct voltage and current 4. Clean the components regularly using a soft brush 5. Check for loose connections as they can lead to voltage drop 6. Check for overheating of the coil as it can shorten the lifespan |
Troubleshooting Guide
- Problem: Solenoid is not activating
Solution: Check for coil burnout, power supply,, and connection (broken wire)
- Problem: Humming noise or any noise
Solution: This usually occurs due to a loosened connection or rapid magnetic field change. Consider using a rubber mount for lesser vibrational noise, or switch to AC
- Problem: Reduction in force overtime
Solution: This usually occurs because of the dust build-up or weak magnetic field. Clean the moving parts, check for continuity, and verify the proper voltage supply
- Problem: Weak magnetic field or no magnetic field at all
Solution: This can occur when the coil is short-circuited or in insufficient power. Monitor the coil using the ohmmeter for short and check the power source and wiring
Watt’s Interesting?
Remember the thrill of 70s and 80s pinball machines? Solenoids launched the balls and triggered gameplay. Fast forward to today, and these components now enhance robotics and medical technologies!
FAQs
- What does “duty cycle” mean for solenoids, and how do I calculate it?
Ans. The duty cycle refers to the percentage of time the solenoid is active vs when it is at rest.
- How do the plunger size and coil winding affect solenoid performance?
Ans. Both plunger size and coil winding can affect the solenoid performance by impacting the force and range of the motion.
- What is the difference between AC and DC solenoids?
Ans. AC and DC solenoids operate similarly but use different electrical currents, which affects things like efficiency, heat generation, and noise. AC solenoids can hum due to alternating current, and DC solenoids usually need rectifiers if used in AC circuits, adding complexity.
- How does a latching solenoid differ from a regular solenoid?
Ans. The major difference is that the latching solenoids hold their position without continuous power, whereas regular solenoids need a constant current to remain actuated.
- Can a solenoid be used as an actuator, and how does it compare to other types?
Ans. Solenoids are technically actuators, but they typically provide linear movement over a short stroke and are best for on/off applications, unlike motors which offer continuous rotation.








