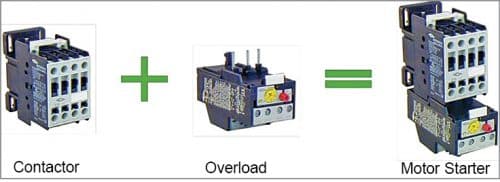
A motor starter is an electrical switching device that starts or turns on a motor safely. It can also reverse, accelerate, and protect the motor. Generally, low-power motors do not require starters. A motor starter has two main blocks—contactor and overload protector.
The contactor supplies current to the motor for starting. It is similar to a relay but is designed to handle a larger amount of electrical current and higher voltages. Unlike a relay, a contactor does not have an energised common pole to switch between the normally open (NO) and normally closed (NC) poles.
The overload protector prevents the motor from drawing too much current and thus getting damaged. Generally, there is current sensing element in the protection unit that senses the amount of current drawn by the motor.
A motor starter is either manual or automatic. Manual starter is operated by pressing a button or switching on the device. The button or switch is mechanically linked to the contactor which, on switching, closes or opens to either provide power or cut power to the motor. A magnetic motor starter offers the benefit of remote starting and automatic operation. A typical motor starter available in the market and its two main components are shown in Figire.
Motor dry-run protection is a type of protection mechanism that prevents a motor or water pump from running when there is no water or liquid available to pump (called dry running). For example, a water pump is likely to get damaged if it runs for some time without water in the underground tank (reservoir) to pump. When a water pump works without water, the pump motor spins faster than its rated speed and the temperature inside the motor starts increasing (also because there is no liquid inside the motor to cool it). This often results in damaging the mechanical parts, bearings, motor coil, shaft, etc due to a thermal shock or melting of some parts.
There are different ways to prevent dry-run by using various switches and sensors. Some common switches are pressure switch, float switch, magnetic switch, electrode relay, level switch, etc. Some dry-run protection circuits constantly check the active power of the motor, set point, and timer. If the power goes beyond the set value, dry-run protection stops the pump immediately in such cases.
Most of the automatic motor pumps have built-in dry-run protection. A typical automatic water pump starts the motor when water level in overhead tank becomes low and switches it off when the water tank becomes full, or there is insufficient water in reservoir, thus preventing dry-running of the motor.
You may refer ‘Automatic 3-Phase Induction Motor Starter’ and ‘Water Pump Dry Run Guard’ DIY articles available on our website.





