Three in one: Ideal for space-constrained applications
The internal 3-chip structure of Infineon’s NovalithIC family comes in a D²Pak (TO-263-7) and comprises a half-bridge driver, an nchannel MOSFET and a p-channel MOSFET in chip-by-chip and chip-on-chip construction (Figure 4). While typically five chips (half-bridge driver and four MOSFETs) are needed, they can be replaced by two devices in a conventional H-bridge application for controlling a bidirectional brushed DC motor. This reduces the component mounting effort and the space saving is in the range of about 30 %.
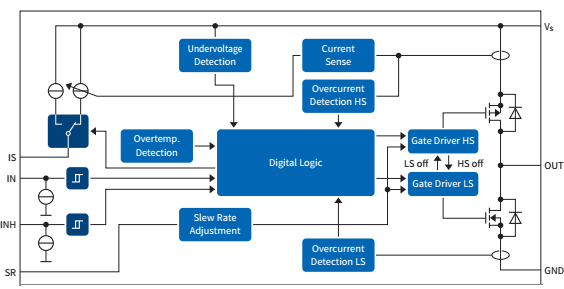
The NovalithIC devices bring the advantages of particularly compact designs to applications beyond 250W without requiring increased cooling efforts. Integrated features – such as overcurrent protection, undervoltage lockout and overtemperature protection – considerably reduce design work and, at the same time, keep system costs (BOM) at a low level.
Since the integrated driver IC works with a logic level input it can be controlled directly by the microcontroller. Latest p-channel MOSFET technology enables a significant reduction of EME (Electro Magnetic Emissions) and power dissipation thanks to an optimized switching shape and the absence of a charge pump.
Minimum parasitic effects
A common problem in the control of highly dynamic systems, such as PWM-controlled brushed DC motors, is the interference effect due to, for example, parasitic stray inductances in the commutator circuit with capacitor, high-side and low-side switch. Even in a layout optimized with a large amount of design work, negative voltage spikes of 5V and lower can be generated by fast dl/dt rates for a 200W drive. These parasitic effects can be eliminated with integrated designs, in which wire lengths are practically negligible, under comparable conditions voltages of only approximately 1V below ground occur.
Diagnosis and protection included
Diagnostic functions, such as a current measurement are vital for efficient motor control. Designers can decide how much effort to invest in the precision of the current measurement depending on individual application requirements. With the NovalithIC for example, an accuracy of ±10% is possible by a simple end-of-line calibration. The tolerance can be further reduced to ±3% with temperature compensation. Without calibration effort by the user, the device offers a worst-case tolerance of ±28% for current measurements across the nominal output range and across the full range of the operating temperatures.
The bridge drivers use a separate internal current measurement function to detect overcurrent situations and protect the device. If the current through the high or low side MOSFET reaches a specified threshold, the device switches to a defined mode, which results in a controlled limitation of the current in combination with an inductive load (motor).
Finally, protection features ensure high reliability. In this example a temperature sensor is located on the logic chip, which is placed directly on the pchannel MOSFET. Once a critical temperature is reached here (e.g.,Tj > 155°C), the http://kitsnspares.com/user1/productdescription.asp?id=1180driver switches itself off and goes into tri-state at the output. From there, it can then be actively powered on again by means of a signal from the microcontroller (latched) if the temperature drops at least by the thermal hysteresis of typ. 7K.
Multi-talent: One chip for a wide range of motor control applications
Infineon’s NovalithIC chips meet the AECQ-100 standard and work in a temperature range of up to Tj = 150°C. This makes them suitable in principle for all automotive applications. With the BTN8982TA, for example, an RDS(on) typ. value of 10mΩ is achieved in the path (high-side and low-side MOSFET combined), and thanks to the excellent thermal performance of the D2PAK, even applications handling more than 250W can be served without significant cooling effort. Concrete application examples include all motor control designs, such as brushed DC (unidirectional and bidirectional) as well as 3-phase brushless motors, in which three NovalithIC chips are used.
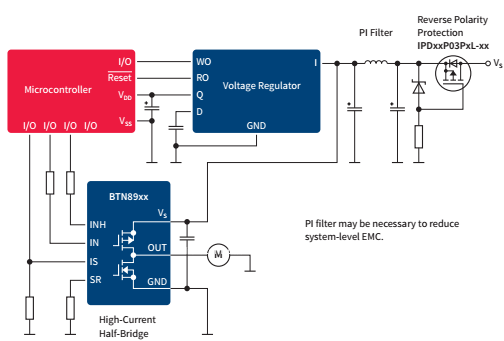
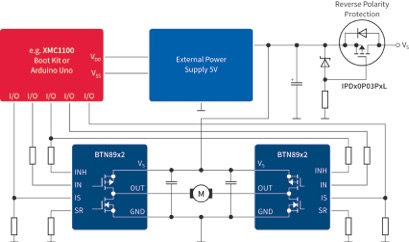
Typical examples, which can be found in the automotive sector, are HVAC blowers, sunroof controllers, park brakes, fuel pumps (figure 5) or power-seats. NovalithIC is also the fit for many industrial electronic applications (figure 6) and home appliances: e.g. coffee machines, electrical controlled bed and sun blinds.
Fast and easy design: with shields for Arduino
Infineon Technologies provides several dedicated shields for the Arduino design community to provide a wider marked access to Infineon semiconductors. Arduino is based on a microcontroller board with a defined form factor and was launched as an open source (hardware and software) platform to enable a fast and easy way to electronic prototype designs. The shields are compatible to Arduino Uno R3 and can be combined with the XMC1100 Boot Kit from Infineon, which is equipped with a 32-bit microcontroller of the XMC1000 family. All XMC1000 products use the ARM® Cortex®-M0 processor.
The DC Motor Control Shield with the NovalithIC BTN8982TA for Arduino (figure 7) enables a fast and cost-effective prototyping of DC motor control designs with easy testing of half-bridge and full-bridge motor control applications. The shield is capable to drive two uni-directional DC motors or one bi-directional DC motor. For this purpose, the shield implements two BTN8982TA fully integrated high-current half-bridge drivers.
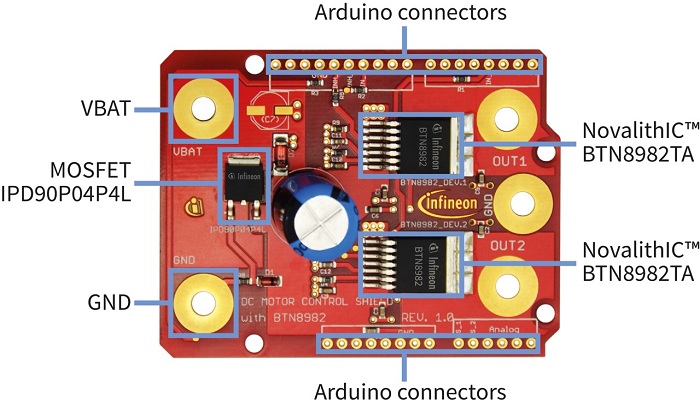
The DC Motor Control Shield with BTN8982TA for Arduino is capable to handle high-frequency PWM inputs of, for example, 30kHz. The shield supports brushed DC motor control up to 250W continuous load (i.e. at 12V / 20A) while the BTN8982TA is having a current limitation, which allows nominal currents of up to min. 55A.
Further informations:
www.infineon.com/novalithIC
www.infineon.com/arduino
www.infineon.com/xmc