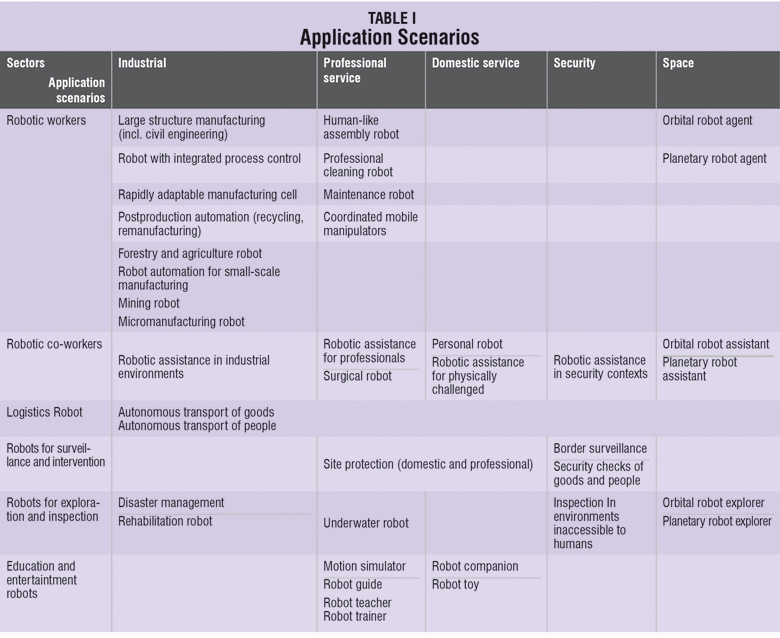
Industrial robots form an essential part of the current manufacturing sector of India. Without the use of robotics technologies or cost-effective production, a pillar of emerging Indian wealth would not be possible. Furthermore, robot-based production increases product quality, improves work conditions and leads to an optimised use of resources. The miniaturisation of robotic technologies and newly developed sensing capabilities mean that these benefits are becoming applicable to an even wider range of manufacturing industries, including those with small and varying lot sizes, materials and product geometries.
Robots can also be effective in areas where there are skill shortages. Significant application opportunities exist in the emerging service robotics sectors, whose products will impact on our everyday lives by contributing high-value-added services and providing safer working conditions. In the fields of medical diagnosis, therapy and rehabilitation, robot-based systems will assist health workers performing novel procedures, thereby increasing their effectiveness. The aging population will drive the application of robotic technologies that improve the quality of life and assist people to live longer and more comfortably in their own homes.

Robotic technologies, such as navigation, motion control and sensing and cognition, will enable a broad range of innovations in today’s products resulting, for example, in more flexible, environmentally friendly transport systems and intelligent household appliances. Eventually these technologies will reach levels of sophistication which will enable widespread use of intelligent robots and robotic devices to perform a variety of tasks in homes, offices and public places.
Driven by the increased security needs of Indian citizens and the higher workload resulting from extended monitoring of our everyday environments, robots already play an increasing role in the security market. Tele-operated mobile systems are now being used in a number of security applications including bomb disposal. In the future, robots will autonomously assist with the protection of offices and homes, and will help secure borders or monitor the environment in both routine and emergency operations.
In space, the use of robots has become almost obligatory. Both unmanned and manned missions, be it in earth orbit or interplanetary, will be preceded or augmented by robots. In addition, the technologies applicable to space robotics will enable a wide range of earth-based exploration and material-processing activities from automated undersea inspection to mining and mineral extraction under hazardous conditions.
Future of robotics
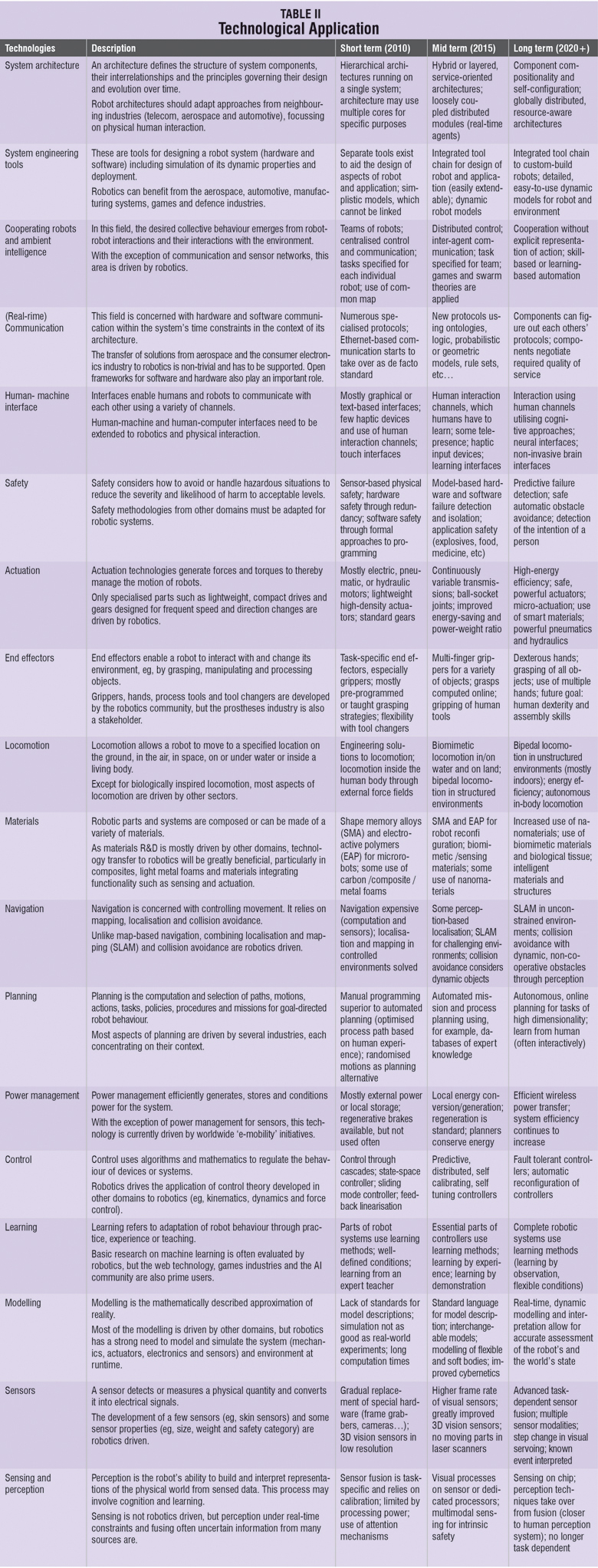
Modern robotics engineers are confronted with the task of developing machines that interact with their creators in modes of increasing compatibility. Understanding the mapping of DNA will not drive the creation of more compassionate robots in the future. Understanding discontent, and its cause, is the key to unlocking this portion of the human algorithm.
Underwater robotics. The ocean covers about 71 per cent of the earth and each year of research and exploitation shows that ocean exploration will be a prime subject of interest for man in the future. The rapidity in the development of robust systems routinely operated, or the design of new solutions, is strongly influenced by the investors involved. Designing an underwater system is an expensive task, but results in a cost-effective tool. In the commercial sector of the hydrographic industry, the unmanned underwater vehicle (UUV) is already making a significant impact. Remotely operated vehicles (ROVs) and autonomous underwater vehicle (AUV) are currently routinely deployed for intervention on immersed structures or surveying wide-range areas.
Considerable research effort has been made to improve process performance and control strategies for the various underwater processes over the last half century. However, there are still many problems to overcome. The major efforts on research and development should be focussed on the following topics:
1. Modelling accuracy should be quantified
2. State estimation error has to be bounded
3. Guidance and control systems should exhibit global practical convergence
4. Mission control system and the hardware and software architectures need to be reactive and determinist
5. Efficient vertical communication
6. Minimal horizontal communication
7. Coordinated maneuvers
8. Obstacle avoidance
9. An efficient management of the terrain knowledge
Futuristic robots may be coming soon to an ocean near you. Underwater robotics promises to open a new chapter in the notoriously challenging exploration of earth’s ocean. Future scope of ocean exploration due to underwater robotics includes:
1. Intelligence, surveillance and reconnaissance
2. Mine countermeasures
3. Anti-submarine warfare
4. Inspection/identification
5. Oceanography
6. Communication/navigation network nodes
7. Payload delivery
8. Information operations
9. Time-critical strike
10. Underwater welding
Nanorobotics
Nanorobotics is the emerging technology field creating machines or robots whose components are at or close to the scale of a nanometer. More specifically, nanorobotics refers to the nanotechnology engineering discipline of designing and building nanorobots, with devices ranging in size from 0.1µm to 10µm and constructed of nanoscale or molecular components. The names nanobots, nanoids, nanites, nanomachines or nanomites have also been used to describe these devices currently under research and development.
Nanomachines are largely in the R&D phase, but some primitive molecular machines and nanomotors have been tested. The first useful applications of nanomachines might be in medical technology which could be used to identify and destroy cancer cells. Another potential application is the detection of toxic chemicals and the measurement of their concentrations in the environment.








