IaaS provides cloud-based computing infrastructure that can help enterprises optimise their IT operations and resource management, improve troubleshooting and reduce operational costs significantly.
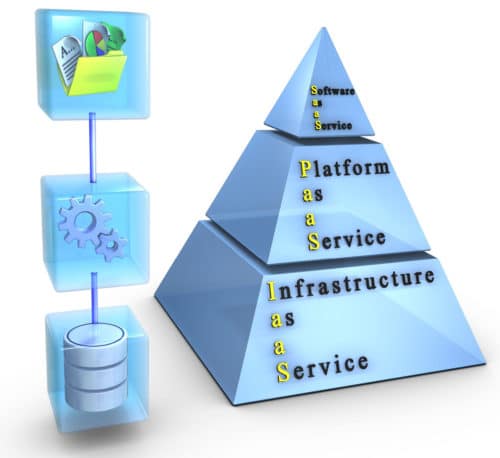
Infrastructure as a service (IaaS) is a form of cloud computing infrastructure that allows virtual computing resources to be managed over the Internet. Cloud computing services have three categories: IaaS, platform as a service (PaaS) and software as a service (SaaS).
IaaS is a self-service model that delivers computer infrastructure to support enterprise operations for accessing, monitoring and managing remote data centres. It handles software, hardware, storage, computation, network components, networking services (like firewall), servers and data centres, and provides all computing resources to support the delivery of applications.
An Iaas provider is responsible for operating and maintaining equipment, databases, messaging queues and other policy-based services above virtualisation. Without any major capital investment in additional hardware, organisations can use IaaS to fulfill additional computing capacity on-demand. Using IaaS, they can manage data, operating systems (OSes), runtimes, middleware and applications. They can also update these to newly-released versions.
Within a service provider’s infrastructure, organisations use their own platforms and applications. An enterprise cloud is a hosted computing environment that delivers IaaS, PaaS and SaaS to business users via a network. Enterprise IT provides the foundational building blocks for businesses across various verticals, including access, data, interconnectivity, interoperability solutions and infrastructure.
Enterprise cloud computing (ECC) enables organisations to deliver computing services in a controlled and secure manner, using a network firewall. Government agencies and healthcare organisations that store, manage or process sensitive data use ECC services, instead of public cloud computing services.
ECC can be implemented in one of two ways: as a private cloud hosted on the premises of an organisation, or as a private cloud hosted externally by a third-party provider. Organisations that use externally-hosted ECC services enjoy the benefits of lower IT infrastructure, maintenance and IT operational expenses due to a decreased need for internal IT support staff.
Need for IaaS
Phanikishore Burre, head of delivery – cloud, infrastructure and security services, CSS Corp., says “Businesses are constantly looking for ways to streamline operations, accelerate business processes, reduce costs and increase service agility. In this context, they need to be intelligent, adaptive and agile when it comes to handling newer expectations. Despite significant adoption and investments in newer technologies, enterprises find it challenging to manage IT due to lack of alignment with businesses, broken business processes and inability to build strong business cases for modernisation. Most carry a baggage of legacy systems, ageing infrastructure and software stacks. This IT infrastructure landscape is making it cumbersome across the technology landscape. Companies are spending a colossal amount of money to streamline their business operations.”
Applications of IaaS
Application areas where IaaS can be successfully deployed are test and development, website hosting, storage, backup and recovery, Web apps, high-performance computing and big data analysis.
Some operational areas where IaaS has been deployed are:
- Pooling server and networking resources to store data and run applications in a business
- Hosting websites on virtual servers founded on underlying physical server resources
- Interconnecting virtual servers through a virtualised network to enhance cloud hosting capabilities or enterprise IT infrastructure
The freely available OpenStack open source framework is increasingly being used as cloud management software. It enables customers to use a largely manufacturer-neutral cloud. Other benefits include modular structure, and automation and orchestration. OpenStack is about easy self-management. Customers are provided with a graphic Web interface to manage their IT resources.
Multi-tenancy of IaaS
This feature enables using the same software and interface to configure resources and isolate customer-specific traffic and data. Multiple users who do not share or see each other’s data can share the same applications while running on the same OS, using the same hardware and data storage mechanism.
In an organisation, software installation on individual employees’ desktops or on a dedicated server is complicated, because all servers or installations need to be upgraded individually. Hence, servers are underused, resources are poorly utilised and maintenance becomes more complicated. Whereas, utilisation of resources improves and costs are lowered by streamlining maintenance when multiple users share same database server and applications.
Some IaaS providers are IBM, CSS Corps, Transworld Technologies, Cyient, Amazon Web Services, Cisco Metapod, Microsoft Azure and Google Compute Engine.
IaaS architecture
IaaS has a structural design that delivers computing resources via cloud as a service. IaaS architecture optimises the use of physical computing resources to maximise cost savings and revenue for an organisation. Its design depends on specific business requirements and goals.
In an IaaS model, a cloud provider hosts various infrastructure services including monitoring, detailed billing, security, log access, backup, replication, recovery, load balancing and clustering. These services are policy-driven and provide greater levels of organisation and automation to IaaS users for important infrastructure tasks, and maintaining application availability and performance.
Users are given access to virtualised components to build their own IT platforms. Computing resources provided to them include virtual server space, bandwidth, IP addresses, network connections and load balancers. Hardware resources are received from multiple servers and networks distributed across different data centres maintained by the cloud provider.
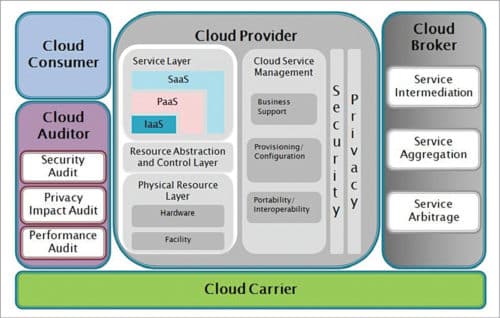
Users can log in to IaaS platform, create virtual machines (VMs), install OSes, deploy databases, create storage for workloads and backups, and install it on that VM. They can then track costs, balance network traffic, troubleshoot application issues, monitor performance and manage disaster recovery through provider services.
Types of IaaS offerings
Bernd Hanstein, vice president – product management – IT, Rittal GmbH & Co. KG, says “Companies should factor in the requirements of data protection laws at the earliest possible stage when selecting a provider. It is important that the provider can offer a physically- (dedicated private) or logically- (virtual private) separate cloud. This is the only way to comply with strict data protection requirements and possible in-house compliance rules.
“Any company that opts to operate its IT from the cloud should select a service provider that offers and orchestrates all services from a single source. A good alternative to traditional co-located data centres and private server rooms are cloud data centres in a container.”
IaaS can be delivered via a public cloud, a private cloud, a community cloud or a hybrid cloud. Public IaaS cloud allows multiple users to share server resources.
Private IaaS cloud servers and resources are dedicated to a single organisation and cannot be used by others.
Hybrid IaaS cloud provides the option to manage some physical servers in a private cloud, while outsourcing other servers to a public cloud.
In a cloud computing stack, IaaS resides on the bottom layer, PaaS delivery occurs on the middle and SaaS delivery occurs on the top. IaaS is bundled together with PaaS and SaaS delivery for a complete cloud computing solution, such as Amazon (Amazon Web Services), Google (App Engine) and Microsoft (Azure and AppFabric).
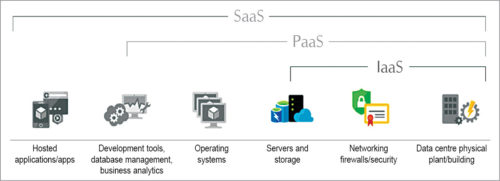
A few examples of IaaS
Burre says, “To expedite our clients’ growth and help them realise the optimal value of their modernisation investments in IaaS, CSS Corp. built Contelli. It is an automated platform that promotes context-driven intelligence for IT operations. It involves managing applications and data in data centres, cloud and hybrid environments.
“Contelli is largely based on a customer’s business-critical metrics and more closely aligned with factors impacting business outcomes. The platform learns from new scenarios, enriching its predictive intelligence to handle issues that may arise in future. It provides three benefits on the infrastructure front: improved service agility, process efficiency and reduced overall cost of operations.”
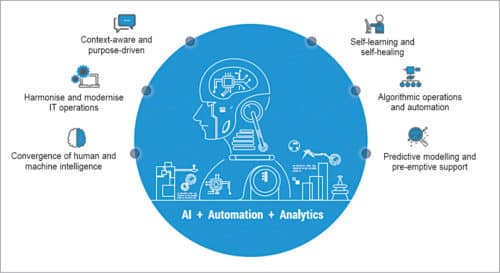
Contelli contextually evaluates and adopts the following approaches to provide faster remediation to challenges in IT operations:
- Reference to knowledge base: Based on the knowledge gained from historical events, Contelli helps enterprises identify early signals of system downtime through log data, and predicts future behaviour, resulting in increased operational efficiency. Through a three-pronged approach, the platform proactively identifies and classifies key incidents that lead to downtimes, failures, sub-optimal performances and outages, and provides immediate resolutions.
- Ability to learn from new scenarios: Contelli also learns from new scenarios and understands system behaviours. The platform has built-in algorithmic scripts that can be applied to real-time scenarios to automate infrastructure completely.
In most scenarios, both levers come together to drive faster resolution and optimisation of the infrastructure ecosystem. Contelli executes interdependency analysis between components, devices and systems for more accurate prediction. The platform can connect to multiple data sources including structured, unstructured and semi-structured data.
Vikram Puri, chief executive officer, Transworld Technologies, says, “We have created Mobile Eye, a smart Edge computing Internet of Things (IoT) device and coupled it with a complete cloud-based machine-to-machine (M2M) IoT platform called FleetView. It is the backbone of FleetView infrastructure.
“FleetView has something for each stakeholder in the supply chain, from driver behaviour and road safety right to load and route optimisation, and full compliance and audits. Drivers can keep track of their rewards and demerits. Companies can monitor safety and compliance, and manage journey risks. Supply chain professionals can plan and optimise their loads and shipments. Fleet owners can manage their cash, billing, fuel and vehicle maintenance.”
Products, including driver management centres, vehicle management services, journey risk management and route map pro, work on the capabilities provided by Mobile Eye. Mobile Eye unit comes with GPS and GSM/GPRS interface, which measures date, time, speed, latitude, longitude and distance travelled by a vehicle continuously online. Information recorded is sent to command data centres periodically for plotting the same on Fleetview Mapping software, and generating exception reports for analysing driving conditions of a vehicle.
FleetView’s vehicle management services module helps predict what is going to happen, rather than what has happened. This empowers a company to make strategic decisions to protect its fleet. Mobile Eye helps enhance fleet operations by providing real-time actionable intelligence to take charge of the supply chain. It helps generate data from the most relevant sources of a journey and converts it into strategic decisions for the business. A good fleet and supply chain management solution provides a clear performance standard for customers of the business, giving a clear competitive edge by improved visibility across operations and consistent, dependable performance.
Dr Sebastian Ritz, founder and chief executive officer, iNNOVO Cloud, says, “We provide a solution package for all scenarios, from leasing a fully-configured container to a turnkey container data centre, including standardised private cloud as a managed or self-managed service. Components can be configured as the smallest hardware unit in the customer’s on-site data centre or in a virtualised environment. These blobs (binary large objects) provide IT output for specific requirements such as high-performance computing, big data systems, high input/output operations per second and database systems with high demand for main memory.”
In the installation offered by Rittal and iNNOVO Cloud, blobs of this kind consist of two IT racks (including power supplies): cooling and standardised active IT components. HPC blobs can be incorporated for high-performance computing applications. Big data blobs are used if a lot of storage and RAM are needed. These are provided locally or as a cloud service. The entire system is also available as a container solution for optimum mobility and security. Once all components are linked, the data centre itself can be offered as a virtual service.
Cloud federation benefits and implementation
Federation of cloud resources (FCR) is facilitated through network gateways to create a hybrid cloud computing environment that connects public, private and/or community clouds. FCR allows a client to choose the best cloud services provider to meet a particular business or technological need, in terms of flexibility, cost and availability of services. It allows an enterprise to implement innovative security models for user access and distribute workloads between disparate networks.
FCR can be implemented behind a firewall to provide a list of cloud services to clients. Cloud providers grant permission to clients to specify an addressing scheme for each server. This enables users to access cloud services without the need for reconfiguration when using resources from different service providers.
Benefits of IaaS
According to Javier Barabas, IBM cloud and cognitive technical leader, cloud computing offers IT managers solutions for more data storage, greater and quicker software accessibility, and cost and effort optimisation. Depending on the needs of the client, IaaS can deliver the following benefits:
- It enables virtualisation of administrative tasks, freeing up time for other work.
- The cloud computing service provider manages the infrastructure, saving time and cost.
- Better resources mean more and constant processing power. A particular resource can be rented as needed.
- Infrastructure is scalable depending on processing and storage needs.
- It avoids the expense and complexity of buying and managing own physical servers and data centre infrastructure.
- The service can be accessed from anywhere using the Internet, available through a public or private cloud.
- If one aspect of the service fails, the service remains unaffected, as data is stored on the cloud. So, there are no single points of failure.
- It can reduce cost, and access applications and data during a disaster or outage.
- It enables quick scaling up of resources to accommodate spikes in demand for applications during the holidays. Scaling down can be done when activity goes down to save money.
- A cloud service provider provides security for applications and data.
An increasing number of companies are obtaining cloud-based parts for their IT infrastructure. Costs of purchasing, setting up and operating the planned IT environment play a big role in this decision.
More important are the strategic opportunities that have opened up by the cloud. For example, IT organisations can provide a standards-based IT infrastructure, while also responding quickly and flexibly to constantly growing resource requirements. IT as a Service (ITaaS) operating model has emerged in recent years, with a focus on business services. Design scope for services of companies opting for ITaaS depends on cloud providers.






