Recent entry of the network-on-chip (NoC) is likely to make system-on-chip (SoC) outdated soon. The new advanced NoC micropocessors can provide better AI integration with low power consumption. Several companies have already started offering NoCs.
Microprocessor technology needs to be more advanced than the devices it is currently being employed in. As a result, nanotechnology needs more advancements to increase the capability of microprocessors. It is time for designers to focus on embedding more capabilities into processors with the same or even smaller size.
Over the past few years, we have observed numerous new types of microprocessors being proposed by different research institutes. However, no one is sure about how long it would take to get these new technologies into commercial form. Hence, there is no point in waiting for them at this point of time.
To increase the capability of your micro device, one option is to use a system-on-chip (SoC). For example, MediaTek recently launched HelioP70 SoC with an artificial intelligence (AI) engine combined with CPU and GPU. It can be effectively used for advanced AI processing. HelioP70 comes with upgraded imaging and camera support, gaming performance boost and advanced connectivity features.
However, the recent entry of the network-on-chip (NoC) is making SoC outdated. The new NoC microcontroller (MCU) can provide more advanced AI integration with low power consumption.
NoC versus SoC
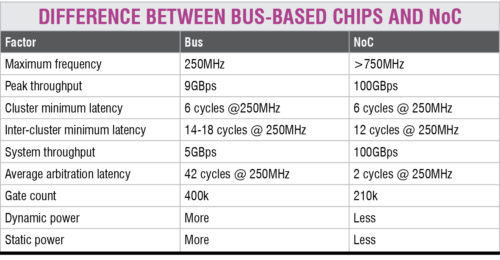
NoC technology applies the theory of computer networking to on-chip communication and brings notable improvements over bus and cross-bar communication architectures. NoC comes in many topologies, many of which are experimental as of 2018. The table above shows a comparison between bus-based chips and NoC.
Replacement of SoC by NoC has resulted in the following advantages:
- Reduced manufacturing cost
- Increased performance
- Reduced time-to-market
- Reduced SoC time-to-volume
- Reduced design risk
War of the NoCs
Quite naturally, demand for NoCs would be increasing because of several advantages, and many companies are now offering these. The next generation of multi-processor SoCs (MPoCs) and chip multi-processors (CMPs) will contain hundreds or even thousands of processors on a single chip. In contrast, NoCs are becoming a promising on-chip communication infrastructure, which is considered an aggressive, long-term approach for on-chip communication.
While designing NoC, methodologies such as flow control routing, arbitration, quality of service, reliability and task scheduling are considered.
Types of NoC
According to Goosens et al (2003), there are two types of NoCs with respect to quality of service (QoS). These are as follows:
- Best-effort (BE) NoC, which offers no commitment and only ensures completion of communication
- Guaranteed service (GS) NoC, which ensures that some service requirements are accomplished
FlexNoC 4 magic
As nano devices beat the compatibility of mega structures like computers, it is inevitable that some of the trends in the PC processor space will also spill over nano devices. One such trend is NoC. Today, there are several commercial vendors offering NoCs, prominent among them are Arteries, Sonics, Net Speed Systems and Aims Technology.
Arteries is described to be the first commercial company to venture into the NoC market. It invented NoC Interconnect technology and started offering its commercial services in 2006. Today, it has a wide range of customers such as Samsung, Huawei/Hi Silicon, Mobileye, Texas Instruments, Sokle Technology and so on.
“Using Arteries FlexNoC 4 allows us to reduce development time and manage project risk. FlexNoC 4’s advanced QoS and debugging features, combined with its multi-protocol support, allow Samsung SUHD TVs to reduce power consumption and die area for complex chips with more than 100 IP interfaces,” says Haejoo Jeong, vice president, visual display business, Samsung Electronics.
“Our customers require the latest, most advanced technology, and Arteries FlexNoC 4 Interconnect IP is a necessary addition to our portfolio. Acquiring FlexNoC 4 licence strengthens our technology platform and design services offerings, and provides our customers with more options to future-proof their solutions,” says Stone Peng, president and chief executive officer, Sokle Technology.
With over 20 years of development and more than 250 completed designs, Sonics’ innovative NoC family provides speed, power efficiency and flexibility for chips of all sizes and performance. SonicsHmGN (SGN) is a fourth-generation configurable NoC.
Water Space Mega Chips Corp., Osaka, Japan is not behind in the manufacture of NoCs. On January 29, 2013, it acquired the licence for Arteries FlexNoC Fabric IP to produce next-generation imaging SoCs.
FlexNoC 4: what to focus on
FlexNoC 4 uses SoC interconnect architecture to both accelerate timing closure and improve QoS by using less slack to meet timing, further reducing SoC silicon area and improving performance.
FlexNoC 4 provides advanced technology such as additional configurable hardware IP, visualisation cockpit, timing estimation engine, automatic pipeline placement and configuration.
FlexNoC 4 is a new MCU that supports multiple wireless standards. It is an advanced platform for the Internet of Things (IoT) applications such as Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE), Zigbee, 6LOWPAN and sub-1GHz.
FlexNoC 4 has the following characteristics:
- Layered and scalable architecture
- Flexible and user defined network topology
- Point-to-point connection
- Globally asynchronous locally synchronous (GALS) implementation
Its advantages are as follows:
- Smaller die area
- Deeply timing closure
- Faster frequency and latency
- Easy configuration
- Shorter schedules
- Automated verification
- Higher profits
FlexNoC 4 marching ahead
Arteries IP is the world’s leading supplier of silicon-proven commercial NoC. On October 31, 2018, it announced its new Arteries IP, FlexNoC version 4. FlexNoC 4 and AI package (FlexNoC 4AI) implement many new technologies that ease the development of today’s most complex AI chips, deep neural network (DNNs) and autonomous driving SoCs.
Such massively parallel processors should meet the requirements of high bandwidth for on-chip and off-chip communications. FlexNoC 4 with AI provides the features required for AI chips in an easy-to-use and highly-configurable form.
One user for FlexNoC 4 of Arteries IP is Mobileye. Arteries IP’s new processor helps Mobileye create multiple on-chip cache coherent sub-systems and develop heterogeneous programmable hardware accelerators. These sub-systems work together to accelerate speed, increase computational bandwidth, and reduce power consumption of AI and ML algorithms to gives near real-time latencies as a car moves.
Applications of FlexNoC 4 are:
• Cloud computing
• Digital home
• The IoT
• Mobiles, cameras, SSD controllers, etc
• Networking
• Storage
• Sensor fusion
• AI for automobiles
• Servers for customers such as Samsung, Huawei, HiSilicon, Mobileye and Texas Instruments
New capabilities in FlexNoC 4 include:
- Automated topology generation for ring, mesh and torus networks
- Multi-cast chip allows for more efficient updates of DNN weights, image maps and other multi-cast data
- Source synchronous communications; the chip helps avoid clock tree synthesis, physical placement and timing closure problems when spanning long distances on AI chips, which can be larger than 400sq mm
- VC-Link; virtual channels allow sharing of long physical links in congested areas of the die while maintaining QoS
- HBM2 and multi-channel memory support
- Up to 2048-bit-wide data support
- Provides long-chip paths
- Provides access to off-chip memory
- Provides homogeneous accelerators
FlexNoC 4 architecture typically models small-world networks (SWNs) and scale-free networks (SFNs) to limit the number, length, area and power consumption of interconnected wires and point-to-point connections. Whether you are using AMBA AXI3, AXI4, AHB, APB, OCB, PIF or a proprietary protocol, Arteries FlexNoC 4 IP reduces the number of wires by nearly half, resulting in fewer gates and a more compact chip floor plan.
Looking ahead
Experts feel that technological advancements are making it necessary to have more sophisticated and an increasing number of CPU cores in a smart processor—and the cores will continue to multiply. FlexNoC 4 processor will push the performance envelope of several sectors and allow several applications and sensor fusion to deliver new experiences, all while extending and saving battery life.
FlexNoC 4 processor is destined to become a reality soon. Rapid increase in consumer demand for multimedia, smart home, growth of Big Data, AI, automobiles, and robotics and more will increase computational speeds. Besides, low power consumption, size and weight are key areas for improvements to be seen in the NoC segment.
Vinayak Ramachandra Adkoli is BE in industrial production. He was lecturer in mechanical department for 10 years in three different polytechnics. Now, he is a freelance writer and cartoonist.









