A power supply converts AC voltage into a regulated DC voltage. Read on to find out how to select the best power supplies for various electronic devices.
A power supply for an electronic equipment is a circuit that converts AC voltage into regulated DC voltage. An electronic device does not normally use electric energy in the form in which it is produced or distributed. It requires some form of energy conversion. A power supply unit (PSU) transfers electric energy from a given source to a given load using electronic circuits. There are different types of PSUs depending on their mode of operation and application.
Basic building components
A PSU derives power from the AC mains supply and performs many tasks before transferring it to the output electronic device. These tasks include:
- Changing the level of supply to a value suitable for driving the load circuit.
- Producing DC supply from the mains supply AC sine wave.
- Preventing any AC signal at supply output.
- Ensuring constant output voltage independent of changes in AC supply voltage, load current and temperature.
To do these things, a basic PSU has four main constituents: transformer, rectifier, filter and regulator circuit.
Input transformer
This is used to transform incoming line voltage (AC) down to the required (AC) level for the power supply. It isolates the output circuit from the line supply.
Rectifier
This converts incoming AC signal into DC signal.
Filter
This is necessary to ensure that AC components from the power line do not enter at output.

Regulator
This circuit provides constant output virtually, regardless of output current or any minor fluctuations in input level. It may use either linear or switching mode technique to bring output voltage to the required level.
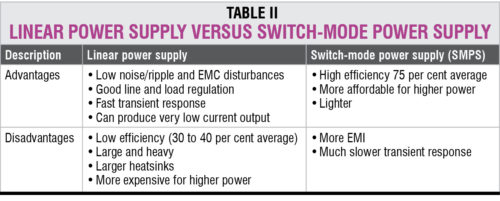
Linear power regulator. This can be used when stepping down of input voltage to regulated output voltage is required. It must be selected based on load current, and input and output voltage requirements.
A linear supply with a low-dropout (LDO) regulator provides clean DC to meet the need. An LDO is a special variant of a linear regulator, which is used when conversion ratio is high. There are two dropout voltages: power supply rejection ratio and common-mode rejection ratio. This is the ability of the power supply to reject differential mode noise that is present between positive and negative inputs.
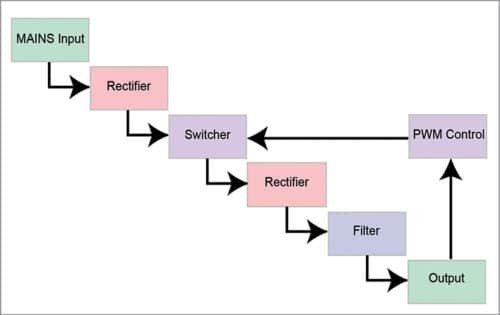
Switching power regulator. Here, transistors operate by switching high frequency between on and off states. An output parameter is controlled by a varying duty cycle, frequency or phase shift of these transitions.
There are different topologies available for switching regulators, namely, buck, synchronous buck, boost, inverting buck-boost, SEPIC, Cuk, Zeta, fly-buck, flyback, two-switch flyback, active-clamp forward, single-switch forward, two-switch forward, half-bridge, full-bridge and phase-shifted full bridge. The most popular ones are buck, boost, buck-boost, SEPIC and Zeta.
Boost format steps up the input while buck format steps it down. A buck-boost converter can do both, in addition to inverting the polarity of output voltage with respect to ground. If you need to change output polarity, Cuk topology is a good option. Transformers provide isolation, and topologies that incorporate it in the design include flyback, clamp forward, push-pull, half-bridge or full-bridge.

Types of power supplies for electronic devices
Most electronic devices work on regulated DC, independent of input supply (AC or DC). Depending on the power supply (AC or DC), all such devices have a different setup to convert it into regulated DC supply. Variable AC power supply is important to evaluate the equipment when it is exposed to over- or under-voltage conditions.
Different types of DC power supplies are as follows:
Uninterruptible power supply
This is a backup power source in case of power failure or fluctuations.
Constant voltage supply
This is adjustable and usually supplied with a meter to show the voltage the supply is set to.
Constant current supply
When in constant current mode, the power supply maintains the set current regardless of changes in load resistance.
Multiple output supply
This has more than one DC output, and is useful and cost-effective for systems that require multiple voltages.
Programmable supply
This is often used as part of a computer-operated system for testing or production.
Multi-range supply
It operates with fixed voltage and current ratings, such as 30V, 3A.
When there is a need for special characteristics or unusual form factors, custom designs are done particularly for harsh environments like in military or avionics.
Specifications to look for
Power supplies have different specifications for different applications. While choosing a power supply, each specification must be considered. It is necessary to understand everything from voltage and current ratings to ripple, load regulation, input voltage regulation and the like. A few important parameters to be taken care of are given below.
- Noise and ripple, which is a small variation in voltage when AC is transformed into DC
- Low dropout to reduce power losses
- Fast dynamic response
- Line regulation, which is the variation in output voltage with change in input or line voltage
- Load regulation, which is the variation in output voltage for a change in load
- Over-current, which can be controlled by internal protection circuit
- Over-temperature, which can be controlled using a temperature sensor and associated circuit
- Over-voltage, which can be controlled by the supply with over-voltage protection circuit
- Electromagnetic compatibility, which uses a design technique to minimise electromagnetic interference (EMI)
- Isolation. An isolated power supply employs a transformer to eliminate the DC path between input and output, whereas a non-isolated one follows a DC path between input and output of the supply
Peeyush Rustagi, assistant manager, ANTPL says, “It is better to have specifications like input voltage range (AC or DC), output voltage (DC or AC) and tolerances, output current requirement, ripple maximum, estimated total power requirement, efficiency requirement, EMI considerations, electrical isolation between input and output requirement, temperature range of operation, peak and average output current, transient exposure and response needs, load- and line-regulation requirement, switching frequency and need for power factor correction. Efficiency is one of the most important power supply characteristics to judge system performance.”
Nishu Kumar Rauniyar, hardware designer, SGS Weather & Environmental Systems, says, “Some power delivery architecture needs to be followed while supplying power for different ICs. Special care is required for high-frequency components, as RF noise can destroy the whole PSU. To work as intended, a proper grounding system is necessary. Special attention needs to be paid to layout design, as it will decide overall system performance.”
Preferred applications
A PSU is used in all electronic equipment that use DC voltage as input, such as radio transmitters, receivers, computers and so on. Switching power supplies are often used in applications where battery life and temperatures are important, such as electrolysis, waste treatment, fuel cells, DC motors, slot cars, aviation and marine, R&D, manufacturing and testing equipment, battery charging for lithium-ion batteries and electroplating.
Linear regulators provide noise-free output voltage but have poor efficiency and are large in size. This makes these suitable for devices that require high frequency and low noise, such as signal processors, control circuits, automated and laboratory test equipment, low-noise amplifiers, data-acquisition sensors and circuits, among others.
For selecting an appropriate power supply for an electronic device, it is important to first understand the requirement of the setup. Explore the different types of power supplies available in the market. Check for the required specification and the preferred application.





How to remove leakage current in the output of a step down transformer which makes an AC line tester neon to glow when the output touched with it ?