There are several types of solid-state storage devices, from small enough to fit in your pocket to all-flash arrays within data centres that can run entire enterprises.
Array-based solid-state drives (SSDs) are manufactured in a variety of lengths (form factors) that can be installed in any storage device. A solid-state array (SSA) is a dedicated all flash storage array. It has its own proprietary data management application and operating system (OS). Samsung 970 Pro NVMe M.2 SSD is among the fastest consumer SSDs. It provides sequential write and read speeds of up to 2700Mbps and up to 3500Mbps, respectively. Samsung V-NAND has a 2-bit MLC flash memory.

NVMe protocol will surely improve in the future. Hence, for best speeds, PCIe-based SSDs are the top choice. Intel Optane memory offers an extremely fast SSD. If you put a card in a four-lane slot, you get four times the bandwidth, at nearly 4Gbps. This makes it fast as compared to a Serial Advanced Technology Attachment (SATA)-based SSD. NVMe is a replacement for AHCI protocol, used in most SATA-based SSDs today.
Common interfaces
The most common SSA interfaces are SATA, Serial Attached SCSI (SAS), Fibre Channel (FC) and Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI). These are available in various form factors, including 4.6cm (1.8-inch), 6.3cm (2.5-inch) and 8.9cm (3.5-inch).
SATA interface provides different data throughputs from 1Gbps to 6Gbps, based on the version. PCI Express and SATA interfaces are widely used in most SSDs.
PCI Express interface uses point-to-point architecture to provide high-speed serial expansion card formats, which is the same for graphic cards. PCI-based SSDs provide both data and power connections when plugged into the motherboard. These allow more bandwidth through multiple lanes and faster signaling. PCI is more efficient and, thus, results in high latency because of direct connection to peripherals.
Automated storage approach
The random access time for an SSD storage array is about 0.1ms as compared to 5ms – 10ms for a hard disk drive (HDD). Automated storage tiering approach decides where to move data based on input or output activities. It does not prioritise based on individual application. This allows the SSD array to provide improved data access. To provide enhanced performance, the SSA employs the SSD to store data in block forms. An SSD array can be accessed through multiple physical hosts, so is easy to set up.
A rich software layer governs the SSD arrays and controls a range of activities like compression, replication and snapshots. The type of software determines the functionalities of SSAs. Software is controlled by storage controllers to control data storage. SSAs have a range of advantages such as easy to set up, low latency and storage efficiency. These are also easy to integrate with data centres and solutions.
NAND is a non-volatile flash memory used in SSDs. It can retain data even after the power is turned off. Single-level cells (SLCs), multi-level cells (MLCs) and triple-level cells (TLCs) are the three different types of NAND.
SLCs have faster write speeds, higher program and erase cycles, lower power consumption but are the most expensive. These offer multiple solutions for enterprise use.
MLCs have low write speeds, higher data density, low cost, and low program and erase cycles. These are used for consumer-grade applications.
TLCs have low write speeds, low program and erase cycles, and high storage density. These are also for consumer-grade solutions, and are the cheapest.
Vikas Jain, team leader – electrical schematics and apparatus, Cyient, says, “The technology we are using for SSA devices is NAND flash (SLC, MLC or TLC). Our primary focus is on endurance, safety of data from EMI/EMC interference, magnetic field, data security and good to work in harsh regions like locomotive/railway engines or metro trains. We use Ethernet, RS485, CAN, MVB, I2C and USB for firmware porting/data backup.”
Gartner Magic Quadrant for SSAs
IT and development and operation companies make the best SSAs in the world, as ranked by Gartner Magic Quadrant visionaries. Tintri VMstore T5000 series was among the top-named SSAs by Gartner.
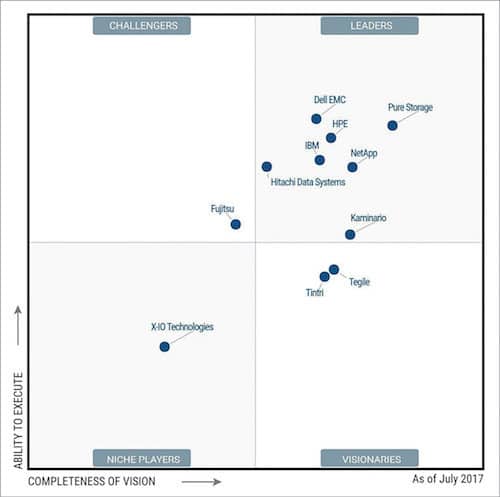
SSA Magic Quadrant is essentially an all-flash array. It has some unique requirements for an array to qualify into the solid-state chart. It is for SSAs that are on the edge of performance that focus on revenue-generating applications. Most products listed on the solid-state chart are from vendors who claim that the listed arrays are acceptable replacements for hard-disk-based systems.
It is expected that within the next 12 months, SSAs will improve in performance by a factor of 10, and double in density and cost-effectiveness, therefore changing the dynamics of the storage market.
Strategic planning assumption says that by 2021, 50 per cent data centres will use SSAs for high-performance computing and Big Data workloads. These systems include a data management software and an OS optimised for solid-state technology.
Design flow of SSDs
Jain says, “The main control unit is interfaced with a flash memory IC having SSD blocks. The interface is normally serial type, which may be high-speed SPI or I2C. For retrieving data from memory, a USB interface is used, or an indirect Ethernet connection to log data to the Web server.”
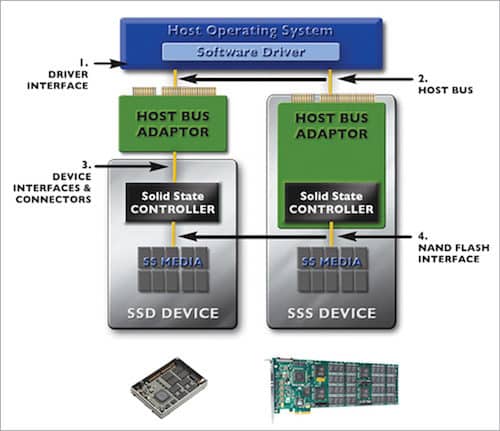
Solid-state storage (SSS) technology infrastructure is based on standards that interact with the host OS. Standards define how components communicate and connect. This drives volume and enables interoperability.
As shown in Fig. 4, there are two types of SSS devices: one that integrates the host bus adaptor (HBA) and connects directly to the host bus, and the other with an HDD-type interface, which connects via a separate HBA card.
Driver interface is a key enabler of a peripheral device and a standard software driver for the host OS. Host Bus PCI Express is a widely-implemented host bus and an SSS device interface.
Open NAND flash interface has developed interface specifications and driven the interface down a path of steadily increasing performance. Non-volatile memory includes block-accessible SSDs in card or drive form factors and byte-accessible devices such as NVDIMM. It operates out of RAM and utilises flash for backup to provide high speed. It is a non-volatile storage that plugs directly into the system memory bus.
Applications of SSDs
Jain says, “At Cyient we provide solutions based on customer requirement. As rail and transportation are being taken into perspective, SSDs are being used in train onboard memories, event and voice recorders, crash-protected memories, main processing units and drivers’ display units, among others.
“Consider a driver’s display unit that is used in the train cabin area for operator/train driver interaction/control and monitoring of train electronics. This display unit has been designed with state-of-the-art microcontrollers suitable for this application. While selecting the microcontroller for such applications, we specially consider memory for cost and size estimation, and go for low cost, high endurance and high temperature grade and trade off among these metrics.”
Cyient designs products that fulfill specific needs and requirements of specific domains and market segments like railway transportation. For the semiconductor industry, Cyient provides services and turn-key solutions for ASICs, SoCs, FPGAs design services, design verification and validation, physical IC design services, custom IC designs, custom memory development using static RAM and ROM. SSDs are suitable for high-load projects with numerous reading and writing operations.
SSS flash media like flash memory and micro flash memory cards are included in smartphones, MP3 players, laptops and desktops, personal computers, digital cameras, printers, tablets and servers.
All-flash drives have ports for flash memory cards. These transfer information from machine to machine.
Non-volatile flash memory cards can be repeatedly erased, reprogrammed and rewritten without being removed.
SSS USB flash drives are used to move data and files from one computer to another. These connect to computers by way of USB ports. Flash drives are plug-and-play devices. There is no need to download any software or drivers before using these.
Advantages of SSDs over HDDs
SSDs do not have any rotating elements as these use memory chips. These make less noise, consume less power and are smaller than HDDs. SSDs are flash based and offer longevity, robustness, high temperature operating range, shock and vibration tolerance, and lower power consumption.
SSDs are also being used in data centres and for cloud storage. This is due to their superior performance, enhanced reliability, high endurance and low prices. Fast write speeds, low energy consumption, and higher program and erase cycles have made SLC SSDs the best option for enterprise use.
SSDs provide a simple user interface to all data centre employees so that they can easily interface with the SSAs. These provide a dedicated platform for administrators to use with ease, irrespective of the scale and size of their venture (small, medium, large or global).
IT staff and developers can easily execute operations such as replication, cloning and taking snapshots because of virtual machine level management. The ability to interface with a universal management platform enables control of all other aspects of the enterprise cloud, other storage types and data centres. SSDs can handle virtual server infrastructures, virtual desktop infrastructures and private cloud deployments.
This article was first update on 4 September 2018 and was updated on 1 April 2021.






